
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.6.6P
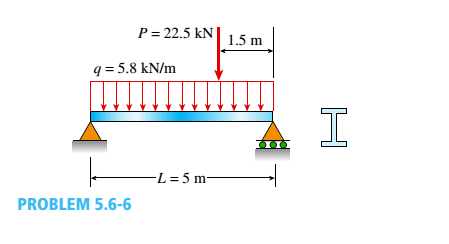
A simple beam of length L = 5 m carries a uniform load of intensity q = 5,8 kN/m and a concentrated load 22.5 kN (see figure).
(a) Assuming tra]]ow = 110 MPa, calculate the required section modulus S. Then select the most economical wide-flange beam (W shape) from Table F-l(b) in Appendix F, and recalculate S, taking into account the weight of the beam. Select a new beam if necessary.
(b) Repeat part (a), but now assume that the design requires that the W shape must be used in weak axis bending (i.e., it must bend about the 2-2 (or y) axis of the cross section).
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Q1. A curved beam of a circular cross section of diameter "d" is fixed at one end and
subjected to a concentrated load P at the free end (Fig. 1). Calculate stresses at points
A and C. Given: P = 800 N, d = 30 mm, a 25 mm, and b = 15 mm.
Fig.1
P
b
B
(10 Marks)
You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of
lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (p = 0.001 kg m-1 s-1) can be approximated
as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates.
The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed,
U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by
a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By
applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that
end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be
y = +h
I
2h = 1 cm
x1
y = -h
u(y)
1 dP
2μ dx
-y² + Ay + B
moving plate
stationary plate
U
2
I2
L = 10 cm
Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm,
into the page.
Question 1
You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of
lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated
as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates.
The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed,
U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by
a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By
applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that
end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be
1 dP
u(y)
=
2μ dx
-y² + Ay + B
y= +h
Ꮖ
2h=1 cm
1
x1
y = −h
moving plate
stationary plate
2
X2
L = 10 cm
Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm,
into the page.
(a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take
the following forms:
U
U
1 dP
A =…
Chapter 5 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 5 - A steel wire with a diameter of d = 1/16 in. is...Ch. 5 - A copper wire having a diameter ofd = 4 mm is bent...Ch. 5 - A 4.75-in, outside diameter polyethylene pipe...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB is loaded by a couple M0at...Ch. 5 - A thin strip of steel with a length of L =19 in....Ch. 5 - A bar of rectangular cross section is loaded and...Ch. 5 - A simply supported beam with a length L = 10 ft...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam is subjected to a concentrated...Ch. 5 - A thin strip of hard copper (E = 16,000 ksi)...Ch. 5 - A steel wire (E = 200 GPa) of a diameter d = L25...
Ch. 5 - A thin, high-strength steel rule (E = 30 x 10ft...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam AB with a span length...Ch. 5 - Beam ABC has simple supports at A and B and an...Ch. 5 - A simply supported beam is subjected to a in early...Ch. 5 - Each girder of the lift bridge (sec figure) is 180...Ch. 5 - A freight-car axle AS is loaded approximately as...Ch. 5 - A seesaw weighing 3 lb/ft of length is occupied by...Ch. 5 - During construction of a highway bridge, the main...Ch. 5 - The horizontal beam ABC of an oil-well pump has...Ch. 5 - A railroad tie (or sleeper) is subjected to two...Ch. 5 - A fiberglass pipe is lifted by a sling, as shown...Ch. 5 - A small dam of height h = 2.0 m is constructed of...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum tensile stress (7, (due to...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum bending stress emaxdue to...Ch. 5 - A simple beam A B of a span length L = 24 ft is...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum tensile stress erand maximum...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam A3, loaded by a uniform load and...Ch. 5 - A canti lever beam A B of a n isosceles t...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam, a C12 x 30 section, is...Ch. 5 - A frame ABC travels horizontally with an...Ch. 5 - A beam ABC with an overhang from B to C supports a...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB with a rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A beam with a T-section is supported and loaded as...Ch. 5 - Consider the compound beam with segments AB and...Ch. 5 - A small dam of a height h = 6 ft is constructed of...Ch. 5 - A foot bridge on a hiking trail is constructed...Ch. 5 - A steel post (E=30×106) having thickness t = 1/8...Ch. 5 - Beam ABCDE has a moment release just right of...