
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 3, Problem 5CTQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:Each central atom that is expected to be
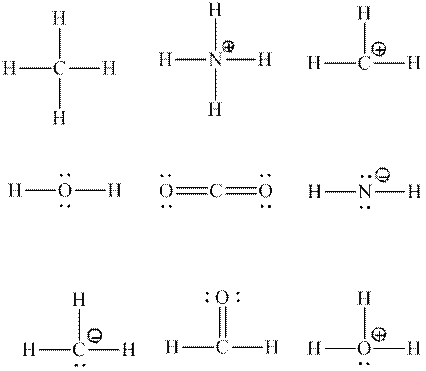
Concept introduction:Two or more of orbitals undergo redistributions of their different energies so as to form mathematically averaged orbitals in terms of energy although they may differ in shape and orientation. This phenomenon is referred as hybridization.
The energy and orientation of the new hybrid orbital depends upon by the kind and number of orbitals used in the hybridization. The new hybrid orbitals are always equal in number to number of atomic orbitals that combine.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Some of the theories used to describe interface structure can be distinguished by:1. the measured potential difference.2. the distribution of ions in solution.3. the calculation of charge density.4. the external Helmoltz plane.
When talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?
Using the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 3 - What neutral atom is represented by the electron...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 3 - Consider any one of the four identical hybrid...Ch. 3 - Prob. 5CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 6CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 7CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 8CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 9CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 10CTQ
Ch. 3 - On the left side of Figure 3.6, label the areas...Ch. 3 - Prob. 12CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 13CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 14CTQCh. 3 - Prob. 15CTQCh. 3 - Now consider the fully formed molecule on the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 1ECh. 3 - Explain why the two molecules below cannot...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3ECh. 3 - Consider the incomplete orbital representation of...Ch. 3 - Consider the following orbital representation of...Ch. 3 - Summarize how one determines the hybridization...Ch. 3 - Explain what is wrong with each of the following...Ch. 3 - Prob. 8ECh. 3 - Prob. 9ECh. 3 - Complete the following tables, and memorize their...Ch. 3 - Draw orbital representations of bonding in water...Ch. 3 - Draw electron configuration diagrams for carbon in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 13E
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY