
(a)
Interpretation:Whether norbornene is chiral or not should be explained.
Concept introduction:Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral. However, the most essential criteria that help to distinguish a chiral or non-chiral system ispresence of any symmetry element. If any plane center or axis of symmetry is identified it makes molecule achiral and optically inactive.
Four kinds of symmetry elements that may be present are tabulated as follows:
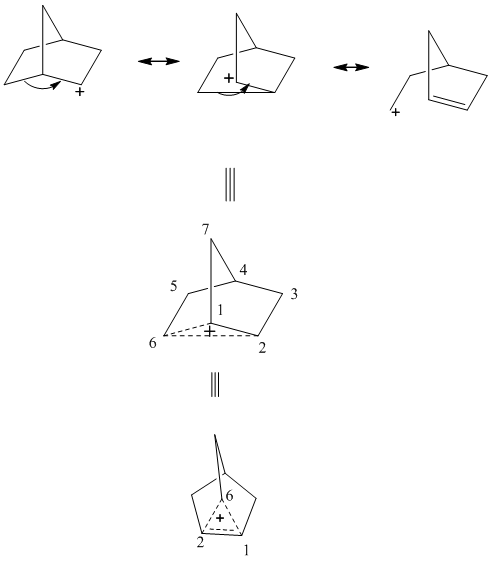
The non-classical cation is unique carbocation that involves delocalization of electron density of filled bonding orbital over three carbons. It exists for systems such as phenonium ions,norbornyltosylate, brosylate, and nortricyclonium cations. They can be understood as carbocation that has transition state for two asymmetric equilibrium cation derived from anchimeric-assistance that represents neighboring group participation in the stabilization of positive charge as illustrated below.
(b)
Interpretation:Three chiral centers in
Concept introduction:Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral. However, the most essential criteria that help to distinguish a chiral or non-chiral system ispresence of any symmetry element. If any plane center or axis of symmetry is identified it makes molecule achiral and optically inactive.
(c)
Interpretation: Chemical structure for the stereoisomer of
Concept introduction: Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral. However, the most essential criteria that help to distinguish a chiral or non-chiral system isthe presence of any symmetry element. If any plane center or axis of symmetry is identified it makes molecule achiral and optically inactive.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Experimental Organic Chemistry: A Miniscale & Microscale Approach (Cengage Learning Laboratory Series for Organic Chemistry)
- Design experiments in UV-Vis to figure the optimal mole ratio of copper (1:1, 2:1, 3:1 and etc)versus ethambutol using all necessary chemicals including dihydrochloride and copper nitrate hemipentahydrate and sodium hydroxide. Show how UV-Vis absorbance and maximum wavelength would change in responsearrow_forwardCorrect each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the condensed structure it would have if it were dissolv a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO—CH,—C—CH,—OH X 5 2 2 2 HO–CH,—CH,—C—CH,—OH Explanation Check Center Accessi ©2025 on 5 Carrow_forwardMake the calculations to prepare 2M H2SO4, from concentrated H2SO4 (98%; density: 1.84 g/mL).arrow_forward
- H CH3 CH3 b) Write the products of your compound and the following reagents. If the reaction would not work for your compound, write "no reaction" and explain the problem. NaCN H* H₂NNHCH5 H* -à NaBH -à CH2MgBr Cro₁₂ --à H3O+ -à c) Would your compound give a positive Tollen's test? Why or why not?arrow_forwardHomework 4 Chem 204 Dr. Hellwig Consider this compound, which will be referred to as "your compound". a) Name your compound according to the IUPAC system. Include stereochemistry (E/Z/R/S) H CH3 CH3arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- 21.50 Determine the combinations of haloalkane(s) and alkoxide(s) that could be used to synthesize the following ethers through Williamson ether synthesis. (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) H₂COarrow_forward1. Arrange the following in order of increasing bond energy (lowest bond energy first, highest bond energy last). Provide your rationale. C=C, C-F, C=C, C-N, C-C List the bond order for each example.arrow_forwardWhat is the major enolate formed when treated with LDA? And why that one?arrow_forward
- 4. Calculate the total number of sigma bonds and total number of pi bonds in each of the following compounds. a. HH :D: +1 I H-N-C-C-O-H I H b. HH H Н :N=C-C-C=C-CEC-H :0: total o H-C-H H-C = `C-H I H. 11 H-C = C= CH H total o total π total π 1 Harrow_forwardIn the following reaction, what quantity in moles of CH₃OH are required to give off 4111 kJ of heat? 2 CH₃OH (l) + 3 O₂ (g) → 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O(g) ∆H° = -1280. kJarrow_forwardIndicate the processes in the dismutation of Cu2O.arrow_forward
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


