
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781119078722
Author: Kim, Nam H., Sankar, Bhavani V., KUMAR, Ashok V., Author.
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 16E
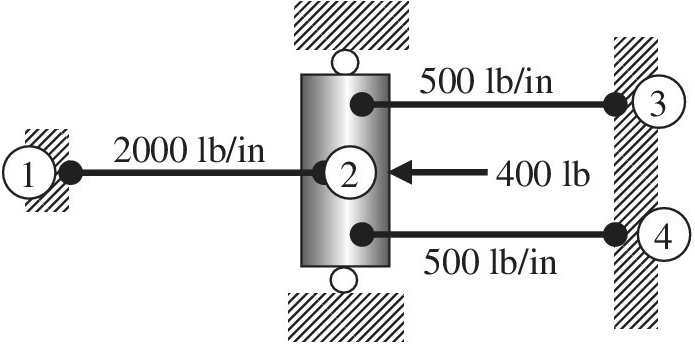
Using the direct stiffness matrix method, find the nodal displacements and the forces in each element and the reactions.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(read image) (Answer: M motor = 0.836 Ib-ft, Mf = 0.1045 Ib-ft)
Please find the torsional yield strength, the yield strength, the spring index, and the mean diameter.
(read image) (Answer Given)
Chapter 1 Solutions
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
Ch. 1 - Answer the following descriptive questions a....Ch. 1 - Calculate the displacement at node 2 and reaction...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 2 by changing node numbers; that...Ch. 1 - Three rigid bodies, 2,3, and 4, are connected by...Ch. 1 - Three rigid bodies, 2,3, and 4, are connected by...Ch. 1 - Consider the spring-rigid body system described in...Ch. 1 - Four rigid bodies, 1, 2, 3, and 4, are connected...Ch. 1 - Determine the nodal displacements, element forces,...Ch. 1 - In the structure shown, rigid blocks are connected...Ch. 1 - The spring-mass system shown in the figure is in...
Ch. 1 - A structure is composed of two one-dimensional bar...Ch. 1 - Two rigid masses, 1 and 2, are connected by three...Ch. 1 - Use the finite element method to determine the...Ch. 1 - Consider a tapered bar of circular cross section....Ch. 1 - The stepped bar shown in the figure is subjected...Ch. 1 - Using the direct stiffness matrix method, find the...Ch. 1 - A stepped bar is clamped at one end and subjected...Ch. 1 - A stepped bar is clamped at both ends. A force of ...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 18 for the stepped bar shown in the...Ch. 1 - The finite element equation for the uniaxial bar...Ch. 1 - The truss structure shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 1 - The properties of the two elements of a plane...Ch. 1 - For a two-dimensional truss structure as shown in...Ch. 1 - The 2D truss shown in the figure is assembled to...Ch. 1 - For a two-dimensional truss structure as shown in...Ch. 1 - The truss shown in the figure supports force Fat...Ch. 1 - Prob. 27ECh. 1 - In the finite element model of a plane truss in...Ch. 1 - Use the finite element method to solve the plane...Ch. 1 - The plane truss shown in the figure has two...Ch. 1 - Two bars are connected as shown in the figure....Ch. 1 - The truss structure shown in the figure supports...Ch. 1 - It is desired to use the finite element method to...Ch. 1 - Determine the member force and axial stress in...Ch. 1 - Determine the normal stress in each member of the...Ch. 1 - The space truss shown has four members. Determine...Ch. 1 - The uniaxial bar shown below can be modeled as a...Ch. 1 - In the structure shown below, the temperature of...Ch. 1 - Prob. 39ECh. 1 - The three-bar truss problem in figure 1.23 is...Ch. 1 - Use the finite element method to determine the...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 41 for the new configuration with...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 42 with an external force added to...Ch. 1 - The properties of the members of the truss in the...Ch. 1 - Repeat problem 44 for the truss on the right side...Ch. 1 - The truss shown in the figure supports the force ....Ch. 1 - The finite element method as used to solve the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 48E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6.76 A wind turbine is operating in a 12 m/s wind that has a den- sity of 1.2 kg/m³. The diameter of the turbine silhouette is 4 m. The constant-pressure (atmospheric) streamline has a diameter of 3 m upstream of the windmill and 4.5 m downstream. Assume that the velocity distributions are uniform and the air is incom- pressible. Determine the force on the wind turbine. m P = Patm 4 Vz 4m 4 m Fx. Problem 6.76arrow_forwardFor the position shown in the figure the spring is unstretched. The spring constant k, is designed such that after the system is released from rest, the speed of the mass is zero just as the 0.6 slug mass touches the floor. Find the spring constant, k and the maximum speed of block A and the location (distance above floor) where this occurs.arrow_forward||! Sign in MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pd X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L10.pX DE MMB241 - Tutorial L11.p x PDF Lecture W12 - Work and X File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L11.pdf PDE Lecture W11 - Power and X Draw Alla | Ask Copilot ++ 3 of 3 | D 6. If the 50-kg load A is hoisted by motor M so that the load has a constant velocity of 1.5 m/s, determine the power input to the motor, which operates at an efficiency € = 0.8. 1.5 m/s 2 7. The sports car has a mass of 2.3 Mg, and while it is traveling at 28 m/s the driver causes it to accelerate at 5m/s². If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind is FD= 0.3v²N, where v is the velocity in m/s, determine the power supplied to the engine at this instant. The engine has a running efficiency of P = 0.68. 8. If the jet on the dragster supplies a constant thrust of T-20 kN, determine the power generated by the jet as a function of time. Neglect drag and rolling resistance, and the loss of fuel. The dragster has a mass of 1…arrow_forward
- Q | Sign in PDE Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdi X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L10.p X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L11.p X Lecture W12-Work and X + File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/Lecture%20W12%20-%20Work%20and%20Energy.pdf ||! Draw | IA | a | Ask Copilot Class Work + 33 of 34 D Question 1 The engine of a 3500-N car is generating a constant power of 50 hp (horsepower) while the car is traveling up the slope with a constant speed. If the engine is operating with an efficiency of € 0.8, determine the speed of the car. Neglect drag and rolling resistance. Use g 9.81 m/s² and 1 hp = 745.7 W. 10 го Question 2 A man pushes on a 60-N crate with a force F. The force is always directed downward at an angle of 30° from the horizontal, as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the force is gradually increased until the crate begins to slide. Determine the crate's initial acceleration once it starts to move. Assume the coefficient of static friction is μ = 0.6, the coefficient of kinetic…arrow_forwardstate is Derive an expression for the volume expansivity of a substance whose equation of RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forwardFor a gas whose equation of state is P(v-b)=RT, the specified heat difference Cp-Cv is equal to which of the following (show all work): (a) R (b) R-b (c) R+b (d) 0 (e) R(1+v/b)arrow_forward
- of state is Derive an expression for the specific heat difference of a substance whose equation RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forwardTemperature may alternatively be defined as T = ди v Prove that this definition reduces the net entropy change of two constant-volume systems filled with simple compressible substances to zero as the two systems approach thermal equilibrium.arrow_forwardUsing the Maxwell relations, determine a relation for equation of state is (P-a/v²) (v−b) = RT. Os for a gas whose av Tarrow_forward
- (◉ Homework#8arrow_forwardHomework#8arrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^ 2. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A бро Barrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License