
The Swanky Hotel provides room service for its guests. The process for room service begins with a room
- a. What is the capacity of the process, and what is the bottleneck?
- b. What is the throughput time of a typical order?
- c. Assume that on Friday evenings an average of 10 room-service orders per hour are placed. How many orders are in the system on average on Friday nights?
a)
To determine: The capacity of the process.
Introduction:
Flow rate is the number of flow units through a business procedure per unit time. Flow rate refers to the number of customers who will be served per hour or the parts produced per minute.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hotel S provides room service for its guests. The process starts at the room, where the guest would place the order through phone. It takes 2 minutes to receive the order by phone, which is taken by the room service manager. The order will be sent to the kitchen and it takes 16 minutes to prepare the food. There are four cooks in the kitchen.
If the guest orders a beverage along with the food, the order details will be sent to the bar at the same time as it is sent to the kitchen. 80 percent of the order comes with beverages. It takes 3 minutes to fill the order in the bar. There are six waiters and it takes 20 minutes to complete the order.
Determine the capacity:
The capacity of the service manager is 30 orders per hour (2 minutes per order).
Determine the capacity of the chefs:
The capacity of Person J’s assistant is 7 minutes per customers (it includes 2 minutes of receiving the order, 2 minutes of packing, and 3 minutes of billing).
Hence, the chefs can handle 15 orders per hour and the bartender can handle 20 orders per hour (as he takes 3 minutes to fill).
Determine the capacity of waiter:
Hence, the waiters can handle 18 orders per hour.
Note: As the capacity of bartender (20 orders per hour) is more than the capacity of the kitchen (15 orders per hour), bar is not a constraint. Hence, kitchen is the bottleneck.
b)
To determine: The average throughput time.
Introduction:
Flow rate is the number of flow units through a business procedure per unit time. Flow rate refers to the number of customers who will be served per hour or the parts produced per minute.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hotel S provides room service for its guests. The process starts at the room, where the guest would place the order through phone. It takes 2 minutes to receive the order by phone, which is taken by the room service manager. The order will be sent to the kitchen and it takes 16 minutes to prepare the food. There are four cooks in the kitchen.
If the guest orders a beverage along with the food, the order details will be sent to the bar at the same time as it is sent to the kitchen. 80 percent of the order comes with beverages. It takes 3 minutes to fill the order in the bar. There are six waiters and it takes 20 minutes to complete the order.
Determine the average throughput time:
Average throughput time is the average of the time taken to receive and deliver the order. The bar time of 3 minutes is not considered, as it is done parallelly.
Hence, the average throughput time is 38 minutes.
c)
To determine: The number of orders in the system.
Introduction:
Flow rate is the number of flow units through a business procedure per unit time. Flow rate refers to the number of customers who will be served per hour or the parts produced per minute.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hotel S provides room service for its guests. The process starts at the room, where the guest would place the order through phone. It takes 2 minutes to receive the order by phone, which is taken by the room service manager. The order will be sent to the kitchen and it takes 16 minutes to prepare the food. There are four cooks in the kitchen.
If the guest orders a beverage along with the food, the order details will be sent to the bar at the same time as it is sent to the kitchen. 80 percent of the order comes with beverages. It takes 3 minutes to fill the order in the bar. There are six waiters and it takes 20 minutes to complete the order. There is an average of 10 room-service placed on Friday evenings.
Formula to determine the average number of orders in the system:
Here
I refers to the number of orders in the systems.
T refers to the average throughout time.
R refers to the average flow rate in the process.
Determine the average number of orders in the system:
It calculated by multiplying the average throughput time with the average flow rate in the process.
Hence, the average number of orders in the system is 6.33 orders.
d)
To determine: The average cost of an order and the minimum cost per order.
Introduction:
Flow rate is the number of flow units through a business procedure per unit time. Flow rate refers to the number of customers who will be served per hour or the parts produced per minute.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hotel S provides room service for its guests. The process starts at the room, where the guest would place the order through phone. It takes 2 minutes to receive the order by phone, which is taken by the room service manager. The order will be sent to the kitchen and it takes 16 minutes to prepare the food. There are four cooks in the kitchen.
If the guest orders a beverage along with the food, the order details will be sent to the bar at the same time as it is sent to the kitchen. 80 percent of the order comes with beverages. It takes 3 minutes to fill the order in the bar. There are six waiters and it takes 20 minutes to complete the order.
Additional information:
Waiters are paid $9 per hour and the chefs are paid $15 per hour. The room service manager is paid $18 per hour and the bartender is paid $10 per hour. The cost of beverages and food averages $6 per order and assume that 60 percent overhead is added to the direct labor.
Determine the total labor costs:
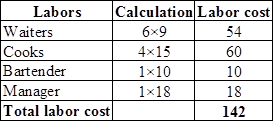
Labor cost can be calculated by multiplying the number of labors and the amount paid to labors per hour. If the overhead is added, the total cost is 227.20 (142+(142×0.6).
Hence, the labor cost per order including overhead is $22.70 per orders when the number of order is 10 orders per hour.
Hence, the average cost per order is $28.70 (sum of labor cost per order and the food and beverage cost).
Determine the minimum cost per order:
It is calculated by adding the value attained by dividing the total labor cost including overhead by the capacity of the chefs to the food beverage cost.
Hence, the minimum cost per order is $21.15.
e)
To determine: The assumptions that are made in the calculations which are not reasonable.