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam having a span length...Ch. 5 - A simply supported beam (L = 4.5 m) must support...Ch. 5 - The cross section of a narrow-gage railway bridge...Ch. 5 - A fiberglass bracket A BCD with a solid circular...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beanie B is loaded by a uniform load...Ch. 5 - A simple beam of length L = 5 m carries a uniform...Ch. 5 - A simple beam AB is loaded as shown in the figure....Ch. 5 - A pontoon bridge (see figure) is constructed of...Ch. 5 - A floor system in a small building consists of...Ch. 5 - The wood joists supporting a plank Floor (see...Ch. 5 - A beam ABC with an overhang from B to C is...Ch. 5 - -12 A "trapeze bar" in a hospital room provides a...Ch. 5 - A two-axle carriage that is part of an over head...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB with a circular cross section...Ch. 5 - A propped cantilever beam A BC (see figure) has a...Ch. 5 - A small balcony constructed of wood is supported...Ch. 5 - A beam having a cross section in the form of an un...Ch. 5 - A beam having a cross section in the form of a...Ch. 5 - Determine the ratios of the weights of four beams...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.6.20PCh. 5 - A steel plate (called a cover ploie) having...Ch. 5 - A steel beam ABC is simply supported at A and...Ch. 5 - A retaining wall 6 ft high is constructed of...Ch. 5 - A retaining wall (Fig. a) is constructed using...Ch. 5 - A beam of square cross section (a = length of each...Ch. 5 - The cross section of a rectangular beam having a...Ch. 5 - A tapered cantilever beam A B of length L has...Ch. 5 - .2 A ligmio.irc ii supported by two vorlical beams...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.7.3PCh. 5 - Prob. 5.7.4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5.7.5PCh. 5 - A cantilever beam AB with rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A simple beam ABC having rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB having rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - The shear stresses t in a rectangular beam arc...Ch. 5 - .2 Calculate the maximum shear stress tmaxand the...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam is subjected to...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam with overhang is...Ch. 5 - Two wood beams, each of rectangular cross section...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam of length L = 2 m supports a...Ch. 5 - A steel beam of length L = 16 in. and...Ch. 5 - A beam of rectangular cross section (width/) and...Ch. 5 - A laminated wood beam on simple supports (figure...Ch. 5 - A laminated plastic beam of square cross section...Ch. 5 - A wood beam AB on simple supports with span length...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam of rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A square wood platform is 8 ft × 8 ft in area and...Ch. 5 - A wood beam ABC with simple supports at A and B...Ch. 5 - A wood pole with a solid circular cross section (d...Ch. 5 - A simple log bridge in a remote area consists of...Ch. 5 - A vertical pole consisting of a circular tube of...Ch. 5 - A circular pole is subjected to linearly varying...Ch. 5 - A sign for an automobile service station is...Ch. 5 - A steel pipe is subjected to a quadratic...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB of length L = 6.5 ft supports...Ch. 5 - A bridge girder A B on a simple span of length L =...Ch. 5 - A simple beam with an overhang supports a uniform...Ch. 5 - A hollow steel box beam has the rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A hollow aluminum box beam has the square cross...Ch. 5 - The T-beam shown in the figure has cross-sectional...Ch. 5 - Calculate the maximum shear stress tmax. in the...Ch. 5 - A prefabricated wood I-beam serving as a floor...Ch. 5 - A welded steel gird crhaving the erass section...Ch. 5 - A welded steel girder having the cross section...Ch. 5 - A wood box beam is constructed of two 260 mm × 50...Ch. 5 - A box beam is constructed of four wood boards as...Ch. 5 - Two wood box beams (beams A and B) have the same...Ch. 5 - A hollow wood beam with plywood webs has the...Ch. 5 - A beam of a T cross section is formed by nailing...Ch. 5 - The T-beam shown in the figure is fabricated by...Ch. 5 - A steel beam is built up from a W 410 × 85 wide...Ch. 5 - The three beams shown have approximately the same...Ch. 5 - Two W 310 × 74 Steel wide-flange beams are bolted...Ch. 5 - A pole is fixed at the base and is subjected to a...Ch. 5 - A solid circular pole is subjected to linearly...Ch. 5 - While drilling a hole with a brace and bit, you...Ch. 5 - An aluminum pole for a street light weighs 4600 N...Ch. 5 - A curved bar ABC having a circular axis (radius r...Ch. 5 - A rigid Trame ABC is formed by welding two steel...Ch. 5 - A palm tree weighing 1000 lb is inclined at an...Ch. 5 - A vertical pole of aluminum is fixed at the base...Ch. 5 - Because of foundation settlement, a circular tower...Ch. 5 - A steel bracket of solid circular cross section is...Ch. 5 - A cylindrical brick chimney of height H weighs w =...Ch. 5 - A flying but tress transmit s a load P = 25 kN,...Ch. 5 - A plain concrete wall (i.e., a wall with no steel...Ch. 5 - A circular post, a rectangular post, and a post of...Ch. 5 - Two cables, each carrying a tensile force P = 1200...