
Concept explainers
Fill in the blanks in each line in the following table. The first line is already completed as an example.
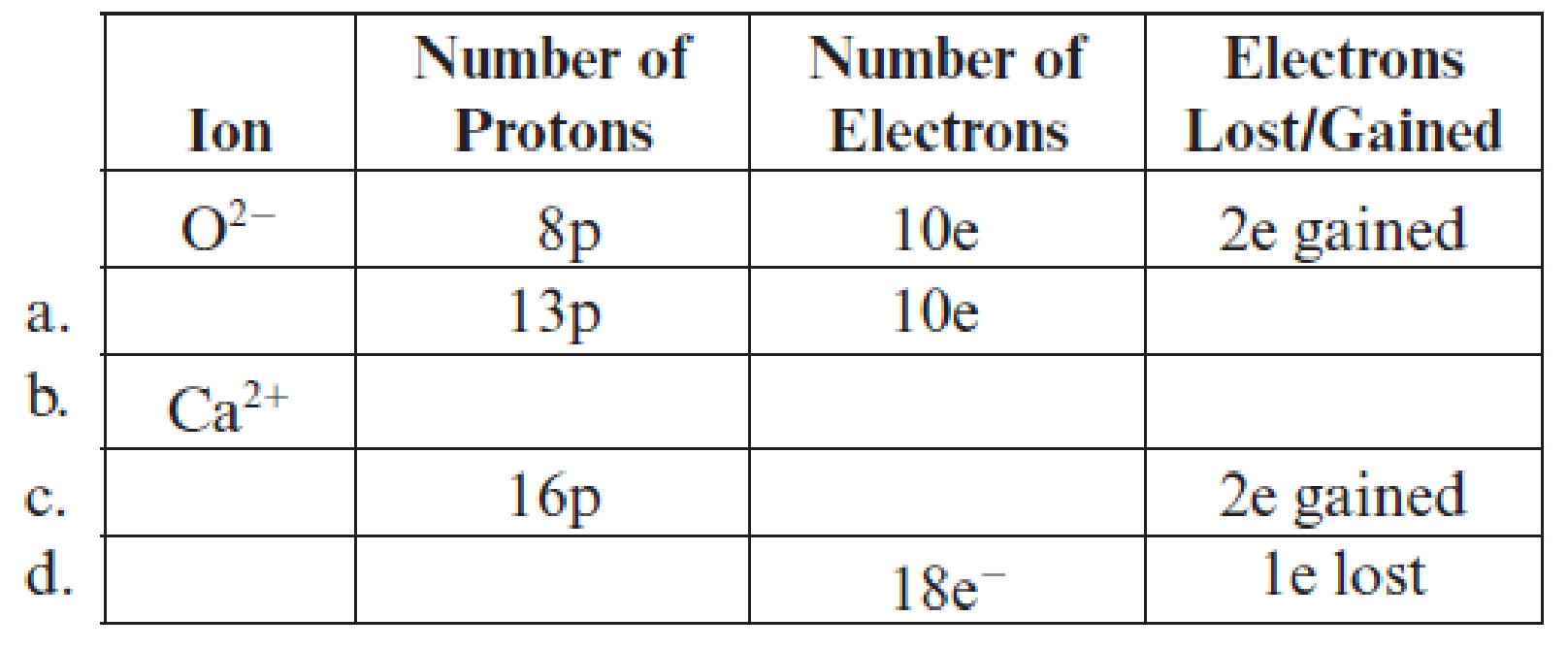
(a)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom forms ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.28EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The charge on an ion and its magnitude is equal to the number of protons minus the number of electrons.
The given ion has
Hence, the symbol of ion is
(b)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom forms ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.28EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The charge on an ion and its magnitude is equal to the number of protons minus the number of electrons.
The atomic number of calcium is
Hence, the number of protons are
(c)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom forms ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.28EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The charge on an ion and its magnitude is equal to the number of protons minus the number of electrons.
The ion has
Hence, ion is
(d)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom form ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.28EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The charge on an ion and its magnitude is equal to the number of protons minus the number of electrons.
The number of electrons in ion is
Potassium has
Hence, ion is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Choose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. i H A B 1. CH3CH2Na 2. H3O+ 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H3O+ 1. CH3MgBr Q C 2. H3O+ 1. H3O+ D 2. CH3MgBr 00 OH Q E CH³MgBrarrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. What is the half-life for this reaction?arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 1. PhNa A 2. H3O+ 1. PhCH2MgBr B 2. H3O+ хё 1. PhMgBr C 2. H3O+ 00 HO Q E D 1. H3O+ 2. PhMgBr PhMgBrarrow_forward
- Please answer all of the questions and provide detailed explanations and include a drawing to show the different signals on the molecule and include which ones should be highlighted.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 1 attempt remaining 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ Q OH ☑ Select to Drawarrow_forwardHow should I graph my data for the Absorbance of Pb and Fe for each mushroom? I want to compare the results to the known standard curve. Software: Excel Spreadsheets Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/Eb2PfHdfEtBJiWh0ipHZ_kkBW4idWWwvpLPPtqoq2WkgbQ?rtime=HxrF0_tR3Ugarrow_forward
- Provide the proper IUPAC name only for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly, but do not use italics in Canvas.arrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. How many minutes will it take for the concentration of A to reach 0.144 Marrow_forwardWhat is the rate for the second order reaction A → Products when [A] = 0.256 M? (k = 0.761 M⁻¹s⁻¹)arrow_forward
- For reaction N2(g) + O2(g) --> 2NO(g) Write the rate of the reaction in terms of change of NO.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardThe reaction of 2-oxacyclopentanone with hydrochloric acid in water (i.e., "excess") produces which of the following carboxylic acids?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