Introduction:
Flow rate is the number of flow units through a business procedure per unit time. Flow rate refers to the number of customers who will be served per hour or the parts produced per minute.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hotel S provides room service for its guests. The process starts at the room, where the guest would place the order through phone. It takes 2 minutes to receive the order by phone, which is taken by the room service manager. The order will be sent to the kitchen and it takes 16 minutes to prepare the food. There are four cooks in the kitchen.
If the guest orders a beverage along with the food, the order details will be sent to the bar at the same time as it is sent to the kitchen. 80 percent of the order comes with beverages. It takes 3 minutes to fill the order in the bar. There are six waiters and it takes 20 minutes to complete the order.
Determine the assumptions that are made in the calculations which are not reasonable:
The assumption that is made in the calculations which is not reasonable is the notion of using the resources fully. In addition, there were no worker breaks, no missing ingredients, and no kitchen downtime. It is also assumed that there is no variation in the flow rates.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN: DECISIONS & CASES (Mcgraw-hill Series Operations and Decision Sciences)
- 1) View the video Service Processing at BuyCostumes (10.41 minutes, Ctrl+Click on the link); what are your key takeaways (tie to one or more of the topics discussed in Chapter 3) after watching this video. (viddler.com/embed/a6b7054c) Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs. 2) Orkhon Foods makes hand-held pies (among other products). The firm’s weekly sales of hand-held pies over the past seven weeks are given in the table. The firm’s operations manager, Amarjargal, wants to forecast sales for week 8. Weeks Sales of hand-held pies(000s) 1 19 2 18 3 17 4 20 5 18 6 22 7 20 Forecast the week 8 sales using the following approaches: a) Naïve approach b) 5-month moving average c) 3-month weighted moving average using the following weights: 0.50 for week 7, 0.30 for week 6, and 0.20 for week 5. d) Exponential smoothing using a smoothing constant of 0.30, assume a…arrow_forwardAnswer all parts to question 4 and show all workingarrow_forward1) View the video Service Processing at BuyCostumes (10.41 minutes, Ctrl+Click on the link); what are your key takeaways (tie to one or more of the topics discussed in Chapter 3) after watching this video. (viddler.com/embed/a6b7054c) Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs. 2) Orkhon Foods makes hand-held pies (among other products). The firm’s weekly sales of hand-held pies over the past seven weeks are given in the table. The firm’s operations manager, Amarjargal, wants to forecast sales for week 8. Weeks Sales of hand-held pies(000s) 1 19 2 18 3 17 4 20 5 18 6 22 7 20 Forecast the week 8 sales using the following approaches: a) Naïve approach b) 5-month moving average c) 3-month weighted moving average using the following weights: 0.50 for week 7, 0.30 for week 6, and 0.20 for week 5. d) Exponential smoothing using a smoothing constant of 0.30, assume a week 2…arrow_forward
- What area of emotional intelligence refers to the ability to manage your emotions, particularly in stressful situations, and maintain a positive outlook despite setbacks? relationship management self awareness social awareness self managementarrow_forwardWhat area of emotional intelligence refers to the ability to manage your emotions, particularly in stressful situations, and maintain a positive outlook despite setbacks? relationship management self awareness social awareness self managementarrow_forwardThis area of emotional intelligence describes your ability to not only understand your strengths and weaknesses but to recognize your emotions and their effect on you and your team’s performance self management self awareness relationship management social awarenessarrow_forward
- Emotional intelligence is defined as the ability to understand and manage your emotions, as well as recognize and influence the emotions of those around you. True Falsearrow_forwardAt the Ford automobile Highland plant, assume the one-millionth vehicle was produced in 1916 at a cost of $8084 (in 2013 US$), by how much did the Ford company reduce his cost with each doubling of cumulative output from 1916 to 1927?arrow_forwardAt the Ford automobile Highland plant,in 1913, how long did the average worker stay with the plant and what was the average tenure of a worker?arrow_forward
- Community Federal Bank in Dothan, Alabama, recently increased its fees to customers who use employees as tellers. Management is interested in whether its new tee policy has increased the number of customers now using its automatic teller machines to that point that more machines are required. The following table provides the number of automatic teller transactions by week. Use trend projection with regression to forecast usage for weeks 13-16.arrow_forwardDavison Electronics manufactures three LED television monitors, identified as Model A, Model B, and Model C. Davison Electronics four manufacturing plants. Each model has its lowest possible production cost when produced at Plant 1. However, Plant 1 does not have the capacity to handle the total production of all three models. As a result, at least some of the production must be routed to the other manufacturing plants. The following table shows the minimum production requirements for next month, the plant capacities in units per month, and the production cost per unit at each plant: Model Production Cost per Unit Minimum Production Requirements Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 A $25 $28 $37 $34 48,000 B $26 $35 $36 $41 75,000 C $20 $31 $26 $23 60,000 Production Capacity 65,000 50,000 32,000 43,000 Davison’s objective is to determine the cost-minimizing production planarrow_forwardAnecdotally, entrepreneurs frequently encounter two critical dilemmas in managing human resources: the timing of hiring and the decision regarding hiring a generalist versus a specialist for their growing venture. Deciding when to expand a team is crucial, as premature hiring (i.e., hiring too soon) can strain resources, while delayed hiring (i.e., hiring too late) might hinder growth opportunities. Moreover, the choice between hiring a generalist or a specialist depends on the specific needs and stage of the venture, with each option presenting distinct advantages and challenges. To address these issues, a management scholar seeks to identify the factors shaping the hiring cycle throughout the entrepreneurial journey and to understand the criteria for choosing between generalists and specialists at various stages of a venture. The scholar has assembled a sample of 20 experienced South African entrepreneurs who have encountered both failure and success in the financial technology…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing


