
Concept explainers
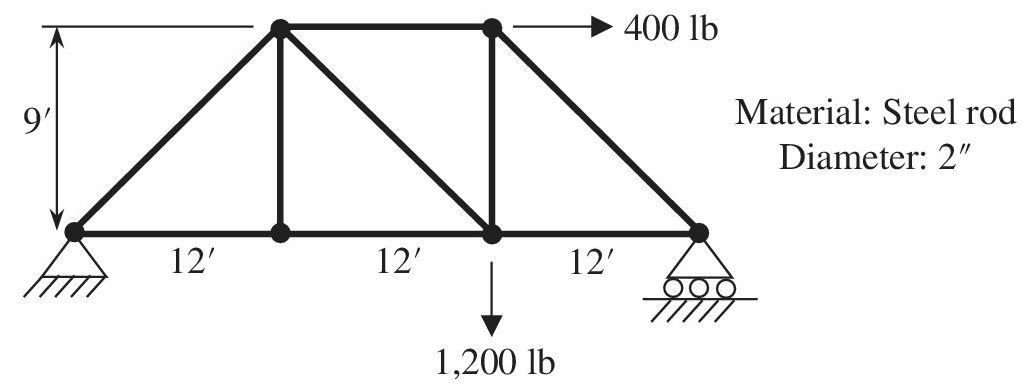
Determine the member force and axial stress in each member of the truss shown in the figure using a commercial finite element analysis program. Assume that Young’s modulus is psi and all cross sections are circular with a diameter of 2 in. Compare the results with the exact solutions that are obtained from the free-body diagram.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Q4 The two solid shafts are connected by gears as shown and are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing stress is 7000 psi. Knowing the diameters of the two shafts are, respectively, dBC determine the largest torque Tc that can be applied at C. 4 and dEF dBC=Last 1 student ID+3 inch dEF=Last 1 student ID+1 inch 7 R=Last 1 Student ID+5 inch 9 R B Tc 2.5 in. E TF Harrow_forwardExperiment تكنولوجيا السيارات - Internal Forced convenction Heat transfer Air Flow through Rectangular Duct. objective: Study the convection heat transfer of air flow through rectangular duct. Valve Th Top Dead Centre Exhaust Valve Class CP. N; ~ RIVavg Ti K 2.11 Te To 18.8 21.3 45.8 Nath Ne Pre Calculations:. Q = m cp (Te-Ti) m: Varg Ac Acca*b Q=hexp As (Ts-Tm) 2 2.61 18.5 20.846.3 Tm = Te-Ti = 25 AS-PL = (a+b)*2*L Nu exp= Re-Vavy D heep Dh k 2ab a+b Nu Dh the- (TS-Tm) Ts. Tmy Name / Nu exp Naxe بب ارتدان العشريarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findarrow_forward
- Procedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thearrow_forwardProcedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2D3D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D ∑Fx=0 ∑Fy=0 ∑Fz=0 ∑Mx=0 ∑My=0 ΣMz=0 2D ΣFx=0 ΣFy=0 ΣMz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of thearrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thearrow_forward
- Procedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the sectionarrow_forwardProcedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the sectionarrow_forwardFor each system below with transfer function G(s), plot the pole(s) on the s-plane. and indicate whether the system is: (a) "stable" (i.e., a bounded input will always result in a bounded output), (b) "marginally stable," or (c) "unstable" Sketch a rough graph of the time response to a step input. 8 a) G(s) = 5-5 8 b) G(s) = c) G(s) = = s+5 3s + 8 s² - 2s +2 3s +8 d) G(s): = s²+2s+2 3s+8 e) G(s): = s² +9 f) G(s): 8 00 == Sarrow_forward
- Please answer the following question. Include all work and plase explain. Graphs are provided below. "Consider the Mg (Magnesium) - Ni (Nickel) phase diagram shown below. This phase diagram contains two eutectic reactions and two intermediate phases (Mg2Ni and MgNi2). At a temperature of 505oC, determine what the composition of an alloy would need to be to contain a mass fraction of 0.20 Mg and 0.80 Mg2Ni."arrow_forwardThe triangular plate, having a 90∘∘ angle at AA, supports the load PP = 370 lblb as shown in (Figure 1).arrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, ß2 = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. φ 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° 2.138 P1 Figure 1 Xarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