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.12.16PCh. 5 - A short column constructed of a W 12 × 35...Ch. 5 - A short column with a wide-flange shape is...Ch. 5 - A tension member constructed of an L inch angle...Ch. 5 - A short length of a C 200 × 17.1 channel is...Ch. 5 - The beams shown in the figure are subjected to...Ch. 5 - The beams shown in the figure are subjected to...Ch. 5 - A rectangular beam with semicircular notches, as...Ch. 5 - A rectangular beam with semicircular notches, as...Ch. 5 - A rectangular beam with notches and a hole (see...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) ← intake normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) 50 m/s H 472 m/s B engine altitude: 14,000 m exhaust nozzle E F exit to atmosphere diameter: DE = 0.30 m E F diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed…arrow_forwardيكا - put 96** I need a detailed drawing with explanation or in wake, and the top edge of im below the free surface of the water. Determine the hydrothed if hydrostatic on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. =--20125 7357 750 X 2.01arrow_forwardYou are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be U y = +h У 2h = 1 cm 1 x1 y=-h u(y) = 1 dP 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B moving plate - U stationary plate 2 I2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page. (a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take the following forms: A = U 2h U 1 dP…arrow_forward
- Question 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) intake engine altitude: 14,000 m D exhaust nozzle→ exit to atmosphere 472 m/s 50 m/s B diameter: DE = 0.30 m EX diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. F a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed of…arrow_forwardgiven below: A rectangular wing with wing twist yields the spanwise circulation distribution kbV1 roy) = kbv. (2) where k is a constant, b is the span length and V. is the free-stream velocity. The wing has an aspect ratio of 4. For all wing sections, the lift curve slope (ag) is 2 and the zero-lift angle of attack (a=0) is 0. a. Derive expressions for the downwash (w) and induced angle of attack a distributions along the span. b. Derive an expression for the induced drag coefficient. c. Calculate the span efficiency factor. d. Calculate the value of k if the wing has a washout and the difference between the geometric angles of attack of the root (y = 0) and the tip (y = tb/2) is: a(y = 0) a(y = ±b/2) = /18 Hint: Use the coordinate transformation y = cos (0)arrow_forward۳/۱ العنوان O не شكا +91x PU + 96852 A heavy car plunges into a lake during an accident and lands at the bottom of the lake on its wheels as shown in figure. The door is 1.2 m high and I m wide, and the top edge of Deine the hadrostatic force on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. = -20125 750 x2.01arrow_forward
- Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm.arrow_forwardQ1/ A vertical, circular gate with water on one side as shown. Determine the total resultant force acting on the gate and the location of the center of pressure, use water specific weight 9.81 kN/m³ 1 m 4 marrow_forwardI need handwritten solution with sketches for eacharrow_forward
- Given answers to be: i) 14.65 kN; 6.16 kN; 8.46 kN ii) 8.63 kN; 9.88 kN iii) Bearing 6315 for B1 & B2, or Bearing 6215 for B1arrow_forward(b) A steel 'hot rolled structural hollow section' column of length 5.75 m, has the cross-section shown in Figure Q.5(b) and supports a load of 750 kN. During service, it is subjected to axial compression loading where one end of the column is effectively restrained in position and direction (fixed) and the other is effectively held in position but not in direction (pinned). i) Given that the steel has a design strength of 275 MN/m², determine the load factor for the structural member based upon the BS5950 design approach using Datasheet Q.5(b). [11] ii) Determine the axial load that can be supported by the column using the Rankine-Gordon formula, given that the yield strength of the material is 280 MN/m² and the constant *a* is 1/30000. [6] 300 600 2-300 mm wide x 5 mm thick plates. Figure Q.5(b) L=5.75m Pinned Fixedarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License