
Concept explainers
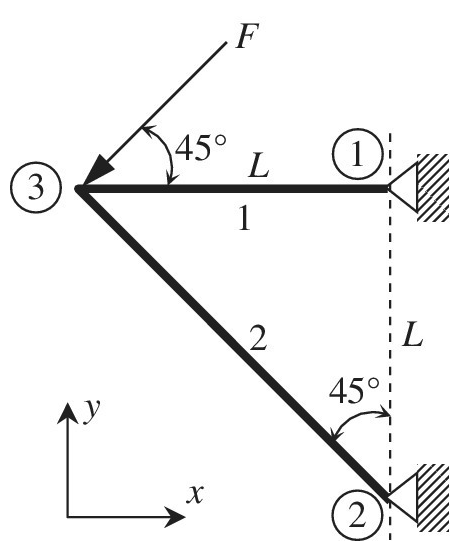
The plane truss shown in the figure has two elements and three nodes. Calculate the
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Modern Database Management
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
- reaction at a is 1.6 wL (pos) handwritten solutions only please. correct answers upvotedarrow_forward1 8 4 Add numbers so that the sum of any row or column equals .30 Use only these numbers: .1.2.3.4.5.6.10.11.12.12.13.14.14arrow_forwardUppgift 2 (9p) I77777 20 kN 10 kN/m 4 [m] 2 2 Bestäm tvärkrafts- och momentdiagram för balken i figuren ovan. Extrempunkter ska anges med både läge och värde i diagrammen.arrow_forward
- **Problem 8-45.** The man has a mass of 60 kg and the crate has a mass of 100 kg. If the coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is \( \mu_s = 0.4 \) and between the crate and the ground is \( \mu_c = 0.3 \), determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. **Diagram Explanation:** The diagram illustrates a scenario where a man is attempting to pull a crate using a rope-and-pulley system. The setup is as follows: - **Crate (C):** Positioned on the ground with a rope attached. - **Rope:** Connects the crate to a pulley system and extends to the man. - **Pulley on Tree:** The rope runs over a pulley mounted on a tree which redirects the rope. - **Angles:** - The rope between the crate and tree forms a \(30^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - The rope between the tree and the man makes a \(45^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - **Man (A):** Pulling on the rope with the intention of moving the crate. This arrangement tests the…arrow_forwardplease solve this problems follow what the question are asking to do please show me step by steparrow_forwardplease first write the line action find the forces and them solve the problem step by steparrow_forward
- please solve this problem what the problem are asking to solve please explain step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problem and determine the stress for each point i like to be explained step by step with the correct answerarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
