
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis structure of 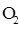 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(b)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 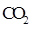 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(c)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis structure of 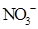 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(d)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis dot structure of 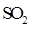 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(e)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis dot structure of 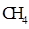 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(f)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 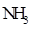 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(g)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 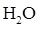 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(2)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure of titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) molecule should be drawn and its geometry should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
- Predict the major products of both organic reactions. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. esc esc Explanation Check 2 : + + X H₁₂O + Х ง WW E R Y qab Ccaps lock shift $ P X Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil T FR F18 9 G t K L Z X V B N M control opption command command T C darrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrohalogenation of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for caps lock Explanation Check 2 W E R + X 5 HCI Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil Y F G H K L ZZ X C V B N M control opption command F10 F10 command 4 BA Ar Carrow_forwardI don't understand why the amide on the top left, with the R attached to one side, doesn't get substituted with OH to form a carboxylic acid. And if only one can be substituted, why did it choose the amide it chose rather than the other amide?arrow_forward
- esc Draw the Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. Explanation Check BBB + X 0 1. Hg (OAc)2, H₂O 2. Na BH 5 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bl P 豆 28 2 28 N 9 W E R T Y A S aps lock G H K L Z X C V B N M T central H command #e commandarrow_forwardC A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. (X) This transformation can't be done in one step. + Tarrow_forwardく Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. Explanation Check OH + + ✓ 2 H₂SO 4 O xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Draw the skeletal ("line") structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Parrow_forwardPredicting edict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. + No reaction. Explanation Check HO Na O H xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Iarrow_forwardChoosing reagents and conditions for acetal formation or hydrolysis 0/5 A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + This transformation can't be done in one step. 5 I H Autumn alo 值 Ar Barrow_forward
- A block of copper of mass 2.00kg(cp = 0.3851 .K) and g temperature 0°C is introduced into an insulated container in which there is 1.00molH, O(g) at 100°C and 1.00 2 atm. Note that C P = 4.184. K for liquid water, and g that A H = 2260 for water. vap g Assuming all the steam is condensed to water, and that the pressure remains constant: (a) What will be the final temperature of the system? (b) What is the heat transferred from the water to the copper? (c) What is the entropy change of the water, the copper, and the total system?arrow_forwardIdentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X + Y OH H+ O O Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H₂O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente ? Earrow_forwardCalculate the solubility of CaF2 in g/L (Kp = 4.0 x 10-8). sparrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





