
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis structure of 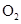 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(b)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 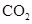 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(c)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis structure of 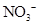 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(d)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis dot structure of 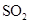 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(e)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis dot structure of 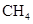 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(f)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 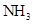 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(g)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 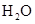 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(3)
Interpretation: The angle of bent geometry of dichlorocarbene should be determined using its Lewis structure.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H :0: CH3 O: OH Q CH3OH2+ Draw Intermediate protonation CH3OH CH3OH nucleophilic addition H Draw Intermediate deprotonation :0: H3C CH3OH2* protonation H 0: H CH3 H.arrow_forwardPredicting the reactants or products of hemiacetal and acetal formation uentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X+Y OH H+ за Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ? olo 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardcan someone please answer thisarrow_forward
- Please, please help me figure out the the moles, molarity and Ksp column. Step by step details because I've came up with about three different number and have no idea what I'm doing wrong.arrow_forwardwhat reagents are used to get this product from this reactant? Br OCH3arrow_forwardcan someone answer this pleasearrow_forward
- can someone do the reaction mechanism for this reaction and draw the molecules for Q2 and q3arrow_forwardIn this question, the product of the aldol condensation is shown. What would be the reactants for this product? Please provide a detailed explanation, as well as a drawing showing how the reactants will react to produce the product.arrow_forward7. Propene undergoes a hydration reaction with water in the presence of an acid. a. There are two possible products for this reaction, both with the formula C,H,O. Show their structural formulas and names. (A1, B2) SCH4UR Name: (answer for part a. here!) VER 3 2021-2022 b. Which of the two products do you predict will form. Explain your choice using details from your learning. (B3)arrow_forward
- What are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





