
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133949640
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.6, Problem 8Q
Use the atomic radii of scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, and lutetium to answer the questions below.
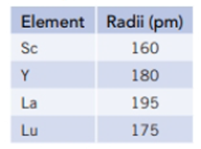
- a. Explain why lutetium has a smaller atomic radius than lanthanum, even though it has a greater number of electrons.
- b. Do the atomic radii argue for the placement of La or Lu below Y in the periodic table? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).
Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).
What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
CH₂CH₂
H
CI
H₂CH₂C
H
CH₂
Selected Answer:
O
(35,4R)-4 chloro-3-ethylpentane
Correct
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Ch. 7.1 - How many electrons can be accommodated in the n =...Ch. 7.1 - Prob. 2RCCh. 7.2 - Based on the Aufbau principle and the n + rule,...Ch. 7.3 - (a) What element has the configuration...Ch. 7.3 - Write one possible set of quantum numbers for the...Ch. 7.3 - Using the periodic table and without looking at...Ch. 7.3 - 1. What is the electron configuration of selenium...Ch. 7.3 - 2. Based on electron configurations, which of the...Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 1CYUCh. 7.4 - Prob. 1RC
Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 2RCCh. 7.4 - Which of the following species is most...Ch. 7.5 - Without looking at the figures for the periodic...Ch. 7.5 - What is the trend in sizes of the ions K+, S2, and...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 2RCCh. 7.6 - Give the electron configurations for iron and the...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 2QCh. 7.6 - Prob. 3QCh. 7.6 - Prob. 4QCh. 7.6 - Prob. 1RCCh. 7.6 - Prob. 2RCCh. 7.6 - The most common oxidation state of a rare earth...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 6QCh. 7.6 - Prob. 7QCh. 7.6 - Use the atomic radii of scandium, yttrium,...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 9QCh. 7.6 - Prob. 10QCh. 7 - Write the electron configurations for P and CI...Ch. 7 - Write the electron configurations for Mg and Ar...Ch. 7 - Using spdf notation, write the electron...Ch. 7 - Using spdf notation, give the electron...Ch. 7 - Prob. 5PSCh. 7 - Prob. 6PSCh. 7 - Use noble gas and spdf notations to depict...Ch. 7 - The lanthanides, once called the rare earth...Ch. 7 - Prob. 9PSCh. 7 - Prob. 10PSCh. 7 - What is the maximum number of electrons that can...Ch. 7 - What is the maximum number of electrons that can...Ch. 7 - Depict the electron configuration for magnesium...Ch. 7 - Depict the electron configuration for phosphorus...Ch. 7 - Using an orbital box diagram and noble gas...Ch. 7 - Using an orbital box diagram and noble gas...Ch. 7 - Using orbital box diagrams, depict an electron...Ch. 7 - Prob. 18PSCh. 7 - Prob. 19PSCh. 7 - Using orbital box diagrams and noble gas notation,...Ch. 7 - Manganese is found as MnO2 in deep ocean deposits....Ch. 7 - One compound found in alkaline batteries is NiOOH,...Ch. 7 - Prob. 23PSCh. 7 - Arrange the following elements in order of...Ch. 7 - Prob. 25PSCh. 7 - Prob. 26PSCh. 7 - Which of the following groups of elements is...Ch. 7 - Arrange the following atoms in order of increasing...Ch. 7 - Compare the elements Na, Mg, O, and P. (a) Which...Ch. 7 - Compare the elements B. Al, C, and Si. (a) Which...Ch. 7 - Explain each answer briefly. (a) Place the...Ch. 7 - Explain each answer briefly. (a) Rank the...Ch. 7 - Identify the element that corresponds to each of...Ch. 7 - Identify the element that corresponds to each of...Ch. 7 - Explain why the photoelectron spectra of hydrogen...Ch. 7 - Sketch the major features (number of peaks and...Ch. 7 - These questions are not designated as to type or...Ch. 7 - The deep blue color of sapphires comes from the...Ch. 7 - Using an orbital box diagram and noble gas...Ch. 7 - Prob. 40GQCh. 7 - Prob. 41GQCh. 7 - Prob. 42GQCh. 7 - Which of the following is not an allowable set of...Ch. 7 - A possible excited state for the H atom has an...Ch. 7 - The magnet in the following photo is made from...Ch. 7 - Name the element corresponding to each...Ch. 7 - Arrange the following atoms in order of increasing...Ch. 7 - Prob. 48GQCh. 7 - Answer the questions below about the elements A...Ch. 7 - Answer (he following questions about the elements...Ch. 7 - Which of the following ions are unlikely to be...Ch. 7 - Prob. 52GQCh. 7 - Answer each of the following questions: (a) Of the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 54GQCh. 7 - Prob. 55GQCh. 7 - Two elements in the second transition series (Y...Ch. 7 - Prob. 57GQCh. 7 - The configuration of an element is given here. (a)...Ch. 7 - Answer the questions below about the elements A...Ch. 7 - Answer the questions below concerning ground state...Ch. 7 - Nickel(II) formate [Ni(HCO2)2] is widely used as a...Ch. 7 - Spinets are solids with the general formula M2+...Ch. 7 - The following questions use concepts from this and...Ch. 7 - Which ions in the following list are not likely to...Ch. 7 - Answer the following questions about first...Ch. 7 - The ionization of the hydrogen atom can be...Ch. 7 - Compare the configurations below with two...Ch. 7 - Prob. 68SCQCh. 7 - Write electron configurations to show the first...Ch. 7 - Prob. 70SCQCh. 7 - (a) Explain why the sizes of atoms change when...Ch. 7 - Which of the following elements has the greatest...Ch. 7 - Prob. 73SCQCh. 7 - Prob. 74SCQCh. 7 - The energies of the orbitals in many elements have...Ch. 7 - The ionization energies for the removal of the...Ch. 7 - Using your knowledge of the trends in element...Ch. 7 - Prob. 78SCQCh. 7 - Prob. 79SCQCh. 7 - Prob. 80SCQCh. 7 - Thionyl chloride. SOCl2, is an important...Ch. 7 - Prob. 82SCQCh. 7 - Slaters rules are a way to estimate the effective...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. I I I H Select to Add Arrows HCI, CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and the follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the intermediates and product of the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and the product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardLook at the following pairs of structures carefully to identify them as representing a) completely different compounds, b) compounds that are structural isomers of each other, c) compounds that are geometric isomers of each other, d) conformers of the same compound (part of structure rotated around a single bond) or e) the same structure.arrow_forward
- Given 10.0 g of NaOH, what volume of a 0.100 M solution of H2SO4 would be required to exactly react all the NaOH?arrow_forward3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forward3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forward
- Concentration Trial1 Concentration of iodide solution (mA) 255.8 Concentration of thiosulfate solution (mM) 47.0 Concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution (mM) 110.1 Temperature of iodide solution ('C) 25.0 Volume of iodide solution (1) used (mL) 10.0 Volume of thiosulfate solution (5:03) used (mL) Volume of DI water used (mL) Volume of hydrogen peroxide solution (H₂O₂) used (mL) 1.0 2.5 7.5 Time (s) 16.9 Dark blue Observations Initial concentration of iodide in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of thiosulfate in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mA) Initial Rate (mA's)arrow_forwardDraw the condensed or line-angle structure for an alkene with the formula C5H10. Note: Avoid selecting cis-/trans- isomers in this exercise. Draw two additional condensed or line-angle structures for alkenes with the formula C5H10. Record the name of the isomers in Data Table 1. Repeat steps for 2 cyclic isomers of C5H10arrow_forwardExplain why the following names of the structures are incorrect. CH2CH3 CH3-C=CH-CH2-CH3 a. 2-ethyl-2-pentene CH3 | CH3-CH-CH2-CH=CH2 b. 2-methyl-4-pentenearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Lanthanoids and its Position in Periodic Table - D and F Block Elements - Chemistry Class 12; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZM04kRxm6tY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY