
Machine Elements in Mechanical Design (6th Edition) (What's New in Trades & Technology)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134441184
Author: Robert L. Mott, Edward M. Vavrek, Jyhwen Wang
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 39P
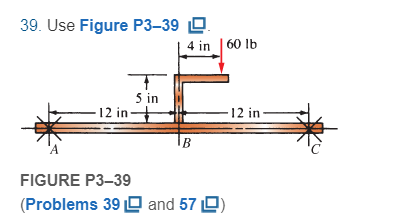
For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body diagram of only the horizontal beam portion of the given figures. Then draw the complete shear and bending moment diagrams. Where used, the symbol X indicates a simple support capable of exerting a reaction force in any direction but having no moment resistance. For beams having unbalanced axial loads, you may specify which support offers the reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In MATLAB, can you help me simulate an orbit under earth J2 perturbation with the Milankovich orbital elements? Also, can you check to see if they fit the Milankovich constraint equaiton?
8. All of the members in the Warren truss of Figure 8 are of length 10 ft. Use the method of
sections to determine the forces in the members BD,CD,CE.
B
A
C
D
E
F
G
2000 lb
3000 lb
5000 lb
Figure 8
H
An acrobat is walking on a tightrope of length L
=20.1 m attached to supports A and B at a
distance of 20.0 m apart. The combined weight
of the acrobat and his balancing pole is 900 N,
and the friction between his shoes and the rope
is large enough to prevent him from slipping.
Neglecting the weight of the rope and any
elastic deformation, determine the deflection (y)
and the tension in portion AC and BC of the
rope for values of x from 0.5 m to 10 m using
0.5 m increments.
1. Determine the maximum deflection (y) in
the rope.
2. Plot tension of AC and BC vs. x (on the
same plot with x on the x-axis). Turn in the
plot and the table of x, TAC, and TBC (clearly
label each).
A
C
20.0 m
B
Chapter 3 Solutions
Machine Elements in Mechanical Design (6th Edition) (What's New in Trades & Technology)
Ch. 3 - A tensile member in a machine structure is...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a round bar having a...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a rectangular bar having...Ch. 3 - A link in a packaging machine mechanism has a...Ch. 3 - Two circular rods support the 3800 lb weight of a...Ch. 3 - A tensile load of 5.00 kN is applied to a square...Ch. 3 - An aluminum rod is made in the form of a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in the middle portion of rod AC...Ch. 3 - Compute the forces in the two angled rods in...Ch. 3 - If the rods from Problem 9 are circular, determine...
Ch. 3 - Repeat Problems 9 and 10 if the angle is 15 .Ch. 3 - Figure P312 shows a small truss spanning between...Ch. 3 - The truss shown in Figure P313 spans a total space...Ch. 3 - Figure P314 shows a short leg for a machine that...Ch. 3 - Consider the short compression member shown in...Ch. 3 - Refer Figure P38 . Each of the pins at A, B, and C...Ch. 3 - Compute the shear stress in the pins connecting...Ch. 3 - Prob. 18PCh. 3 - Prob. 19PCh. 3 - Prob. 20PCh. 3 - Prob. 21PCh. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a circular...Ch. 3 - If the shaft of Problem 22 is 850 mm long and is...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress due to a torque...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a solid...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the angle of twist for the hollow shaft of...Ch. 3 - A square steel bar, 25 mm on a side and 650 mm...Ch. 3 - A 3.00 in-diameter steel bar has a flat milled on...Ch. 3 - A commercial steel supplier lists rectangular...Ch. 3 - A beam is simply supported and carries the load...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute its weight if...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, draw the...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, design the...Ch. 3 - Figure P336 shows a beam made from 4 in schedule...Ch. 3 - Select an aluminum I-beam shape to carry the load...Ch. 3 - Figure P338 represents a wood joist for a...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42PCh. 3 - Prob. 43PCh. 3 - Prob. 44PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 50PCh. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress in the bracket...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile and compressive...Ch. 3 - For the lever shown in Figure P353 (a), compute...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress at sections A...Ch. 3 - Prob. 55PCh. 3 - Refer to Figure P38. Compute the maximum tensile...Ch. 3 - Prob. 57PCh. 3 - Refer to P342. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Refer to P343. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 60PCh. 3 - Figure P361 shows a valve stem from an engine...Ch. 3 - The conveyor fixture shown in Figure P362 carries...Ch. 3 - For the flat plate in tension in Figure P363,...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - Prob. 68PCh. 3 - Figure P369 shows a horizontal beam supported by a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 70PCh. 3 - Prob. 71PCh. 3 - The beam shown in Figure P372 is a stepped, flat...Ch. 3 - Figure P373 shows a stepped, flat bar having a...Ch. 3 - Figure P374 shows a bracket carrying opposing...Ch. 3 - Prob. 75PCh. 3 - Figure P376 shows a lever made from a rectangular...Ch. 3 - For the lever in P376, determine the maximum...Ch. 3 - Figure P378 shows a shaft that is loaded only in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 79PCh. 3 - Prob. 80PCh. 3 - A hanger is made from ASTM A36 structural steel...Ch. 3 - A coping saw frame shown in Figure P382 is made...Ch. 3 - Prob. 83PCh. 3 - Figure P384 shows a hand garden tool used to break...Ch. 3 - Figure P385 shows a basketball backboard and goal...Ch. 3 - Prob. 86P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. A 4000 lb block of concrete is attached by light inextensible cables to the truss in Figure 5. Determine the force in each member. State whether each member is in tension or compression. 