
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781119078722
Author: Kim, Nam H., Sankar, Bhavani V., KUMAR, Ashok V., Author.
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 8E
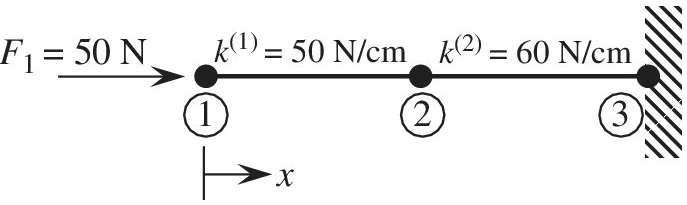
Determine the nodal displacements, element forces, and reaction forces using the direct stiffness method for the two-bar truss shown in the figure.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Example-1:
l
D
A uniform rotor of length 0.6 m and diameter 0.4 m is made of steel (density 7810 kg/m³)
is supported by identical short bearings of stiffness 1 MN/m in the horizontal and vertical
directions. If the distance between the bearings is 0.7 m, determine the natural frequencies
and plot whirl speed map.
Solution:
B
find the laplace transform for the
flowing function
2(1-e)
Ans. F(s)=-
S
12)
k
0
Ans. F(s)=
k
s(1+e)
0 a
2a 3a 4a
13)
2+
Ans. F(s)=
1
s(1+e")
3
14) f(t)=1, 0
Find the solution of the following Differential Equations
Using Laplace Transforms
1) 4y+2y=0.
y(0)=2.
y'(0)=0.
2) y+w²y=0,
(0)=A,
y'(0)=B.
3) +2y-8y 0.
y(0)=1.
y'(0)-8.
4)-2-3y=0,
y(0)=1.
y'(0)=7.
5) y-ky'=0,
y(0)=2,
y'(0)=k.
6) y+ky'-2k²y=0,
y(0)=2,
y'(0) = 2k.
7) '+4y=0,
y(0)=2.8
8) y+y=17 sin(21),
y(0)=-1.
9) y-y-6y=0,
y(0)=6,
y'(0)=13.
10) y=0.
y(0)=4,
y' (0)=0.
11) -4y+4y-0,
y(0)=2.1.
y'(0)=3.9
12) y+2y'+2y=0,
y(0)=1,
y'(0)=-3.
13) +7y+12y=21e".
y(0)=3.5.
y'(0)=-10.
14) "+9y=10e".
y(0)=0,
y'(0)=0.
15) +3y+2.25y=91' +64.
y(0)=1.
y'(0) = 31.5
16)
-6y+5y-29 cos(2t).
y(0)=3.2,
y'(0)=6.2
17) y+2y+2y=0,
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=1.
18) y+2y+17y=0,
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=12.
19) y"-4y+5y=0,
y(0)=1,
y'(0)=2.
20) 9y-6y+y=0,
(0)-3,
y'(0)=1.
21) -2y+10y=0,
y(0)=3,
y'(0)=3.
22) 4y-4y+37y=0,
y(0)=3.
y'(0)=1.5
23) 4y-8y+5y=0,
y(0)=0,
y'(0)=1.
24)
++1.25y-0,
y(0)=1,
y'(0)=-0.5
25) y 2 cos(r).
y(0)=2.
y'(0) = 0.
26)
-4y+3y-0,
y(0)=3,
y(0) 7.
27) y+2y+y=e
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=0.
28) y+2y-3y=10sinh(27),
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=4.
29)…
Chapter 1 Solutions
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
Ch. 1 - Answer the following descriptive questions a....Ch. 1 - Calculate the displacement at node 2 and reaction...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 2 by changing node numbers; that...Ch. 1 - Three rigid bodies, 2,3, and 4, are connected by...Ch. 1 - Three rigid bodies, 2,3, and 4, are connected by...Ch. 1 - Consider the spring-rigid body system described in...Ch. 1 - Four rigid bodies, 1, 2, 3, and 4, are connected...Ch. 1 - Determine the nodal displacements, element forces,...Ch. 1 - In the structure shown, rigid blocks are connected...Ch. 1 - The spring-mass system shown in the figure is in...
