
(a)
Interpretation:The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
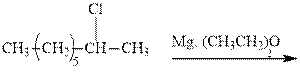
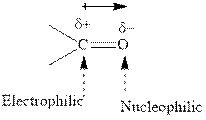
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick
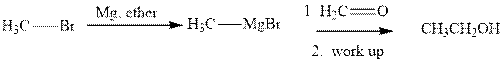
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
(b)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
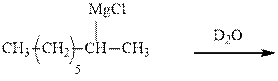
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
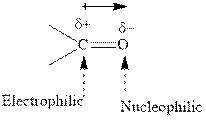
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
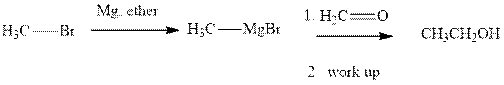
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
(c)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
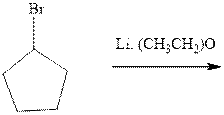
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
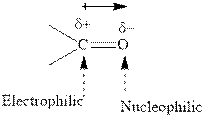
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
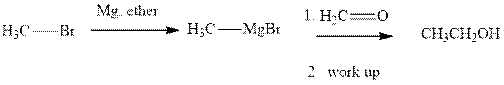
(d)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
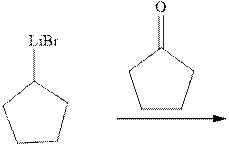
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
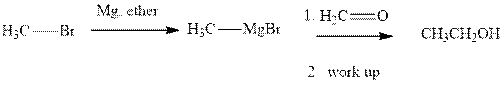
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(e)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
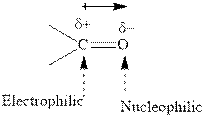
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
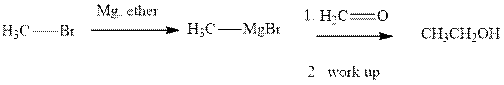
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(f)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
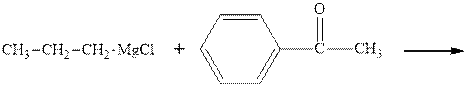
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
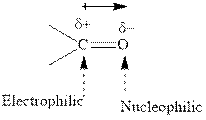
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
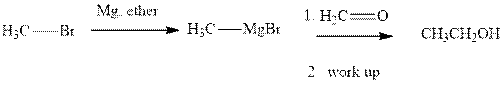
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
(g)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
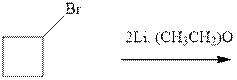
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
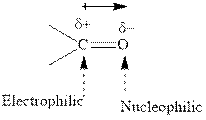
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
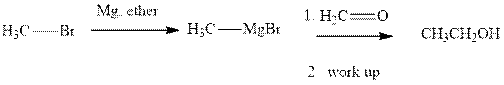
(h)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be written.
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
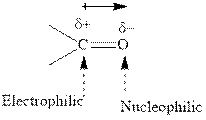
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
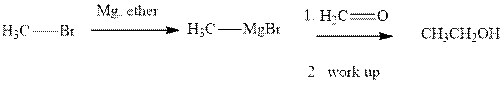
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-PACKAGE
- Indicate the substitutes in one place, if they are a diazonio room.arrow_forwardIndicate the product formed in each reaction. If the product exhibits tautomerism, draw the tautomeric structure. a) о + CH3-NH-NH2 CO2C2H5 b) + CoH5-NH-NH2 OC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward
- Synthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole from 1,2-diaminobenceno.arrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole.arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward
- Identify the mechanism through which the following reaction will proceed and draw the major product. Part 1 of 2 Br KOH EtOH Through which mechanism will the reaction proceed? Select the single best answer. E1 E2 neither Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the major product formed as a result of the reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardWhat is single-point calibration? Provide an example.arrow_forwardDraw the major product formed via an E1 pathway.arrow_forward
- Part 9 of 9 Consider the products for the reaction. Identify the major and minor products. HO Cl The E stereoisomer is the major product and the Z stereoisomer is the minor product ▼ S major product minor productarrow_forwardConsider the reactants below. Answer the following questions about the reaction mechanism and products. HO Clarrow_forwardjulietteyep@gmail.com X YSCU Grades for Juliette L Turner: Orc X 199 A ALEKS - Juliette Turner - Modul X A ALEKS - Juliette Turner - Modul x G butane newman projection - Gox + www-awa.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IBxzaplnN4HsoQggFsejpgqKoyrQrB2dKVAN-BcZvcye0LYa6eXZ8d4vVr8Nc1GZqko5mtw-d1MkNcNzzwZsLf2Tu9_V817y?10Bw7QYjlb il Scribbr citation APA SCU email Student Portal | Main Ryker-Learning WCU-PHARM D MySCU YSCU Canvas- SCU Module 4: Homework (Ch 9-10) Question 28 of 30 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited H₂SO heat OH The mechanism of this reaction involves two carbocation intermediates, A and B. Part 1 of 2 KHSO 4 rearrangement A heat B H₂O 2 OH Draw the structure of A. Check Search #t m Save For Later Juliet Submit Assignm 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
