
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule which shows shared and unshared pair of electrons. It is helpful to determine the shape of a molecule.
(a)
Answer to Problem 35A
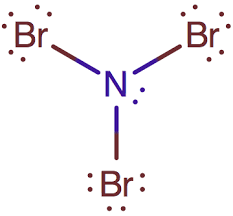
Explanation of Solution
Nitrogen has five valence electrons. Each electron is shared by each bromine atom and two electrons are left unshared. There will be 3 lone pair each on the Br atom because Br atoms have total of 7 valence electrons and only 1 electron is involved in bonding.
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule which shows shared and unshared pair of electrons. It is helpful to determine the shape of a molecule.
(b)
Answer to Problem 35A
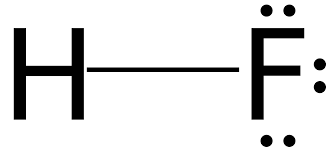
Explanation of Solution
Fluorine has seven valence electrons and hydrogen has one valence electron. So, both share one electron with each other to complete doublet of hydrogen and octet of fluorine. Also, there will be 3 lone pair of electrons on F atom.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule which shows shared and unshared pair of electrons. It is helpful to determine the shape of a molecule.
(c)
Answer to Problem 35A
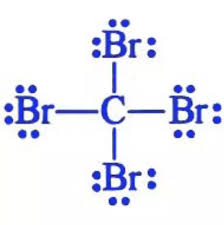
Explanation of Solution
Carbon has four valence electrons. Each electron is shared by one bromine atom and no electrons are left unshared. There will be 3 lone pair each on the Br atom because Br atoms have total of 7 valence electrons and only 1 electron is involved in bonding.
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule which shows shared and unshared pair of electrons. It is helpful to determine the shape of a molecule.
(d)
Answer to Problem 35A
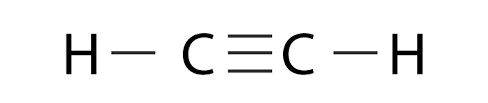
Explanation of Solution
Carbon has four valence electrons. One electron of carbon is shared with hydrogen to complete its doublet and carbon shares three electrons with other carbon to complete octet and no electrons are left unshared.
Chapter 12 Solutions
World of Chemistry
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward2,2-Dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Indicate the products obtained.arrow_forward
- Add conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformationADS fint anditions 百 Abl res condinese NC ง Add on condtions 1.0 B H,N.arrow_forward3. Provide all the steps and reagents for this synthesis. OHarrow_forwardSteps and explanationarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





