
University Physics Volume 2
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168161
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 37P
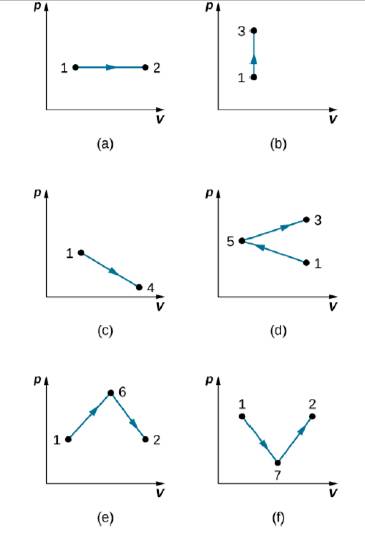
Find the work done in the quasi-static processes shown below. The states are given as (p, V) values for the points in the PV plane: 1 (3 atm, 4 L), 2 (3 atm, 6 L), 3 (5 atm, 4 L), 4 (2 atm, 6 L), 5 (4 atm, 2 L), 6 (5 atm, 5 L) and 7 (2 atm, 5 L).
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Point charges of 6.50 μC and -2.50 μC are placed 0.300 m apart. (Assume the negative charge is located to the right of the positive charge. Include the sign of the value in your answers.)
(a) Where can a third charge be placed so that the net force on it is zero?
0.49
m to the right of the -2.50 μC charge
(b) What if both charges are positive?
0.49
xm to the right of the 2.50 μC charge
Find the electric field at the location of q, in the figure below, given that q₁ =9c9d = +4.60 nC, q = -1.00 nC, and the square is 20.0 cm on a side. (The +x axis is directed to the right.)
magnitude
direction
2500
x
What symmetries can you take advantage of? What charges are the same magnitude and the same distance away? N/C
226
×
How does charge sign affect the direction of the electric field? counterclockwise from the +x-axis
9a
9b
%
9
9d
would 0.215 be the answer for part b?
Chapter 3 Solutions
University Physics Volume 2
Ch. 3 - The paths ABC, AC, and ADC represent three...Ch. 3 - Check Your Understanding The quantities below...Ch. 3 - Check Your Understanding Why was it necessary to...Ch. 3 - Check Your Understanding When 1.00 g of ammonia...Ch. 3 - Consider these scenarios and state whether work is...Ch. 3 - Is it possible to determine whether a change in...Ch. 3 - When a liquid is vaporized, its change in internal...Ch. 3 - Why does a bicycle pump feel warm as you inflate...Ch. 3 - Is it possible for the temperature of a system to...Ch. 3 - What does the first law of thermodynamics tell us...
Ch. 3 - Does adding heat to a system always increase its...Ch. 3 - A great deal of effort, time, and money has been...Ch. 3 - When a gas expands isothermally, it does work....Ch. 3 - If the pressure and volume of a system are given,...Ch. 3 - It is unlikely that a process can be isothermal...Ch. 3 - How can an object transfer heat if the object does...Ch. 3 - Most materials expand when heated. One notable...Ch. 3 - Why are there two specific heats for gases Cp and...Ch. 3 - Is it possible for to be smaller than unity? `Ch. 3 - Would you expect to be larger for a gas or a...Ch. 3 - There is no change in the internal of an ideal gas...Ch. 3 - Does a gas do any work when it expands...Ch. 3 - A gas follows on an isothermal curve, where p is...Ch. 3 - A mole of gas has isobaric expansion coefficient...Ch. 3 - Find the equation of state of a solid that has an...Ch. 3 - A gas at a pressure of 2.00 atm undergoes a...Ch. 3 - It takes 500 J of work to compress...Ch. 3 - It is found that, when a dilute gas expands...Ch. 3 - In a quasi-static isobaric expansion. 500 J of...Ch. 3 - When a gas undergoes a quasi-static isobaric...Ch. 3 - An ideal gas expands quasi-statically and...Ch. 3 - As shown below, calculate the work done by the gas...Ch. 3 - (a) Calculate the work done by the gas along the...Ch. 3 - An ideal gas expands quasi-statically to three...Ch. 3 - A dilute gas at a pressure of 2.0 atm and a volume...Ch. 3 - What is the average mechanical energy of the atoms...Ch. 3 - What is the internal energy of 6.00 mol of an...Ch. 3 - Calculate the internal energy of 15 mg of helium...Ch. 3 - Two monatomic ideal gases A and B are at the same...Ch. 3 - The van der Waals coefficients for oxygen are...Ch. 3 - Find the work done in the quasi-static processes...Ch. 3 - When a dilute gas expands quasi-statically from...Ch. 3 - In a quasi-static isobaric expansion, 500 J of...Ch. 