
Concept explainers
What is the geometry around the central atom in the following molecular models? (There are no “hidden” atoms: all atoms in each model are visible.)
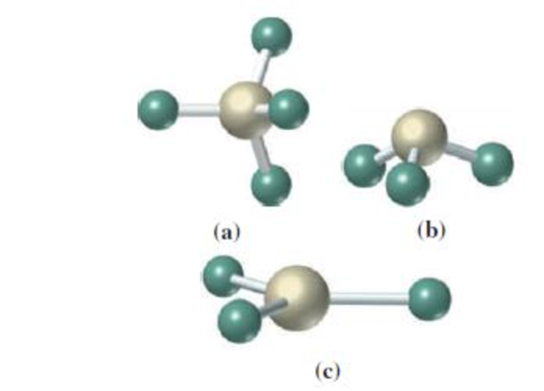
(a)
Interpretation:
The geometry around the central atom in the given molecular model is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Molecular shape can be predicted from the Lewis structure by using the valence-shell Electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model.
- Count the number of valence electron pairs (bond pairs and lone pairs).
- Assume that the valence electron pairs form a structure that allows them to be as far away from each other as possible.
- If there are only two bond pair electrons, the molecule is linear.
- If there are three bond pair electrons, the molecule is shaped like a trigonal planar.
- If there are four bond pair electrons, the molecule is shaped as a regular tetrahedral.
- Repulsion between lone pair-bond pair of electrons effect the geometry of molecules.
Bond angle is the angle between two bonds of a molecule and it is determined based on the geometry.
[Bond angles:
Answer to Problem 4.25UKC
The geometry around the central atom in the given molecular model is tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
In the given molecular model,
Four atoms are bonded to the central atom. The angle around the central atom is around
Therefore,
The geometry of the given molecular model is tetrahedral.
(b)
Interpretation:
The geometry around the central atom in the given molecular model is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Molecular shape can be predicted from the Lewis structure by using the valence-shell Electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model.
- Count the number of valence electron pairs (bond pairs and lone pairs).
- Assume that the valence electron pairs form a structure that allows them to be as far away from each other as possible.
- If there are only two bond pair electrons, the molecule is linear.
- If there are three bond pair electrons, the molecule is shaped like a trigonal planar.
- If there are four bond pair electrons, the molecule is shaped as a regular tetrahedral.
- Repulsion between lone pair-bond pair of electrons effect the geometry of molecules.
Bond angle is the angle between two bonds of a molecule and it is determined based on the geometry.
[Bond angles:
Answer to Problem 4.25UKC
The geometry around the central atom in the given molecular model is pyramidal.
Explanation of Solution
In the given molecular model,
Three atoms are bonded to the central atom. Three atoms are bonded to the central atom. The angle around the central atom is around
Therefore,
The geometry of the given molecular model is pyramidal.
(c)
Interpretation:
The geometry around the central atom in the given molecular model is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Molecular shape can be predicted from the Lewis structure by using the valence-shell Electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model.
- Count the number of valence electron pairs (bond pairs and lone pairs).
- Assume that the valence electron pairs form a structure that allows them to be as far away from each other as possible.
- If there are only two bond pair electrons, the molecule is linear.
- If there are three bond pair electrons, the molecule is shaped like trigonal planar.
- If there are four bond pair electrons, the molecule is shaped as a regular tetrahedral.
- Repulsion between lone pair-bond pair of electrons effect the geometry of molecules.
Bond angle is the angle between two bonds of a molecule and it is determined based on the geometry.
[Bond angles:
Answer to Problem 4.25UKC
The geometry around the central atom in the given molecular model is trigonal planar.
Explanation of Solution
In the given molecular model,
Three atoms are bonded to the central atom. The angle around the central atom is around
Therefore,
The geometry of the given molecular model is trigonal planar.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Calculate pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 1.60g of sodium acetate, in 88.5 mL of 0.10 M acetic acid. Assume the volume change upon dissolving the sodium acetate is negligible. Ka is 1.75 x 10^-5arrow_forwardShow a mechanism that leads to the opening of the ring below under acid-catalyzed conditions. Give the correct Fischer projection for this sugar.arrow_forwardWhat is the stereochemical relationship between B & C?arrow_forward
- Don't use ai or any chat gpt will dislike okk just use accurate information okkk okkk just solve full accurate. don't use guidelines okk just did it accurate 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okkk follow all instructions requirements okkkarrow_forwardhow would you make this plot in excel?arrow_forwardwhat is the productarrow_forward
- Balance the following equation and list of coefficients in order from left to right. SF4+H2O+—-> H2SO3+HFarrow_forwardProblem 15 of 15 Submit Using the following reaction data points, construct Lineweaver-Burk plots for an enzyme with and without an inhibitor by dragging the points to their relevant coordinates on the graph and drawing a line of best fit. Using the information from this plot, determine the type of inhibitor present. 1 mM-1 1 s mM -1 [S]' V' with 10 μg per 20 54 10 36 20 5 27 2.5 23 1.25 20 Answer: |||arrow_forward12:33 CO Problem 4 of 15 4G 54% Done On the following Lineweaver-Burk -1 plot, identify the by dragging the Km point to the appropriate value. 1/V 40 35- 30- 25 20 15 10- T Км -15 10 -5 0 5 ||| 10 15 №20 25 25 30 1/[S] Г powered by desmosarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning





