
Concept explainers
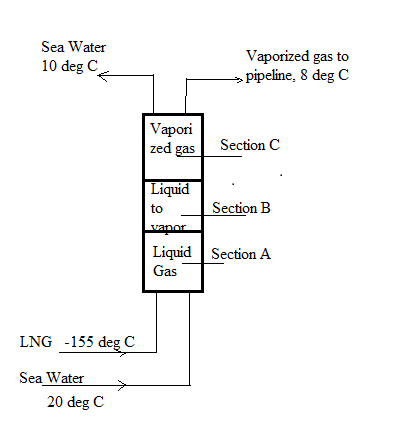
A liquefied natural gas (LNG) regasification facilityutilizes a vertical heat exchanger or vaporizer that consists of a shell with a single-pass tube bundle used toconvert the fuel to its vapor form for subsequent delivery through a land-based pipeline. Pressurized LNG isoff-loaded from an oceangoing tanker to the bottom ofthe vaporizer at
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
- I REPEAT!!!!! I NEED HANDDRAWING!!!!! NOT A USELESS EXPLANATION!!!! I REPEAT SUBMIT A HANDDRAWING IF YOU CANNOT UNDERSTAND THIS SKIP IT ! I need the real handdrawing complete it by adding these : Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding.arrow_forwardI need the real handdrawing complete it by adding these : Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding.arrow_forwardAn elastic bar of the length L and cross section area A is rigidly attached to the ceiling of a room, and it supports a mass M. Due to the acceleration of gravity g the rod deforms vertically. The deformation of the rod is measured by the vertical displacement u(x) governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + b(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = Edx du Hooke's law (1) b(x) = gp= body force per unit volume where E is the constant Young's modulus, p is the density, and σ(x) the axial stress in the rod. g * I u(x) L 2arrow_forward
- An elastic bar of the length L and cross section area A is rigidly attached to the ceiling of a room, and it supports a mass M. Due to the acceleration of gravity g the rod deforms vertically. The deformation of the rod is measured by the vertical displacement u(x) governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + b(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = Edx du Hooke's law (1) b(x) = gp= body force per unit volume where E is the constant Young's modulus, p is the density, and σ(x) the axial stress in the rod. g * I u(x) L 2arrow_forwardمتوسعة الفرج بو عمامة المستوى رم الواجب المنزلي رقم 04 تمرین الوان حسب يتمعن العبارات الأتية : A= (+2)+(-45) B=(+13)- C = (+17)-(+13)-(-20)+(-19 D= [(-15)-(+15)]-[(+20) + هست قیم مدرج مبدؤه النقطة ة الطول :tcm A(-2,5): B(+ 2,5) ≤ C (+5) المسافتين : BAD ين الثاني لمستوي مبدؤه 8 وحدتهarrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on AI, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer!!!!! You can borrow ideas from AI, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! ( If you write by hand or don't use AI, I'll give you a big thumbs up ) Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forward
- A thin uniform rod of mass m and length 2r rests in a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius r. A moment M = mgr horizontal plane. is applied to the rod. Assume that the bowl is fixed and its rim is in the HINT: It will help you to find the length l of that portion of the rod that remains outside the bowl. M 2r Ꮎ a) How many degrees of freedom does this system have? b) Write an equation for the virtual work in terms of the angle 0 and the motion of the center of mass (TF) c) Derive an equation for the variation in the position of the center of mass (i.e., Sŕƒ) a. HINT: Use the center of the bowl as the coordinate system origin for the problem. d) In the case of no applied moment (i.e., M = 0), derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation e) In the case of an applied moment (i.e., M: = mgr 4 -) derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation. f) Can the angle 0 and…arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forward= The frame shown is fitted with three 50 cm diameter frictionless pulleys. A force of F = 630 N is applied to the rope at an angle ◊ 43°. Member ABCD is attached to the wall by a fixed support at A. Find the forces indicated below. Note: The rope is tangent to the pully (D) and not secured at the 3 o'clock position. a b •C *су G E e d BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 81 cm b 50 cm с 59 cm d 155 cm For all answers, take x as positive to the right and positive upward. At point A, the fixed support exerts a force of: A = + ĴN and a reaction couple of: →> ΜΑ Member CG is in Select an answer magnitude У as k N-m. and carries a force of N.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





