
Concept explainers
A plate-tin heat exchanger is used to condense a saturated refrigerant vapor in an air-conditioning system.The vapor has a saturation temperature of
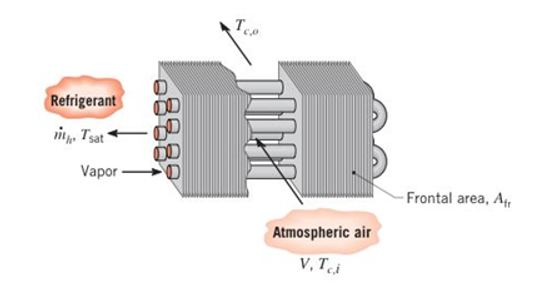
(a) The condenser design is to be based on a nominal air inlet temperature of
(b) From the manufacturer of the heat exchangercore, it is also known that
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
DeGarmo's Materials and Processes in Manufacturing
Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Applied Fluid Mechanics (7th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
- The food storage room requires a cooling system with a capacity of 10 tons of refrigeration that operates at an evaporator temperature of -17.8 ° C and a condenser temperature of 30.1 ° C. The refrigerant used is R-717 and the system operates in saturated conditions. Specifi :COP, Refrigerant flow rate ,Heat loss rate in condensesarrow_forwardWater inter a condenser at a mass flow rate of (2.5 kg/s) and (21 kPa and 65 C), and exit with (h= 251.5 kJ/kg). Find: a) The mass flow rate of water flow at the exit section b) the rate of heat removed from the water in the condenser. From table: at T1-60-C & P1-21 kPa -hl=2423x10 J/kgarrow_forwardIn an ammonia refrigeration system, the pressure in the evaporator is 251 kPaa, and the ammonia at the evaporator entry is 0.1511 dry while at exit is 0.95 dryIf the rate of ammonia circulation is 4.56 kg / m * i * n , determine the refrigerating capacity of the system. Use the properties of ammonia from refrigerantstablearrow_forward
- A Cascade refrigeration system using R-32 and a heat exchanger is operating an evaporator with a capacity of 6 tons at a temperature of -30°C. If the heat exchanger pressure is 0.80 MPa and the condensing temperature is 50°C, determine the COP and the refrigerating efficiency of the system. Draw the schematic diagram of the system and assume ideal conditions.arrow_forwardQ6 Kindly answer correctly.Please show all the necessary stepsarrow_forwardBy taking the limit as DT2 DT1, show that when DT1 = DT2 for a heat exchanger, the DTlm relation reduces to DTlm = DT1 = DT2.arrow_forward
- You are designing a piping system to facilitate the transfer of water from one industrialprocess to the next. You need the water to condense from saturated vapor to saturatedliquid at a constant 1000 kPa as it flows through the piping system. The pipe is to be madeof plain carbon steel with thermal conductivity ? = 60 W m-K⁄ and inner and outer radii?? = 5 cm and ?? = 7 cm, respectively. The thermodynamic property table at the end of thisproblem will be helpful throughout your analysis.a) If the convection coefficient between the steam and inner wall of the pipe is “verylarge”, what is the temperature of the inner pipe wall along its entire length?(Hint: Isobaric phase change is also iso___?)b) The fluid surrounding the pipe has temperature ?∞ = 30°C and the convectioncoefficient from the pipe to this fluid is ℎ = 100 W/m2⋅K. What is the heat transferrate out of the pipe, per unit meter of pipe? You may neglect radiation effects. Usea thermal resistance network in your analysis.c) The…arrow_forwardIn a hydrocarbon processing plant, Fluid A (cp = 4.31 kJ/kg-K) entering the tube side is used to heat Fluid B (cp = 2.05 kJ/kg-K) in a heat exchanger with an overall heat transfer coefficient of 150 W/m2.°C. Based on the information given in TABLE Q3, determine the outlet temperatures of Fluid A and Fluid B. If the surface area of the heat exchanger increases 30%, what would be the effect on outlet temperatures? Justify your answer with calculation. Comment your answer. TABLE Q3 Type of heat exchanger Mass flow Inlet Surface rate, kg/s temperature, °C area, A, m2 Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid A в А B 3.0 5.5 150 20 150 Cross flow, both fluid unmixed 3.arrow_forwardFor two heat exchangers under similar conditions except that one is cross flow and the other one is parallel flow, the amount of heat transfer of the cross flow heat exchanger should be higher than that of the parallel flow heat exchanger, for a given heat transfer area. Select one: O True O False In a condenser, the driving force of the heat transfer process is the fluid velocity. Select one: O True O False Heating a fluid flowing inside a closed circular conduit or pipe is the most important conductive heat-transfer process industry. Select one: O True O Falsearrow_forward
- An adiabatic heat exchanger is used to heat cold water át 8 C entering at a rate of 3 kg/s by hot air at 150 C entering also at rate of 3 kg/s. If the exit temperature of hot air is 30 C, the exit temperature of cold water is which of the following: (use constant specific heats evaluated at 300 K). 128.4 C O28.6 C O 31.2 C 36.9 C O 149.7 Carrow_forwardMilk is flowing through a heat exchanger at a rate of 2000 kg/h. The heat exchanger supplies 111,600 kJ/h. The outlet temperature of the product is 95℃. Determine the inlet temperature of the milk. The product specific heat is 3.9kJ/(kg℃). Show PBD and complete solution.arrow_forwardExhaust gasses from a diesel engine are used to heat water in an insulated heat exchanger. Refer to the figure and table below to determine the water flow rate (kg/s) when the exhaust gas flow rate is 0.12 kg/s. Water vapor in the exhaust can be treated as an ideal gas Tonh gas in = 700°C Tenh gas out = 200°C → Twater in = 25°C Twater out = 75°C Exhaust Gas Composition Species Molar Analysis Carbon dioxide Water vapor Nitrogen 13% 13% 74%arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
