
Concept explainers
Waves in the Earth and the Ocean
In December 2004, a large earthquake off the coast of Indonesia produced a devastating water wave, called a tsunami, that caused tremendous destruction thousands of miles away from the earthquake's epicenter. The tsunami was a dramatic illustration of the energy carried by waves.
It was also a call to action. Many of the communities hardest hit by the tsunami were struck hours after the waves were generated, long after seismic waves from the earthquake that passed through the earth had been detected al distant recording stations, long after the possibility of a tsunami was first discussed. With better detection and more accurate models of how a tsunami is formed and how a tsunami propagates, the affected communities could have received advance warning. The study of physics may seem an abstract undertaking with few practical applications, but on this day a better scientific understanding of these waves could have averted tragedy.
Let’s use our knowledge of waves to explore the properties of a tsunami. In Chapter 15, we saw that a vigorous shake of one end of a rope causes a pulse to travel
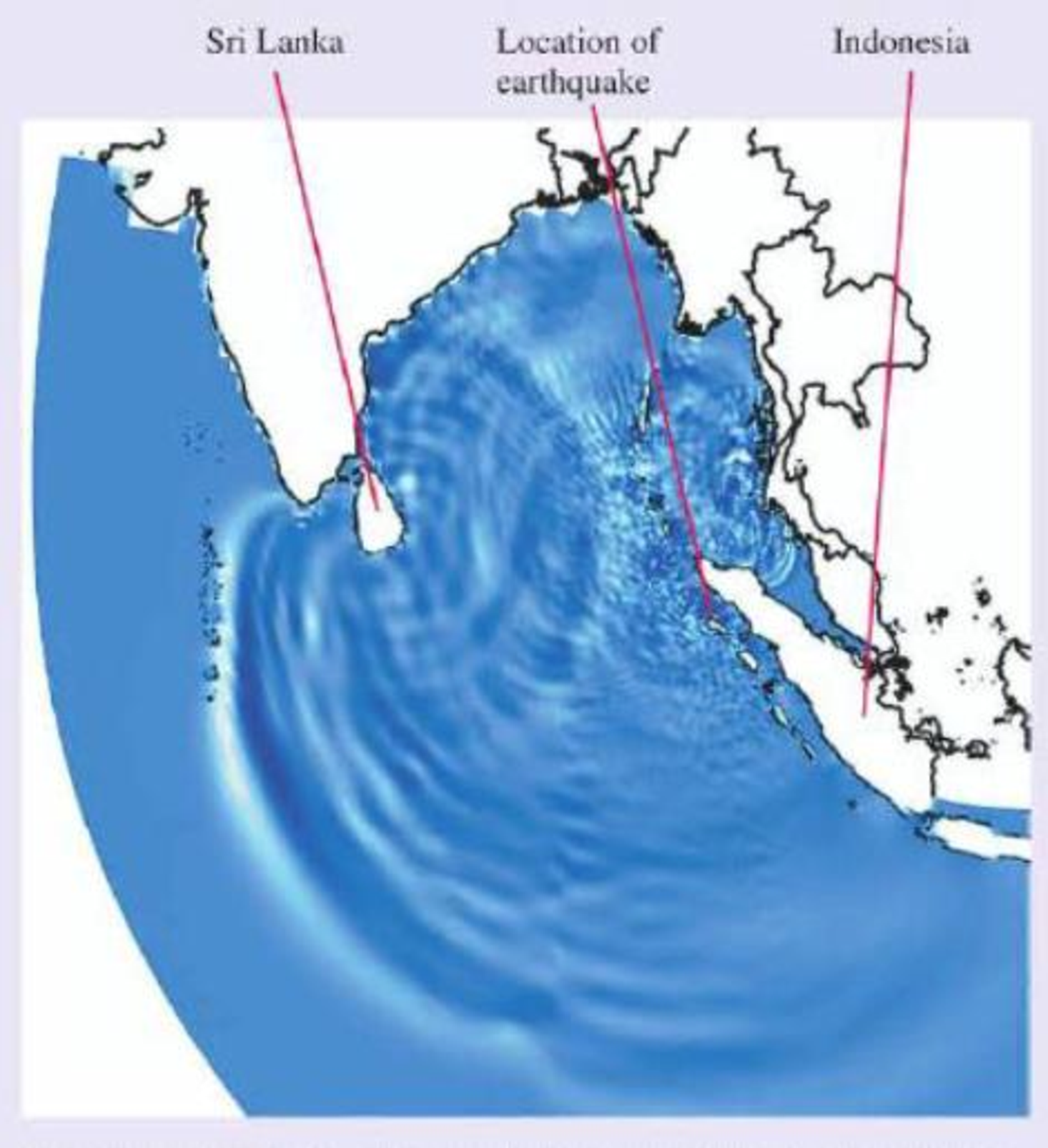
One frame from a computer simulation of the Indian Ocean tsunami three hours after the earthquake that produced it. The disturbance propagating outward from the earthquake is clearly seen, as are wave reflections from the island of Sri Lanka.
along it, carrying energy as it goes. The earthquake that produced the Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004 caused a sudden upward displacement of the seafloor that produced a corresponding rise in the surface of the ocean. This was the disturbance that produced the tsunami, very much like a quick shake on the end of a rope. The resulting wave propagated through the ocean, as we see in the figure.
This simulation of the tsunami looks much like the ripples that spread when you drop a pebble into a pond. But there is a big difference—the scale. The fact that you can see the individual waves on this diagram that spans 5000 km is quite revealing. To show up so clearly, the individual wave pulses must be very wide—up to hundreds of kilometers from front to back.
A tsunami is actually a “shallow water wave,” even in the deep ocean, because the depth of the ocean is much less than the width of the wave. Consequently, a tsunami travels differently than normal ocean waves. In Chapter 15 we learned that wave speeds are fixed by the properties of the medium. That is true for normal ocean waves, but the great width of the wave causes a tsunami to “feel the bottom.” Its wave speed is determined by the depth of the ocean: The greater the depth, the greater the speed. In the deep ocean, a tsunami travels at hundreds of kilometers per hour, much faster than a typical ocean wave. Near shore, as the ocean depth decreases, so docs the speed of the wave.
The height of the tsunami in the open ocean was about half a meter. Why should such a small wave—one that ships didn't even notice as it passed—be so fearsome? Again, it's the width of the wave that matters. Because a tsunami is the wave motion of a considerable mass of water, great energy is involved. As the front of a tsunami wave nears shore, its speed decreases, and the back of the wave moves faster than the front. Consequently, the width decreases. The water begins to pile up, and the wave dramatically increases in height.
The Indian Ocean tsunami had a height of up to 15 m when it reached shore, with a width of up to several kilometers. This tremendous mass of water was still moving at high speed, giving it a great deal of energy. A tsunami reaching the shore isn’t like a typical wave that breaks and crashes. It is a kilometers-wide wall of water that moves onto the shore and just keeps on coming. In many places, the water reached 2 km inland.
The impact of the Indian Ocean tsunami was devastating, but it was the first tsunami for which scientists were able to use satellites and ocean sensors to make planet-wide measurements. An analysis of the data has helped us better understand the physics of these ocean waves. We won’t be able to stop future tsunamis, but with a better knowledge of how they are formed and how they travel, we will be better able to warn people to get out of their way.
The following questions are related to the passage“Waves in the Earth and the Ocean ” on the previous page.
Rank from fastest to slowest the following waves according to their speed of propagation:
A. An earthquake wave
B. A tsunami
C. A sound wave in air
D. A light wave
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Please help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Graph of centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line.arrow_forwardBased on your graph, explain how centripetal force is affected when the hanging mass changes. Does your graph verify the relationship in the equation r = x^i + y^j = r cos ωt I + r sin ωt^j?arrow_forwardDid your experiment results in Data Table 3 verify, to within a reasonable experimental error, the condition of equilibrium of Equation 6: Στanti-clockwise = Στclockwise? Support your response with experimental data. My data shows that they are not equal to each other. So what does this mean? Thanks!arrow_forward
- Please help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Graph of centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line.arrow_forwardExplain how your experiment met the condition for equilibrium in Equation 4: ΣFvertical = ΣFy = 0.arrow_forwardCan i get answer and solution for this question and can you teach me What we use to get the answer.arrow_forward
- Can i get answer and solution and can you teach me how to get it.arrow_forwardConsider a image that is located 30 cm in front of a lens. It forms an upright image 7.5 cm from the lens. Theillumination is so bright that that a faint inverted image, due to reflection off the front of the lens, is observedat 6.0 cm on the incident side of the lens. The lens is then turned around. Then it is observed that the faint,inverted image is now 10 cm on the incident side of the lens.What is the index of refraction of the lens?arrow_forward2. In class, we discussed several different flow scenarios for which we can make enough assumptions to simplify the Navier-Stokes equations enough to solve them and obtain an exact solution. Consulting the cylindrical form of the Navier-Stokes equations copied below, please answer the following questions. др a 1 a + +0x- + +O₂ = Pgr + μl 18²v, 2 ave ²v₁] az2 + at or r de r Əz dr ar Vodvz др [18 + + +Or + +Vz = Pgz +fl at ar r 20 ôz ôz dr ave дов V,Ve ave +Or + + = pge at dr r 80 Əz + az2 a.) In class, we discussed how the Navier-Stokes equations are an embodiment of Newton's 2nd law, F = ma (where bolded terms are vectors). Name the 3 forces that we are considering in our analysis of fluid flow for this class. др a 10 1 ve 2 av 2200] + +μ or 42 30 b.) If we make the assumption that flow is "fully developed" in the z direction, which term(s) would go to zero? Write the term below, describe what the term means in simple language (i.e. do not simply state "it is the derivative of a with…arrow_forward
- 1. Consult the form of the x-direction Navier-Stokes equation below that we discussed in class. (For this problem, only the x direction equation is shown for simplicity). Note that the equation provided is for a Cartesian coordinate system. In the spaces below, indicate which of the following assumptions would allow you to eliminate a term from the equation. If one of the assumptions provided would not allow you to eliminate a particular term, write "none" in the space provided. du ди at ( + + + 매일) du ди = - Pgx dy др dx ²u Fu u + fl + ax2 ay² az2 - дх - Əz 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Assumption Flow is in the horizontal direction (e.g. patient lying on hospital bed) Flow is unidirectional in the x-direction Steady flow We consider the flow to be between two flat, infinitely wide plates There is no pressure gradient Flow is axisymmetric Term(s) in equationarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardwhy did the expert subtract the force exerted by the hand and the elbow by the force due to the weight of the hand and forearm and force exerted by the tricep. Does the order matter and how do you determine what to put first. Question 4 AP, CHAPTER 13 FROM BASIC BIOMECHANICS 8TH EDITIONarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





