
Machine Elements in Mechanical Design (6th Edition) (What's New in Trades & Technology)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134441184
Author: Robert L. Mott, Edward M. Vavrek, Jyhwen Wang
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 82P
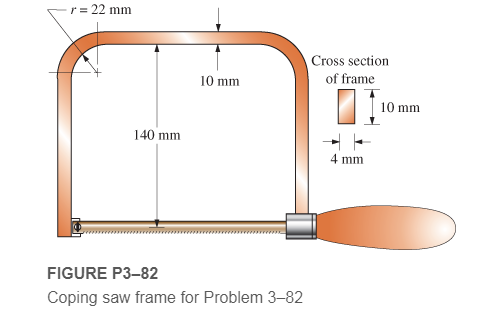
A coping saw frame shown in Figure P3−82 is made from SAE 1020 CD steel. A screw thread in the handle draws the blade of the saw into a tension of 120 N. Determine the resulting design factor based on yield strength in the area of the corner radii of the frame.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The A/D converter wit the specifications listed below is planned to be used in an environment in which the A/D
converter temperature may change by ± 10 °C. Estimate the contributions of conversion and quantization errors
to the uncertainty in the digital representation of an analog voltage by the converter.
FSO
N
Linearity error
Temperature drift error
Analog to Digital (A/D)
Converter
0-10 V
12 bits
± 3 bits
1 bit/5 °C
6-13. A smooth tube in the form of a circle of radius r rotates in its vertical plane with a
constant angular velocity w. The position of a particle of mass m that slides inside
the tube is given by the relative coordinate p. Find the differential equation for .
e
О
E
g
ω
Figure P6-13
Problem 2
Consider the power drawn by a resistance load in a DC circuit. The power is calculated as P = VI or P = 1²R. It is
given that the normalized uncertainty or % percentage uncertainty in measurements of I, R, and V are the same.
Find the uncertainty in P using the two different expressions for power. Is the uncertainty using the two methods
the same? If not, WHY, explain?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Machine Elements in Mechanical Design (6th Edition) (What's New in Trades & Technology)
Ch. 3 - A tensile member in a machine structure is...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a round bar having a...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a rectangular bar having...Ch. 3 - A link in a packaging machine mechanism has a...Ch. 3 - Two circular rods support the 3800 lb weight of a...Ch. 3 - A tensile load of 5.00 kN is applied to a square...Ch. 3 - An aluminum rod is made in the form of a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in the middle portion of rod AC...Ch. 3 - Compute the forces in the two angled rods in...Ch. 3 - If the rods from Problem 9 are circular, determine...
Ch. 3 - Repeat Problems 9 and 10 if the angle is 15 .Ch. 3 - Figure P312 shows a small truss spanning between...Ch. 3 - The truss shown in Figure P313 spans a total space...Ch. 3 - Figure P314 shows a short leg for a machine that...Ch. 3 - Consider the short compression member shown in...Ch. 3 - Refer Figure P38 . Each of the pins at A, B, and C...Ch. 3 - Compute the shear stress in the pins connecting...Ch. 3 - Prob. 18PCh. 3 - Prob. 19PCh. 3 - Prob. 20PCh. 3 - Prob. 21PCh. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a circular...Ch. 3 - If the shaft of Problem 22 is 850 mm long and is...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress due to a torque...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a solid...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the angle of twist for the hollow shaft of...Ch. 3 - A square steel bar, 25 mm on a side and 650 mm...Ch. 3 - A 3.00 in-diameter steel bar has a flat milled on...Ch. 3 - A commercial steel supplier lists rectangular...Ch. 3 - A beam is simply supported and carries the load...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute its weight if...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, draw the...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, design the...Ch. 3 - Figure P336 shows a beam made from 4 in schedule...Ch. 3 - Select an aluminum I-beam shape to carry the load...Ch. 3 - Figure P338 represents a wood joist for a...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42PCh. 3 - Prob. 43PCh. 3 - Prob. 44PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 50PCh. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress in the bracket...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile and compressive...Ch. 3 - For the lever shown in Figure P353 (a), compute...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress at sections A...Ch. 3 - Prob. 55PCh. 3 - Refer to Figure P38. Compute the maximum tensile...Ch. 3 - Prob. 57PCh. 3 - Refer to P342. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Refer to P343. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 60PCh. 3 - Figure P361 shows a valve stem from an engine...Ch. 3 - The conveyor fixture shown in Figure P362 carries...Ch. 3 - For the flat plate in tension in Figure P363,...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - Prob. 68PCh. 3 - Figure P369 shows a horizontal beam supported by a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 70PCh. 3 - Prob. 71PCh. 3 - The beam shown in Figure P372 is a stepped, flat...Ch. 3 - Figure P373 shows a stepped, flat bar having a...Ch. 3 - Figure P374 shows a bracket carrying opposing...Ch. 3 - Prob. 75PCh. 3 - Figure P376 shows a lever made from a rectangular...Ch. 3 - For the lever in P376, determine the maximum...Ch. 3 - Figure P378 shows a shaft that is loaded only in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 79PCh. 3 - Prob. 80PCh. 3 - A hanger is made from ASTM A36 structural steel...Ch. 3 - A coping saw frame shown in Figure P382 is made...Ch. 3 - Prob. 83PCh. 3 - Figure P384 shows a hand garden tool used to break...Ch. 3 - Figure P385 shows a basketball backboard and goal...Ch. 3 - Prob. 86P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A piston–cylinder device contains 3 kg of nitrogen initially at 100 kPa and 25°C. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV1.3 = constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine the work done and the heat transfer for this process. The gas constant of N2 is R = 0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K. The cv value of N2 at the anticipated average temperature of 350 K is 0.744 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2b). The work done for this process is kJ. The heat transfer for this process is kJ.arrow_forwardI tried solving this one but I have no idea where I went wrong can you please help me out with this?arrow_forwardDuring a picnic on a hot summer day, all the cold drinks disappear quickly, and the only available drinks are those at the ambient temperature of 85°F. In an effort to cool a 12- fluid-oz drink in a can, a person grabs the can and starts shaking it in the iced water of the chest at 32°F. Using the properties of water for the drink, determine the mass of ice that will melt by the time the canned drink cools to 37°F. The density and specific heat of water at the average temperature of (85+37)/2 = 61ºF are ρ = 62.3 lbm/ft3 and cp = 1.0 Btu/lbmºF (Table A-3E). The heat of fusion of water is 143.5 Btu/lbm. The mass of ice that will melt by the time the canned drink cools to 37°F is lbm.arrow_forward
- Steam enters a nozzle at 400°C and 800 kPa with a velocity of 10 m/s and leaves at 375°C and 400 kPa while losing heat at a rate of 26.5 kW. For an inlet area of 800 cm2, determine the velocity and the volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit. Use steam tables. At the left side of the lines, 800 kilo Pascal, 400 degree Centigrade, 10 meters per second are shown. At the right side of the lines, 400 kilo Pascal, 375 degree Centigrade are shown. The velocity of the steam at the nozzle exit is m/s. The volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit is m3/s.arrow_forwardA saturated liquid–vapor mixture of water, called wet steam, in a steam line at 1450 kPa is throttled to 50 kPa and 100°C. What is the quality in the steam line? Use data from the steam tables. Above the right side of the tube, 50 kilos 100 degree Centigrade indicated. The quality in the steam line is .arrow_forwardI tried this problems a couple of ways but I don't know what I'm doing wrong can you help me please?arrow_forward
- Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor at 180 kPa as a saturated vapor with a flow rate of 0.35 m3/min and leaves at 900 kPa. The power supplied to the refrigerant during the compression process is 2.35 kW. What is the temperature of R-134a at the exit of the compressor? The temperature of R-134a at the exit of the compressor is °C.arrow_forwardAir enters the compressor of a gas-turbine plant at ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 25°C with a low velocity and exits at 1 MPa and 347°C with a velocity of 90 m/s. The compressor is cooled at a rate of 1500 kJ/min, and the power input to the compressor is 250 kW. Determine the mass flow rate of air through the compressor. The inlet and exit enthalpies of air are 298.2 kJ/kg and 628.07 kJ/kg. The mass flow rate of air is kg/s.arrow_forwardConsider a 1000-W iron whose base plate is made of 0.5-cm-thick aluminum alloy 2024-T6 (ρ = 2770 kg/m3 and cp = 875 J/kg·°C). The base plate has a surface area of 0.03 m2. Initially, the iron is in thermal equilibrium with the ambient air at 22°C. Assuming 90 percent of the heat generated in the resistance wires is transferred to the plate, determine the minimum time needed for the plate temperature to reach 240°C. The minimum time needed for the plate temperature to reach 240°C is s.arrow_forward
- A desktop computer is to be cooled by a fan whose flow rate is 0.34 m3/min. Determine the mass flow rate of air through the fan at an elevation of 3400 m where the air density is 0.7 kg/m3. Also, if the average velocity of air is not to exceed 123 m/min, determine the diameter of the casing of the fan. The mass flow rate of air through the fan is kg/min. The diameter of the casing of the fan is cm.arrow_forwardThe diffuser in a jet engine is designed to decrease the kinetic energy of the air entering the engine compressor without any work or heat interactions. Calculate the velocity at the exit of a diffuser when air at 100 kPa and 30°C enters it with a velocity of 359 m/s and the exit state is 200 kPa and 90°C. The specific heat of air at the average temperature of 60°C = 333 K is cp = 1.007 kJ/kg·K. The velocity at the exit is m/sarrow_forwardA piston–cylinder device contains 3 kg of nitrogen initially at 100 kPa and 25°C. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV1.3 = constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine the work done and the heat transfer for this process. The gas constant of N2 is R = 0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K. The cv value of N2 at the anticipated average temperature of 350 K is 0.744 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2b). The work done for this process is kJ. The heat transfer for this process is kJ.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stresses Due to Fluctuating Loads Introduction - Design Against Fluctuating Loads - Machine Design 1; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3FBmQXfP_eE;License: Standard Youtube License