
Concept explainers
To analyze:
Michelle Khan and her coworkers studied cervical cancer and human papillomavirus (HPV) status in 20,514 women for 10 years and published their findings in 2003. They performed papanicolaou test at regular intervals, and the DNA probe hybridization test was performed to detect the presence of a specific type of HPV in the women’s cervical cells. No woman was infected with cervical cancer when the test began.
The percentage of women at 110 months, not infected with any type of cancer-causing HPV, had cervical cancer, and the percentage of women suffering from cervical cancer also had HPV16 infection, is to be analyzed from the graphs of their published results, given below.
The results for Michelle and her coworkers’ studies are shown in a graphical pattern below:
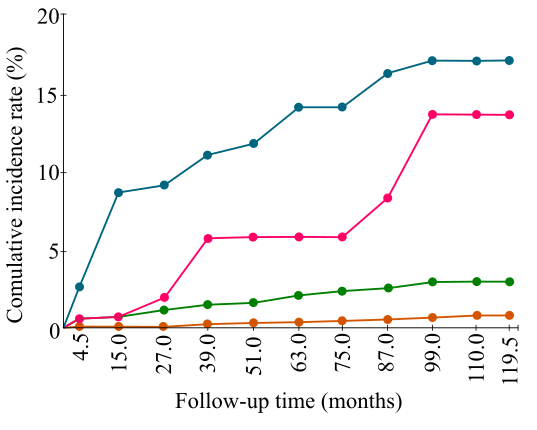
The keys for the graph are given below:

Introduction:
Cervical cancer is a major type of cancer found in women, mainly caused by a virus called the human papilloma virus (HPV). This virus causes cancer in the cervical cells of the uterus. There are more than 100 strains of HPV present, but only a few causes cervical cancer. The most commonly noticed cervical cancers are caused by HPV16 and HPV18.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 45 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
- please fill in the empty sports, thank you!arrow_forwardIn one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forward
- The Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