Ch. 1 - A structure is composed of two one-dimensional bar...Ch. 1 - Two rigid masses, 1 and 2, are connected by three...Ch. 1 - Use the finite element method to determine the...Ch. 1 - Consider a tapered bar of circular cross section....Ch. 1 - The stepped bar shown in the figure is subjected...Ch. 1 - Using the direct stiffness matrix method, find the...Ch. 1 - A stepped bar is clamped at one end and subjected...Ch. 1 - A stepped bar is clamped at both ends. A force of ...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 18 for the stepped bar shown in the...Ch. 1 - The finite element equation for the uniaxial bar...Ch. 1 - The truss structure shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 1 - The properties of the two elements of a plane...Ch. 1 - For a two-dimensional truss structure as shown in...Ch. 1 - The 2D truss shown in the figure is assembled to...Ch. 1 - For a two-dimensional truss structure as shown in...Ch. 1 - The truss shown in the figure supports force Fat...Ch. 1 - Prob. 27ECh. 1 - In the finite element model of a plane truss in...Ch. 1 - Use the finite element method to solve the plane...Ch. 1 - The plane truss shown in the figure has two...Ch. 1 - Two bars are connected as shown in the figure....Ch. 1 - The truss structure shown in the figure supports...Ch. 1 - It is desired to use the finite element method to...Ch. 1 - Determine the member force and axial stress in...Ch. 1 - Determine the normal stress in each member of the...Ch. 1 - The space truss shown has four members. Determine...Ch. 1 - The uniaxial bar shown below can be modeled as a...Ch. 1 - In the structure shown below, the temperature of...Ch. 1 - Prob. 39ECh. 1 - The three-bar truss problem in figure 1.23 is...Ch. 1 - Use the finite element method to determine the...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 41 for the new configuration with...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 42 with an external force added to...Ch. 1 - The properties of the members of the truss in the...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 44 for the truss on the right side...Ch. 1 - The truss shown in the figure supports the force ....Ch. 1 - The finite element method as used to solve the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 48E
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain why you cannot convert the following if-else-if statement into a switch statement. if (temp == 100) x =...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Is the following comment written using single-line or multi-line comment symbols? / This program was written by...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Explore the data included in Table 4-9. Assume that the primary key of this relation consists of two components...
Modern Database Management
Explain forward-only cursors. Give an example of their use.
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
In the following exercises, write a program to carry out the task. The program should use variables for each of...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
The following code appears in the program in Listing 10.7: Why doesnt this code really include an infinite loop...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Auto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardThe 120 kg wheel has a radius of gyration of 0.7 m. A force P with a magnitude of 50 N is applied at the edge of the wheel as seen in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Find the acceleration and angular acceleration of the wheel.arrow_forwardAuto Controls Using MATLAB , find the magnitude and phase plot of the compensators NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward
- 4-81 The corner shown in Figure P4-81 is initially uniform at 300°C and then suddenly exposed to a convection environment at 50°C with h 60 W/m². °C. Assume the = 2 solid has the properties of fireclay brick. Examine nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and deter- mine the maximum time increment which may be used for a transient numerical calculation. Figure P4-81 1 2 3 4 1 cm 5 6 1 cm 2 cm h, T + 2 cmarrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardAuto Controls Hand sketch the root Focus of the following transfer function How many asymptotes are there ?what are the angles of the asymptotes?Does the system remain stable for all values of K NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward
- Please draw the section view of the following problemsarrow_forward7) Please draw the front, top and side view for the following object. Please cross this line outarrow_forwardA 10-kg box is pulled along P,Na rough surface by a force P, as shown in thefigure. The pulling force linearly increaseswith time, while the particle is motionless att = 0s untilit reaches a maximum force of100 Nattimet = 4s. If the ground has staticand kinetic friction coefficients of u, = 0.6 andHU, = 0.4 respectively, determine the velocityof the A 1 0 - kg box is pulled along P , N a rough surface by a force P , as shown in the figure. The pulling force linearly increases with time, while the particle is motionless at t = 0 s untilit reaches a maximum force of 1 0 0 Nattimet = 4 s . If the ground has static and kinetic friction coefficients of u , = 0 . 6 and HU , = 0 . 4 respectively, determine the velocity of the particle att = 4 s .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY