
Concept explainers
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
(a) 3, 3-Dimethyl-4-octyne
(b) 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1, 6, 8-decatriyne
(c) 2, 2, 5, 5-Tetramethyl-3-hexyne
(d) 3, 4-Dimethylcyclodecyne
(e) 3, 5-Heptadien-1-yne
(f) 3-Chloro-4, 4-dimethyl-1-nonen-6-yne
(g) 3-sec-Butyl-1-heptyne
(h) 5-tert-Buty1-2-methyl-3-octyne
a) 3,3-Dimethyl-4-octyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,3-Dimethyl-4-octyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne is
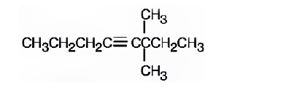
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain eight carbons with a triple bond between C4 & C5 and two methyl groups should be present on C3.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne is

b) 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne is
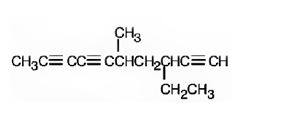
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain ten carbons with three triple bonds, one between C1 & C2, another between C6 & C7 a third one between C8 & C9, an ethyl group on C3 and a methyl group on C5.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne is

c) 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne is
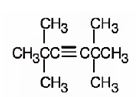
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain six carbons with a triple bond between C3 & C4 and four methyl groups, two on C2 and another two on C5.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne is

d) 3,4-Dimethylcyclodeceyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,4-Dimethylcyclodeceyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,4-dimethyl cyclodeceyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,4-dimethyl cyclodeceyne is
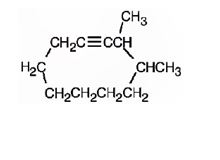
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the compound contains a ring made up of ten carbon atoms with a triple bond attached to two methyl groups on C3 and C4.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,4-dimethyl cyclodeceyne is

e) 3,5-Heptadiene-1-yne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. Compounds containing both double bond and triple bonds are called as enynes. The chain is numbered from the end nearer to the multiple bonds, double or triple. When there is a choice in numbering the double bond is given preference and the lowest number is assigned to it.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne is
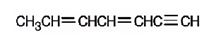
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain seven carbons with a triple bond between C1 & C2 and two double bonds, one between C3 & C4 and another between C5 & C6.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne is
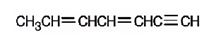
f) 3-Chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. Compounds containing both double bond and triple bonds are called as enynes. The chain is numbered from the end nearer to the multiple bonds, double or triple. When there is a choice in numbering the double bond is given preference and the lowest number is assigned to it.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne is
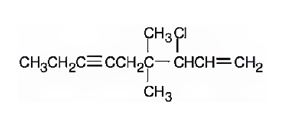
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain nine carbons with a triple bond between C6 & C7, one double bond between C1 & C2, a chlorine atom on C3 and two methyl groups on C4.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne is

g) 3-sec-Butyl-1-heptyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-sec-Butyl-1-heptyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-sec-butyl-1-heptyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-sec-butyl-1-heptyne is
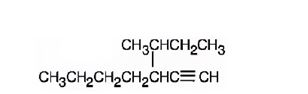
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain seven carbons with a triple bond between C1 & C2 and a sec-butyl group on C3.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-sec-butyl-1-heptyne is

h) 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne.
Interpretation:The structure of 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne is
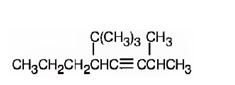
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain eight carbons with a triple bond between C3 & C4, a tert-butyl group on C5 and a methyl group on C2.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- 1) The isoamyl acetate report requires eight paragraphs - four for comparison of isoamyl alcohol and isoamyl acetate (one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR) and four for comparison of acetic acid and isoamyl acetate ((one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR. 2) For MS, the differing masses of molecular ions are a popular starting point. Including a unique fragmentation is important, too. 3) For HNMR, CNMR and IR state the peaks that are different and what makes them different (usually the presence or absence of certain groups). See if you can find two differences (in each set of IR, HNMR and CNMR spectra) due to the presence or absence of a functional group. Include peak locations. Alternatively, you can state a shift of a peak due to a change near a given functional group. Including peak locations for shifted peaks, as well as what these peaks are due to. Ideally, your focus should be on not just identifying the differences but explaining them in terms of…arrow_forward№3 Fill in the below boxes. HN 1. LAH 2. H3O+ NH2arrow_forwardFor the photochemical halogenation reaction below, draw both propagation steps and include the mechanism arrows for each step. H CH ot CH3 CI-CI MM hv of CH H-CI CH3 2nd attempt See Periodic Table See Hint Draw only radical electrons; do not add lone pair electrons. Note that arrows cannot meet in "space," and must end at either bonds or at atoms. 1 i Add the missing curved arrow notation to this propagation step. 20 H ن S F P H CI Br 品arrow_forward
- The radical below can be stabilized by resonance. 4th attempt Draw the resulting resonance structure. DOCEarrow_forwardUse curved arrows to generate a second resonance form for the allylic radical formed from 2-methyl-2-pentene. 1 Draw the curved arrows that would generate a second resonance form for this radical. D 2 H S F A Бг Iarrow_forwardDraw the resulting product(s) from the coupling of the given radicals. Inlcude all applicable electrons and non-zero formal charges. H.C öö- CH3 2nd attempt +1 : 招 H₂C CH CH₂ See Periodic Table See H H C S F P Br CH₂ Iarrow_forward
- Please, help me out with the calculation, step by step on how to find what's blank with the given information.arrow_forwardPredict the following products. Then show the mechanism. H₂N NH2arrow_forwardBF3, Boron Trifluoride, known to contain three covalent boron-fluorine bonds. suggest and illustrate all of the processes as well as their energetical consequences for the formation of BF3 from its elements.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism of the reaction.arrow_forward9. Draw all of the possible Monochlorination Products that would Result From the Free Radical Chlormation OF 23,4-TRIMethyl Pentane b. Calculate the To Yield For the major • Product given the Following Relative Restritus For 1° 2° and 30 Hydrogens toward Free Radical Chloration 5.0: 38 : 1 30 2° 1° C. what would be the major product in the Free Radical brominator Of the Same Molecule. Explain your Reasoning.arrow_forwardWhat is the complete reaction mechanism for the chlorination of Ethane, C2H6?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





