
Bundle: Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305705159
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.79P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The fatty acids are called as fatty acid as they bear a
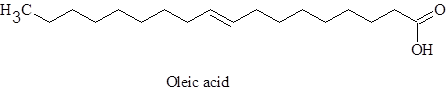
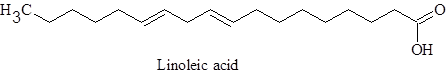
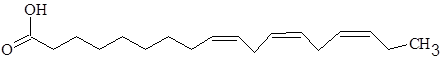
Linolenic acid.
Draw the possible structure of each of the fatty acids showing all cis configuration.
Concept Introduction:
Cis trans isomers are geometrical isomers resulted from different spatial arrangement of atoms or group of atoms on double bond.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
13C NMR is good for:
a) determining the molecular weight of
the compound
b) identifying certain functional groups.
c) determining the carbon skeleton, for
example methyl vs ethyl vs propyl groups
d) determining how many different kinds
of carbon are in the molecule
6
D
2. (1 pt) Limonene can be isolated by performing steam distillation of orange peel.
Could you have performed this experiment using hexane instead of water? Explain.
3. (2 pts) Using GCMS results, analyze and discuss the purity of the Limonene obtained
from the steam distillation of orange peel.
Part III. Arrange the following carbons (in blue) in order of increasing chemical shift.
HO
B
NH 2
A
CI
Chapter 12 Solutions
Bundle: Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.1PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.2PCh. 12.3 - Problem 12-3 Write the IUPAC name for each...Ch. 12.3 - Problem 12-4 Draw structural formulas for the...Ch. 12.3 - Problem 12-5 How many stereoisomers are possible...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.6PCh. 12.5 - Problem 12-7 Propose a two-step mechanism for the...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.8PCh. 12.5 - Problem 12-9 Propose a three-step reaction...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.10P
Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.11PCh. 12 - Answer true or false. Both ethylene and acetylene...Ch. 12 - 12-13 What is the difference in structure between...Ch. 12 - There are three compounds with the molecular...Ch. 12 - 12-15 Name and draw structural formulas for all...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.16PCh. 12 - Draw a structural formula for at least one...Ch. 12 - Each carbon atom in ethane and in ethylene is...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.19PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.20PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12 - 12*22 Draw a structural formula for each compound....Ch. 12 - 12-23 Draw a structural formula for each compound....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.24PCh. 12 - 12-25 Write the IUPAC name for each unsaturated...Ch. 12 - Explain why each name is incorrect and then write...Ch. 12 - 12-27 Explain why each name is incorrect and then...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.28PCh. 12 - 12-29 Which of these alkenes show cis-trans...Ch. 12 - 12-30 Which of these alkenes shows cis-trans...Ch. 12 - 12-31 Cyclodecene exists as both cis and trans...Ch. 12 - Arachidonic acid is a naturally occurring C„o...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.33PCh. 12 - If you examine the structural formulas for the...Ch. 12 - 12*35 For each molecule that shows eis-trans...Ch. 12 - Name and draw structural formulas for all...Ch. 12 - /3-Ocimene, a triene found in the fragrance of...Ch. 12 - Answer true or false. Alkenes and alkynes are...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.39PCh. 12 - 12-40 Define alkene addition reaction. Write an...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.41PCh. 12 - 12-42 Complete these equations.Ch. 12 - Draw structural formulas for all possible...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12 - 12-45 Draw a structural formula for the product of...Ch. 12 - Draw a structural formula for an alkene with the...Ch. 12 - 12-47 Draw a structural formula for an alkene with...Ch. 12 - Draw a structural formula for an alkene with the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.49PCh. 12 - 12-50 Draw the structural formula of an alkene...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.51PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.52PCh. 12 - Following is the structural formula of...Ch. 12 - Propose an explanation for the following...Ch. 12 - There are nine alkenes with the molecular formula...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12 - 12-57 Hydrocarbon A, Cf,Hs, reacts with 2 moles of...Ch. 12 - 12-58 Show how to convert ethylene to these...Ch. 12 - 12-59 Show how to convert 1-butene to these...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.60PCh. 12 - 12-61 (Chemical Connections 12A) What is one...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.62PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.63PCh. 12 - 12-64 (Chemical Connections 120 What is the...Ch. 12 - (Chemical Connections 120 Assume that 1 X IO-12 g...