
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure and resonating structures (if possible) of given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule which shows shared and unshared pair of electrons. It is helpful to determine the shape of a molecule.
(a)
Answer to Problem 37A
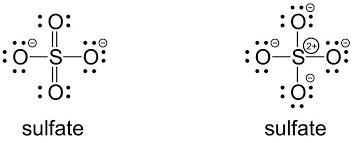
Resonating structures:
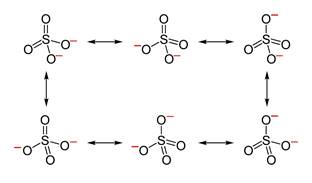
Explanation of Solution
Sulphur has six valence electrons. One electron is shared by each oxide ion and two electrons are shared by oxygen atom and no electron pairs are left unshared.
Its resonating structure is also possible as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure and resonating structures (if possible) of given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule which shows shared and unshared pair of electrons. It is helpful to determine the shape of a molecule.
(b)
Answer to Problem 37A
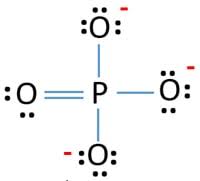
Resonating structures:
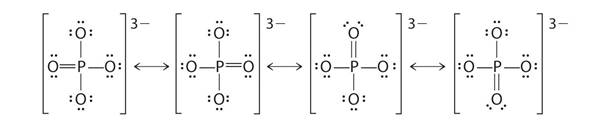
Explanation of Solution
Phosphorus has five valence electrons. One electron is shared by each oxide ion and two electrons are shared by oxygen atom and no electron pairs are left unshared.
Its resonating structure is also possible.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure and resonating structures (if possible) of given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule which shows shared and unshared pair of electrons. It is helpful to determine the shape of a molecule.
(c)
Answer to Problem 37A
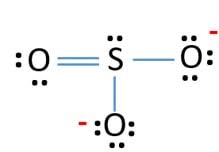
Resonating structures of
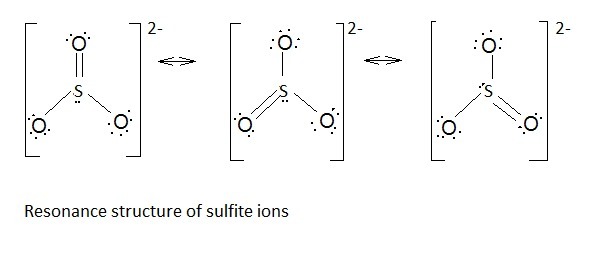
Explanation of Solution
Sulphur has six valence electrons. One electron is shared by each oxide ion and two electrons are shared by oxygen atom and one electron pair is left unshared.
Three resonating structures are possible for
Chapter 12 Solutions
World of Chemistry
- Construct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeH2. Sketch the MO pictures (schematic representation) for the HOMO and LUMO of BeH2 [Orbital Potential Energies, H (1s): -13.6 eV; Be (2s): -9.3 eV, Be (2p): -6.0 eV]arrow_forwardIndicate the isomers of the A(H2O)6Cl3 complex. State the type of isomerism they exhibit and explain it briefly.arrow_forwardState the formula of the compound potassium μ-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate.arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forwardWhat constitutes a 'reference material', and why does its utilization play a critical role in the chemical analysis of food products? Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain what calibration is and why it is essential in relation to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





