
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications, 7th Edition
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134485201
Author: Allan R. Hambley
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.13P
Derive an expression for
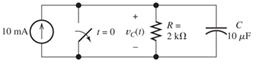
Figure P4.13
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule05:15
Students have asked these similar questions
help about this question in control systems?
Solve on paper not using chatgpt
Consider the phasor circuit in the following figure and find all currents
Solve on paper not using chatgpt or AI
Chapter 4 Solutions
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications, 7th Edition
Ch. 4 - Suppose we have a capacitance C discharging...Ch. 4 - The dielectric materials used in real capacitors...Ch. 4 - The initial voltage across the capacitor shown in...Ch. 4 - A 100F capacitance is initially charged to 1000 V....Ch. 4 - At t = 0, a charged 10{ F capacitance is connected...Ch. 4 - At time t1 , a capacitance C is charged to a...Ch. 4 - Given an initially charged capacitance that begins...Ch. 4 - The initial voltage across the capacitor shown in...Ch. 4 - In physics, the half-life is often used to...Ch. 4 - We know that a 50F capacitance is charged to an...
Ch. 4 - We know that the capacitor shown in Figure P4.11...Ch. 4 - The purchasing power P of a certain unit of...Ch. 4 - Derive an expression for vC(t) in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Suppose that at t= 0, we connect an uncharged 10 F...Ch. 4 - Suppose we have a capacitance C that is charged to...Ch. 4 - A person shuffling across a dry carpet can be...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.17PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.18. Prior...Ch. 4 - List the steps for dc steady-state analysis of RLC...Ch. 4 - Explain why we replace capacitances with open...Ch. 4 - Solve for the steady-state values of i1, i2, and...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.22. What...Ch. 4 - In the circuit of Figure P4.23, the switch is in...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.24 has been set up...Ch. 4 - Solve for the steady-state values of i1 , i2, i3,...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.26 is operating in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.27PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit of Figure P4.28 in which the...Ch. 4 - For the circuit shown in Figure P4.29, the switch...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit of Figure P4.30 in which the...Ch. 4 - Give the expression for the time constant of a...Ch. 4 - A circuit consists of switches that open or close...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.33 is operating in...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.34. The...Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.34 given iL(0)=0A .Ch. 4 - Real inductors have series resistance associated...Ch. 4 - Determine expressions for and sketch is(t) to...Ch. 4 - For the circuit shown in Figure P4.38,, find an...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.39 is operating in...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.40. A...Ch. 4 - Due to components not shown in the figure, the...Ch. 4 - The switch shown in Figure P4.42 has been closed...Ch. 4 - Determine expressions for and sketch vR(t) to...Ch. 4 - What are the steps in solving a circuit having a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.45PCh. 4 - Solve for vC(t) for t > 0 in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 4 - Solve for v(t) for t > 0 in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.48PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown inFigure P4.49. The...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.50. The...Ch. 4 - The voltage source shown in Figure P4.51 is called...Ch. 4 - Determine the form of the particular solution for...Ch. 4 - Determine the form of the particular solution for...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.54PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.55PCh. 4 - How can first-or second-order circuits be...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.57PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.58PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.59PCh. 4 - Sketch a step response for a second-order system...Ch. 4 - A dc source is connected to a series RLC circuit...Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.61 for R = 40 .Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.61 for R = 20 .Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.64PCh. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.64 for R=50 .Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.64 for R=500 .Ch. 4 - Solve for i(t) for t > 0 in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.68PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.69PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.70PCh. 4 - Use MATLAB to derive an expression for vc(t)in the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.72PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in FigureP4.50 in which...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.74PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.75PCh. 4 - Use MATLAB to solve for the mesh currents in the...Ch. 4 - The switch m the circuit shown in Figure T4.1 is...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.2PTCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure T4.3. Figure...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure T4.4 in which...Ch. 4 - Write the MATLAB commands to obtain the solution...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Handwritten solution required do not use chatgptarrow_forwardA conductor 300 mm long carries a current of 13A and is at right-angles to a magnetic fieldbetween two circular pole faces, each of diameter 80 mm. If the total flux between the polefaces is 0.75 mWb, calculate the force exerted on the conductor. [ANS = 0.582 N]arrow_forwarda) find Rthb) Find Vth in the circuit c)Draw the Thevenin Equivalent of the circuit to tge left of the a and b terminalsarrow_forward
- An electric car runs on batteries, but needs to make constant stops to re-charge. If a trailer is attached to the car that carries a generator, and the generator is turned by a belt attached to the wheels of the trailer, will the car be able to drive forever without stopping?arrow_forwardA singl core cable of voltage 30 kv. The diameter of Conductor is 3 cm. The diameter of cable is 25 cm. This cable has Two layer of insulator having arelative permittivity 5-3 respectively of The ratio of maximum electric stress of maximum electric stress 8 First layer to the of second layer is 10 Find & 1- The thickness of each layers. 3- The voltage of each layers. §. Layers The saving in radius of cable if another ungrading cable has the Same maximum electric stress, Total village, Conductor diameter of grading cable.arrow_forward66 KV sing care Cable has a drameter of conductor of 3 cm. The radius of cable is 10 cm. This Cable house Two relative permmitivity of insulation 6 and 4 respectively. If The ratio of maximum electric stress of first layer to the maximum eledric streep & second layer is s 1- find the village & each layers. 2- Min- electric stress J Cable 3- Compare the voltage of ungrading Cable has the same distance and relectric stresses.arrow_forward
- Prelab Information 1. Laboratory Preliminary Discussion First-order Low-pass RC Filter Analysis The first-order low-pass RC filter shown in figure 1 below represents all voltages and currents in the time domain. It is of course possible to solve for all circuit voltages using time domain differential equation techniques, but it is more efficient to convert the circuit to its s-domain equivalent as shown in figure 2 and apply Laplace transform techniques. vs(t) i₁(t) + R₁ ww V₁(t) 12(t) Lic(t) Vout(t) = V2(t) R₂ Vc(t) C Vc(t) VR2(t) = V2(t) + Vs(s) Figure 1: A first-order low-pass RC filter represented in the time domain. I₁(s) R1 W + V₁(s) V₂(s) 12(s) Ic(s) + Vout(S) == Vc(s) Vc(s) Zc(s) = = VR2(S) V2(s) Figure 2: A first-order low-pass RC filter represented in the s-domain.arrow_forwarduse matlabarrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward
- How do we know that D1 is forward bias and D2 is reverse biased?arrow_forwardSolve it in a different way than the previous solution that I searched forarrow_forwardA lossless uncharged transmission line of length L = 0.45 cm has a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. It is driven by an ideal voltage generator producing a pulse of amplitude 10V and width 2 nS. If the transmission line is connected to a load of 200 ohms, sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for the interval 0 < t < 20 nS. You may assume that the propagation velocity of the transmission is c/2. Answered now answer number 2. Repeat Q.1 but now assume the width of the pulse produced by the generator is 4 nS. Sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for 0 < t < 20 nS.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Capacitors Explained - The basics how capacitors work working principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X4EUwTwZ110;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY