
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Provide the formula of potassium hydroxide.
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
(b)
Interpretation:
Provide the name of 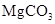
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
Interpretation:
Provide the formula of iron (III) cyanide.
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
(d)
Interpretation:
Provide the formula of iron (II) oxalate
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
(e)
Interpretation:
Provide the name of
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
Interpretation:
Provide the name of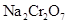
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





