
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis structure of 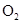 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(b)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 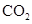 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(c)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis structure of 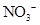 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
align="center"Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(d)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis dot structure of 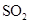 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(e)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional shape and Lewis dot structure of 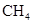 should be determined
should be determined
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(f)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 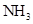 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(g)
Interpretation: The three-dimensional structure and Lewis dot structure of 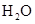 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
- Lewis dot structure: The structure which shows the distribution valance electrons of all the atoms involved in bonding. This includes bonding electrons as well as lone pair of electrons.
(1)
Interpretation: The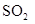 and
and 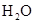 does not have linear structure should be explained
does not have linear structure should be explained
Concept Introduction:
- VSEPR theory: This theory was developed to predict the shapes of covalent molecules in which atoms are joined together with single covalent bond. According to this theory
- The electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule tend to stay in space as far as possible so that repulsive forces between electron pairs are minimum
- The geometry or shape of the molecule is determined by the orientation of electron pairs.
- The shape of the molecule is regular if the electron pairs around the central atom are shared pairs only because they exert repulsive forces equally
- The shape are irregular if they have shared as well as lone pair around the central atom because they exert repulsive forces unequally.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





