
Concept explainers
A Howe scissors roof truss is loaded as shown. Determine force in members DF, DG, and EG.
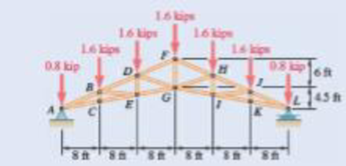
Fig. P6.57 and P6.58
The force in the members
Answer to Problem 6.57P
The force in the members
Explanation of Solution
The Howe scissors roof truss is loaded as shown in the figure. There is load at all the point on the top. The free body diagram of the given arrangement is given by Figure 1.
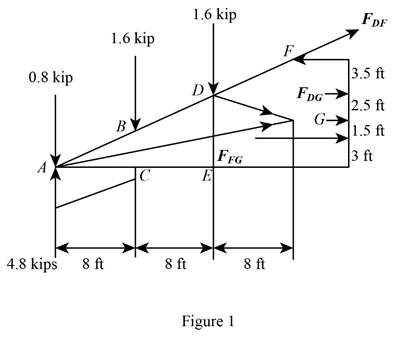
The total load on the truss is given from the figure as,
By symmetry the
From the diagram the sum of the moments in the counter clockwise direction about
From the diagram the sum of the moments in the counter clockwise direction about
From the diagram the sum of the moments in the counter clockwise direction about
Conclusion:
Solve for
Solve for
Solve for
Therefore, the force in the members
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
- PROBLEM 15.225 The bent rod shown rotates at the constant rate @₁ = 5 rad/s and collar C moves toward point B at a constant relative speed u = 39 in./s. Knowing that collar C is halfway between points B and D at the instant shown, determine its velocity and acceleration. Answers: v=-45 +36.6)-31.2 k in./s āc = -2911-270} in./s² 6 in 20.8 in. 14.4 in.arrow_forwardNeed help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!..arrow_forwardNeed help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!...arrow_forward
- FL y b C Z Determine the moment about O due to the force F shown, the magnitude of the force F = 76.0 lbs. Note: Pay attention to the axis. Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 1.90 ft b 2.80 ft с 2.60 ft d 2.30 ft Mo 144 ft-lb = -212 × 1 + xk) ☑+212arrow_forward20 in. PROBLEM 15.206 Rod AB is connected by ball-and-socket joints to collar A and to the 16-in.-diameter disk C. Knowing that disk C rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate ₁ =3 rad/s in the zx plane, determine the velocity of collar A for the position shown. 25 in. B 8 in. Answer: -30 in/s =arrow_forwardB Z 001 2.5 ft PROBLEM 15.236 The arm AB of length 16 ft is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. In the position shown, arm AB is being raised at the constant rate de/dt = 0.25 rad/s; simultaneously, the unit is being rotated about the Y axis at the constant rate ₁ =0.15 rad/s. Knowing that 20°, determine the velocity and acceleration of Point B. Answers: 1.371 +3.76)+1.88k ft/s a=1.22 -0.342)-0.410k ft/s² Xarrow_forward
- F1 3 5 4 P F2 F2 Ꮎ Ꮎ b P 3 4 5 F1 The electric pole is subject to the forces shown. Force F1 245 N and force F2 = 310 N with an angle = 20.2°. Determine the moment about point P of all forces. Take counterclockwise moments to be positive. = Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 2.50 m b 11.3 m C 13.0 m The moment about point P is 3,414 m. × N- If the moment about point P sums up to be zero. Determine the distance c while all other values remained the same. 1.26 m.arrow_forwardZ 0.2 m B PROBLEM 15.224 Rod AB is welded to the 0.3-m-radius plate, which rotates at the constant rate ₁ = 6 rad/s. Knowing that collar D moves toward end B of the rod at a constant speed u = 1.3 m, determine, for the position shown, (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D. Answers: 1.2 +0.5-1.2k m/s a=-7.21-14.4k m/s² A 0.25 m 0.3 marrow_forwardI am trying to code in MATLAB the equations of motion for malankovich orbitlal elements. But, I am having a problem with the B matrix. Since f matrix is 7x1 and a_d matrix has to be 3x1, the B matrix has to be 7x3. I don't know how that is possible. Can you break down the B matrix for me and let me know what size it is?arrow_forward
- I am trying to code the solution to the problem in the image in MATLAB. I wanted to know what is the milankovich constraint equation that is talked about in part b.arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardAir modeled as an ideal gas enters an insulated compressor at a temperature of 300 K and 100 kPa, and leaves at 600 kPa. The mass flowrate of air entering the compressor is 50 kg/hr, and the power consumed by the compressor is 3 kW. (Rair = 0.287 kJ/kg-K, k = 1.4, cp = 1.0045 kJ/kg-K, cv = 0.718 kJ/kg-K) Determine the isentropic exit temperature (Te,s) of the air in [K]. Determine the actual exit temperature (Te) of the air in [K]. Determine the isentropic efficiency of the compressor. (Answer: ηc,s = 93.3%) Determine the rate of entropy generated through the compressor in [kW/K]. (Answer: Ṡgen = 0.000397 kW/K)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





