
a)
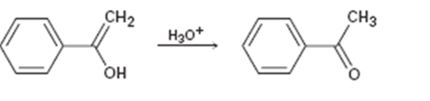
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation ion then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
b)
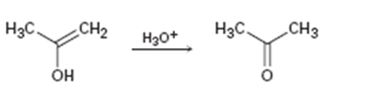
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an alkyne under acidic conditions is the tautomerization of the enol intermediate to give the corresponding ketone. The mechanism involves protonation followed by deprotonation. Based on this information a mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
c)
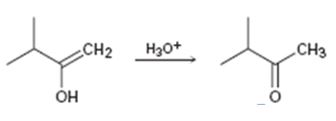
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an alkyne under acidic conditions is the tautomerization of the enol intermediate to give the corresponding ketone. The mechanism involves protonation followed by deprotonation. Based on this information a mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Consider this reaction (molecular weights are under each compound): HC=CH + 2 HCI --> C2H4Cl 2 MW = 26 36.5 99 If 4.4 g of HC=CH are reacted with 110 mL of a 2.3 M HCI solution, and 6.0 g of product are actually produced, what is the percent yield?arrow_forwardWhat is the name of the major product of this reaction? OH CH3 H₂SO4, heat 1-methylcyclohexene O2-methyl-1-cyclohexene O 3-mthylcyclohexene 1-methyl-2-cyclohexenearrow_forwardWe added a brown solution of Br2 to one of our products, and the brown color disappeared. This indicated that our product wasarrow_forward
- Rank the following according to reactivity toward nitration: a) benzene b) bromobenzene c) nitrobenzene d) phenol Od) greatest, c) least Od) greatest, b) least Od) greatest, a) least a) greatest, b) least a) greatest, c) least Oa) greatest, d) least Ob) greatest, a) least O b) greatest, c) least Ob) greatest, d) least O c) greatest, a) least O c) greatest, b) least O c) greatest, d) leastarrow_forwardO-Nitrophenol was distilled over with the steam in our experiment while the other isomer did not. This is due to: O intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the ortho isomer O intermolecular hydrogen bonding in the the ortho isomer O the ortho isomer has a lower density O the ortho isomer has a lower molecular weightarrow_forwardK 44% Problem 68 of 15 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :6: :: :CI: CI CI: :0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows H H Cl CI: CI CI: Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows H :CI: Alarrow_forward
- I I H :0: Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. 0:0 :0: CI ΑΙ :CI: :CI: :0: CI Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows cl. :0: Cl © ハ CI:: CI H CO Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows 10: AI ::arrow_forwardOrder the following compounds from slowest to fastest in a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. ii 요 OB D A E C OCE Darrow_forwardI need the most help figuring out how to find [I^-] mol/ L, [S2O8^2-] mol/L. 1st and 2nd Blank columns.arrow_forwardCan someone help me whats the issue?arrow_forwarda. The change in the Gibbs energy of a certain constant pressure process is found to fit the expression: AG-85.1 J mol −1 +36.5 J mol ¹K-1 × T A. Calculate the value of AS for the process. B. Next, use the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation: (a(AG/T)) ΔΗ - T2 to calculate the value of AH for the process.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