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.66PCh. 12 - 12-67 (Chemical Connections 12D ) In which isomer...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.68PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.69PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.70PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.71PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.72PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.73PCh. 12 - Propose a structural formula for the product!s)...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.75PCh. 12 - Draw the structural formula of an alkene that...Ch. 12 - 12-77 Show how to convert cyclopentene into these...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.78PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.79PCh. 12 - In omega-3 fatty adds, the last carbon of the last...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.81P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals as carbonyl, aryl, or alkyl. 100 ō (ppm) 50 0 7. 200 150 Assign all of the protons on the spectrum below. 8. A B 4 E C 3 ō (ppm) 2 1 0 Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals to the corresponding protons. OH 6 OH 3 2 1 0 4 ō (ppm)arrow_forwardIn the Thermo Fisher application note about wine analysis (Lesson 3), the following chromatogram was collected of nine components of wine. If peak 3 has a retention time of 3.15 minutes and a peak width of 0.070 minutes, and peak 4 has a retention time of 3.24 minutes and a peak width of 0.075 minutes, what is the resolution factor between the two peaks? [Hint: it will help to review Lesson 2 for this question.] MAU 300 200 T 34 5 100- 1 2 CO 6 7 8 9 0 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2 Minutes 3.22 0.62 1.04 O 1.24arrow_forwardThe diagram shows two metals, A and B, which melt at 1000°C and 1400°C. State the weight percentage of the primary constituent (grains of C) that would be obtained by solidifying a 20% alloy of B. 1000°C a+L L+C 900°С 12 α a+C 45 1200 C L+y 140096 C+Y a+ß 800°C 700°C C+B 96 92 a+B 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 A % peso B Barrow_forward
- 8. Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals to the corresponding protons. 2 4 3 ō (ppm) OH 4 6 6 СОН 2 1 0arrow_forward7. Assign all of the protons on the spectrum below. A B 2 C E 2 1 3 6 4 3 2 1 0arrow_forwarde. If (3R,4R)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane and (3R,4S)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane are in a solution at the same concentration, would this solution be expected to rotate plane polarized light (that is, be optically active)? Please provide your reasoning for your answer. [If you read this problem carefully, you will not need to draw out the structures to arrive at your answer...]arrow_forward
- 1. How many neighbors does the proton that produces the multiplet below have? 2. 3. اللـ Draw a partial structure from the multiplet below. (The integration of the multiplet is 6) M Using the additivity constants found in appendix G of your lab manual, calculate the approximate chemical shifts of the protons indicated below. (Show your work!!!) B A Br SHarrow_forward1) Suppose 0.1 kg ice at 0°C (273K) is in 0.5kg water at 20°C (293K). What is the change in entropy of the ice as it melts at 0°? To produce the original "water gas" mixture, carbon (in a combustible form known as coke) is reacted with steam: 131.4 kJ + H20(g) + C(s) → CO(g) + H2(g) From this information and the equations in the previous problem, calculate the enthalpy for the combustion or carbon to form carbon dioxide. kindly show me how to solve this long problem. Thanksarrow_forward4. An 'H-NMR of a compound is acquired. The integration for signal A is 5692 and the integration for signal B is 25614. What is the simplest whole number ratio of protons for signals A and B? (Show your work!!!) 5. Assign the carbons in the NMR below as either carbonyl, aromatic, or alkyl. 200 150 100 50 ō (ppm) 1arrow_forward
- Speaking of composite materials, indicate the correct option:(A). Composite materials can only be: metal-polymer or polymer-polymer.(B). Composite materials can be made up of particles, but not fibers or sheets.(C). When the reinforcing particles are uniformly distributed in a composite material, there may be a greater tendency for it to have isotropic properties.(D). None of the above is correct.arrow_forwardIf we are talking about viscoelastic modulus or viscoelastic relaxation modulus in polymers, indicate the correct option.(A). It reports the variation of elastic behavior as a function of time.(B). It is only useful for defining its glass transition temperature.(C). It only allows us to define the polymer degradation temperature.(D). Neither option is correct.arrow_forwardWhen natural light falls perpendicularly on a material A, it has a reflectivity of 0.813%. Indicate the value of the refractive index.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION; Author: 7activestudio;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxtMFmDTv3Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY