
Concept explainers
Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the double-pitch roof truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.
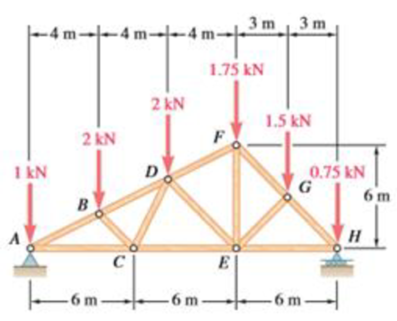
The force in each of the member of the double-pitch roof truss using method of joints and whether each member is in tension or compression.
Answer to Problem 6.165RP
The force in member
Explanation of Solution
The free-body diagram of the truss is shown in figure 1.
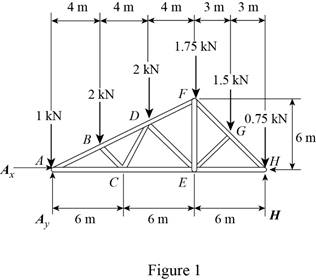
The sum of the moments about the point
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (I).
The
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (II).
The
Here,
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (III).
Here,
Substitute
The free-body diagram of joint A is shown in figure 2.
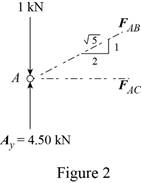
The joint A is subject to the forces exerted by
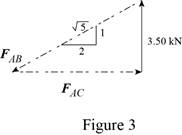
Obtain the magnitudes of the two forces from proportion.
Here,
The free-body diagram of the joint B is shown in figure 4.
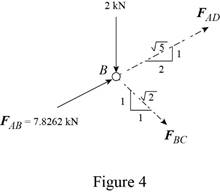
Write the equilibrium equations.
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (IV).
The
Here,
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (VI).
Multiply equation (V) by
Subtract equation (VII) from (V).
The free-body diagram of the joint C is shown in figure 5.
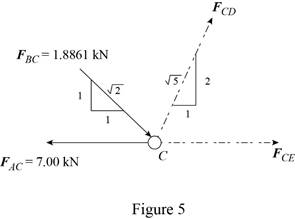
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (VI).
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (IV).
The free-body diagram of the joint D is shown in figure 6.
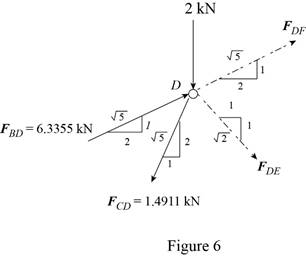
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (IV).
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (VI).
Add equations (VIII) and (IX).
Subtract equation (IX) from equation (VIII).
Consider the joint F. The free-body diagram of the joint F is shown in figure 7.
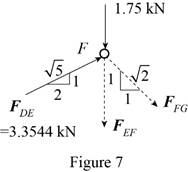
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (IV).
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (VI).
Consider the joint G. The free-body diagram of the joint G is shown in figure 8.
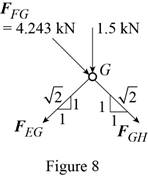
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (IV).
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (VI).
Add equations (X) and (XI).
Subtract equation (X) from equation (XI).
Consider the joint H. The free-body diagram of the joint H is shown in figure 9.
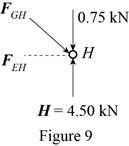
The joint H is subject to the forces exerted by
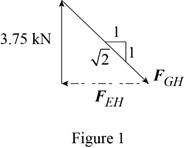
Obtain the magnitudes of the force from proportion.
Conclusion:
Thus, the force in member
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
- Using the Method of Joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member of the truss is in tension or compression. You do not need any "helper hints" for this problem as this problem is self-checking. 5 kip D 3 kip 6 ft 3 kip 5 kip -10 ft- -10 ftarrow_forward3. Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression. 2000 lb 1000 lb -12 ft - -12 ft- A B 8 ft D -12 ft 6 ft 6 ftarrow_forwardDetermine the force acting in members BD, BE, CE and DE of the Bowstring truss shown below. Indicate whether tension or compression. Use the method of joints.arrow_forward
- Using method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. Indicate whether the members are in tension or compression.arrow_forwardUse the method of joints to determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether the force is in tension or compression.arrow_forwardProblem #1: Determine the force in each member of the truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression using the method of joint 3m 2m 4m 75 KNarrow_forward
- Determine the member forces for all members in each truss shown using the method on joints. Remember to list each member force as either tension or compression.arrow_forwardUsing the method of joints, calculate the force in each memberof the trusses shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.arrow_forwardUsing the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression. 1.4 m -0.75 m- T 0.4 m B 2.8 kNarrow_forward
- Using the method of joint. Determine the force in each member of the truss shown in Fig. 5. Also, state if the members are in tension or compression.arrow_forwardProblem #2: Determine the force in each member at joint A, B and C of the truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression using the method of joint. 5kips 8kips C 3kips 8' D. A E 3 bays @ 6'arrow_forwardDetermine the force in members GE, GC, and BC of the truss as shown below. Indicate whether the members are in tension or compression OPTION:(MULTI CORRECT(MAY BE)): 1.Force in Member BC is about 800 N Compressive 2.Force in Member GE is about 800 N Compression 3.Force in Member GC is about 500 N Tensile 4.Force in Member GC is about 600 N Tensile 5.Force in Member GE is about 700 N Compressive 6.Force in Member BC is about 900 N Compressive 7.Force in Member GC is about 500 N Compressive 8.Force in Member BC is about 900 N Tensile 9.Force in Member BC is about 800 N Tensile 10Force in Member GE is about 700 N Tensile 11.Force in Member GE is about 800 N Tensile 12.Force in Member GC is about 600 N Compressivearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





