
(a)
To find: The motion of the object with the mass and the damping factor.
(a)
Answer to Problem 29AYU
The direction of the bob is negative, the mass of the bob is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given covered by the bob is
Calculation:
Consider the given equation for distance is,
The bob is released from left to right it represents a negative direction and the motion described by the bob is damped.
Consider the general expression for the damped motion is,
From the given equation and from the above equation the amplitude of the displacement at
The value of
The damping factor is,
(b)
To find: The initial displacement of the bob.
(b)
Answer to Problem 29AYU
The initial displacement is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given covered by the bob is
Calculation:
Consider the given equation for distance is,
From above the initial displacement of the bob is,
The initial displacement is
(c)
To find: The graph of the motion.
(c)
Answer to Problem 29AYU
The required diagram is shown in Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given covered by the bob is
Calculation:
Consider the given equation for distance is,
By the use of MAPPLE, the graph of
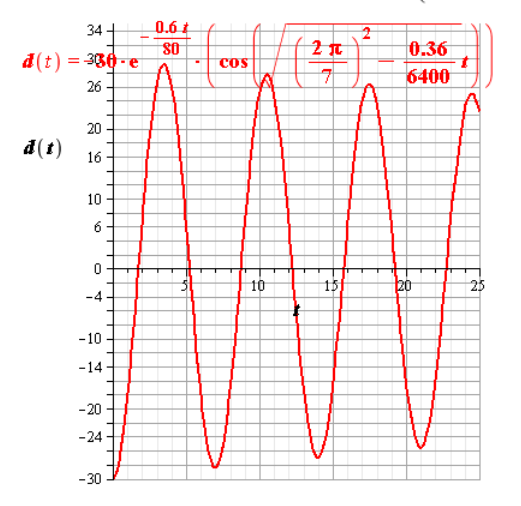
Figure 1
(d)
To find: The displacement of the bob at the start of the second oscillation.
(d)
Answer to Problem 29AYU
Thestart of the second oscillation is approximately
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given covered by the bob is
Calculation:
Consider the given equation for distance is,
From the graph shown in Figure 1, the displacement of the graph at the start of the second oscillation is approximately
(e)
To find: The displacement of the bob as the time increases without bound.
(e)
Answer to Problem 29AYU
The displacement of the bob as the time increases without bound reduces to zero.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given covered by the bob is
Calculation:
Consider the given equation for distance is,
From the graph is shown in Figure 1, as
Chapter 8 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- Evaluate the double integral ' √ √ (−2xy² + 3ry) dA R where R = {(x,y)| 1 ≤ x ≤ 3, 2 ≤ y ≤ 4} Double Integral Plot of integrand and Region R N 120 100 80- 60- 40 20 -20 -40 2 T 3 4 5123456 This plot is an example of the function over region R. The region and function identified in your problem will be slightly different. Answer = Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forwardFind Te²+ dydz 0 Write your answer in exact form.arrow_forwardxy² Find -dA, R = [0,3] × [−4,4] x²+1 Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forward
- Find the values of p for which the series is convergent. P-?- ✓ 00 Σ nº (1 + n10)p n = 1 Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER [-/4 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 8.3.513.XP. Consider the following series. 00 Σ n = 1 1 6 n° (a) Use the sum of the first 10 terms to estimate the sum of the given series. (Round the answer to six decimal places.) $10 = (b) Improve this estimate using the following inequalities with n = 10. (Round your answers to six decimal places.) Sn + + Los f(x) dx ≤s ≤ S₁ + Jn + 1 + Lo f(x) dx ≤s ≤ (c) Using the Remainder Estimate for the Integral Test, find a value of n that will ensure that the error in the approximation s≈s is less than 0.0000001. On > 11 n> -18 On > 18 On > 0 On > 6 Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward√5 Find Lª³ L² y-are y- arctan (+) dy dydx. Hint: Use integration by parts. SolidUnderSurface z=y*arctan(1/x) Z1 2 y 1 1 Round your answer to 4 decimal places.arrow_forwardFor the solid lying under the surface z = √√4-² and bounded by the rectangular region R = [0,2]x[0,2] as illustrated in this graph: Double Integral Plot of integrand over Region R 1.5 Z 1- 0.5- 0 0.5 1 1.5 205115 Answer should be in exact math format. For example, some multiple of .arrow_forward
- Find 2 S² 0 0 (4x+2y)5dxdyarrow_forward(14 points) Let S = {(x, y, z) | z = e−(x²+y²), x² + y² ≤ 1}. The surface is the graph of ze(+2) sitting over the unit disk.arrow_forward6. Solve the system of differential equations using Laplace Transforms: x(t) = 3x₁ (t) + 4x2(t) x(t) = -4x₁(t) + 3x2(t) x₁(0) = 1,x2(0) = 0arrow_forward
- 3. Determine the Laplace Transform for the following functions. Show all of your work: 1-t, 0 ≤t<3 a. e(t) = t2, 3≤t<5 4, t≥ 5 b. f(t) = f(tt)e-3(-) cos 4τ drarrow_forward4. Find the inverse Laplace Transform Show all of your work: a. F(s) = = 2s-3 (s²-10s+61)(5-3) se-2s b. G(s) = (s+2)²arrow_forward1. Consider the differential equation, show all of your work: dy =(y2)(y+1) dx a. Determine the equilibrium solutions for the differential equation. b. Where is the differential equation increasing or decreasing? c. Where are the changes in concavity? d. Suppose that y(0)=0, what is the value of y as t goes to infinity?arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