3 ΘΑ D E cables all dimensions in feet.arrow_forwardA block hangs from the end of bar AB that is 5.80 meters long and connected to the wall in the xz plane. The bar is supported at end A by a ball joint such that it carries only a compressive force along its axis. The bar is supported in equilibrium at end B by cables BD and BC that connect to the xz plane at points C and D respectively with coordinates given in the figure. The z components of the moments exerted on the bar by these two cables sum to 0. The tension in cable BD is measured to be 210 Newtons. Input answers of zero as 0.00 to avoid an invalid answer due to significant figures. Determine the equivalent force and couple system acting at A that models only the forces exerted by both cables BD → and BC on the bar at B. Enter your results for Feq and Meg in Cartesian Components. Z D (c, 0, d) C (a, 0, b). X A f m B y cc 040 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a…arrow_forwardA bent tube is attached to a wall with brackets as shown. A force of F = 785 lb is applied to the end of the tube with direction indicated by the dimensions in the figure. a.) Determine the moment about point D due to the force F Enter your answer in Cartesian components with units of ft- lbs. b.) Determine the moment about a line (i.e. axis) running from D to C due to the force F. Enter your answer in Cartesian components with units of ft-lbs. 2013 Michael Swanbom x BY NC SA g Z h A с FK kaz Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the table below. Note the figure may not be to scale. Be sure to align your cartesian unit vectors with the coordinate axes shown in the figure. Variable Value α 4.84 in b 13.2 in с 12.5 in d 30.8 in h 18.7 in 22.0 in →> a. MD=( i+ k) ft- lb →> b. MDC = î + k) ft- lbarrow_forward
- F1 3 4 5 P F2 F2 Ꮎ e b 200 3 4 5 F1 The electric pole is subject to the forces shown. Force F1 245 N and force F2 = 310 N with an angle 0 = 20.2°. Determine the moment about point P of all forces. Take counterclockwise moments to be positive. = Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 2.50 m b 11.3 m с 13.0 m The moment about point P is m. N- If the moment about point P sums up to be zero. Determine the distance c while all other values remained the same. m.arrow_forwardF y b C 10 Z Determine the moment about O due to the force F shown, the magnitude of the force F = 76.0 lbs. Note: Pay attention to the axis. Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 1.90 ft b 2.80 ft с 2.60 ft d 2.30 ft Mo = lb + k) ft-arrow_forwardThe shelf bracket is subjected to the force F = 372 Newtons at an angle = 21.4°. Compute the moment (in N-m) that this force exerts about each of the two attachment points (screw locations in the figure). Take counterclockwise moments to be positive. a duk F -0 2013 cc Michael Swanbom BY NC O SA Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 43.0 cm b 32.3 cm с 2.58 cm The moment about the upper attachment point is N-m. The moment about the lower attachment point is N-m.arrow_forward
- A man skis down a slope. His initial elevation was 150 m and his velocity at the bottom of the slope is 17 m/s. What percentage of his initial potential energy was consumed due to friction and air resistance? Use the accounting equation in your calculations.arrow_forwardIn direct calorimetry, a person is placed in a large, water-insulated chamber. The chamber is kept at a constant temperature. While in the chamber, the subject is asked to perform a number of normal activities, such as eating, sleeping, and exercising. The rate of heat released from the subject’s body can be measured by the rate of heat gain by the water bath. Would direct calorimetry be a practical way to measure metabolic rate? Why or why not?A person is placed inside a calorimetric chamber for 24 hours. During this time, the 660-gallon water bath heats up by 3.2°F. What is the subject’s metabolic rate during this period? Report your answer in kcal/day. Assume that there is no heat loss from the water to the surroundings.arrow_forwardUpon reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere, the bottom of a space shuttle heats up to dangerous levels as the craft slows for landing. If the velocity of the shuttle is 28,500 km/hr at the beginning of reentry and 370 km/hr just prior to landing, how much energy is lost as heat? The shuttle has a mass of 90,000 kg. Assume that the change in potential energy is negligible compared to the change in kinetic energy.arrow_forward
- of the basket of the balloon at point A, and their other ends are staked to the ground. The hook is located in the geometric center of the basket. The balloon and the air inside it have a combined mass of 3000 kg. You want to determine the resultant of the tension forces in the four cables acting on the hook at point A. It is known that the magnitudes of the tension in the cables are as follows: TAB = 207 N; TAC = 355 N; TAD = 250 N; and TAE = 486 N. B E 2.5 m C E 5.5 m D 2.5 m 3.5 m 1.5 m Using the information provided in the problem, express the force on the hook at point A by cable AC in rectangular component form. The force on the hook at point A by cable AC in rectangular component form is given below. T AC N) i+ N) + N) Rarrow_forwardWater in the glass tube is at a temperature of 40°C. Plot the height of the water as a function of the tube's inner diameter D for 0.5mm≤D≤3mm. Use increments of 0.5mm. Take sigma=69.6mN/m, and theta=0° for the contact angle.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance h that the column of mercury in the tube will be depressed when the tube is inserted into the mercury at a room temperature of 68 F. Plot this relationship of h (vertical axis) versus D for 0.5 in≤D≤0.150in. Give values for increments of ΔD=0.025in. Discuss this resultarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C-FEVzI8oe8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bending Stress; Author: moodlemech;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9QIqewkE6xM;License: Standard Youtube License