3 - An ideal gas quasi-statically and isothermally...Ch. 3 - As shown below, if the heat absorbed by the gas...Ch. 3 - During the isobaric expansion from A to B...Ch. 3 - (a) What is the change in internal energy for the...Ch. 3 - When a gas expands along path AC shown below, it...Ch. 3 - When a gas expands along AB (see below), it does...Ch. 3 - A dilute gas is stored in the left chamber of a...Ch. 3 - Ideal gases A and B are stored in the left and...Ch. 3 - An ideal monatomic gas at a pressure of 2.0105N/m2...Ch. 3 - Consider the process for steam in a cylinder shown...Ch. 3 - The state of 30 moles of steam in a cylinder is...Ch. 3 - A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a quasi-static...Ch. 3 - A metallic container of fixed volume of 2.5103 m3...Ch. 3 - A gas in a cylindrical closed container is...Ch. 3 - Two moles of a monatomic ideal gas at (5 MPa, 5 L)...Ch. 3 - Consider a transformation from point A to B in a...Ch. 3 - Consider a cylinder with a movable piston...Ch. 3 - An ideal gas expands isothermally along AB and...Ch. 3 - Consider the processes shown below. In the...Ch. 3 - Two moles of helium gas axe placed in a...Ch. 3 - An amount of n moles of a monatomic ideal gas in a...Ch. 3 - The temperature of an ideal monatomic gas rises by...Ch. 3 - For a temperature increase of 10 at constant...Ch. 3 - If the gases of the preceding problem are...Ch. 3 - Consider 0.40 mol of dilute carbon dioxide at a...Ch. 3 - When 400 J of heat are slowly added to 10 mol of...Ch. 3 - One of a dilute diatomic gas occupying a volume of...Ch. 3 - A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a quasi-static...Ch. 3 - An ideal gas has a pressure of 0.50 atm and a...Ch. 3 - Pressure and volume measurements of a dilute gas...Ch. 3 - An ideal monatomic gas at 300 K expands...Ch. 3 - An ideal diatomic gas at 80 K is slowly compressed...Ch. 3 - An ideal diatomic gas at 80 K is slowly compressed...Ch. 3 - Compare the charge in internal energy of an ideal...Ch. 3 - The temperature of n moles of an ideal gas changes...Ch. 3 - A dilute gas expands quasi-statically to three...Ch. 3 - (a) An ideal gas expands adiabatically from a...Ch. 3 - On an adiabatic process of an ideal gas pressure,...Ch. 3 - Two moles of a monatomic ideal gas such as helium...Ch. 3 - Consider the process shown below. During steps AB...Ch. 3 - A car tile contains 0.0380 m3 of air at a pressure...Ch. 3 - A helium-filled toy balloon has a gauge pressure...Ch. 3 - Steam to drive an old-fashioned steam locomotive...Ch. 3 - A hand-driven tire pump has a piston with a...Ch. 3 - Calculate the net work output of a heat engine...Ch. 3 - What is the net work output of a heat engine that...Ch. 3 - Five moles of a monatomic ideal gas in a cylinder...Ch. 3 - Four moles of a monatomic ideal gas in a cylinder...Ch. 3 - Helium gas is cooled from 20 to 10 by expanding...Ch. 3 - In an adiabatic process, oxygen gas in a container...Ch. 3 - A cylinder containing three moles of a monatomic...Ch. 3 - A cylinder containing three moles of nitrogen gas...Ch. 3 - Two moles of a monatomic ideal gas such as oxygen...Ch. 3 - An insulated vessel contains 1.5 moles of argon at...Ch. 3 - One mole of an ideal monatomic gas occupies a...Ch. 3 - One mole of an ideal gas is initially in a chamber...Ch. 3 - A bullet of mass 10 g is traveling horizontally at...Ch. 3 - The insulated cylinder shown below is closed at...Ch. 3 - In a diesel engine, the fuel is ignited without a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Name the components (including muscles) of the thoracic cage. List the contents of the thorax.
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS Balancing selection can maintain variation at a locus (see Concept 23.4). Based on the foragi...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
All of the following terms can appropriately describe humans except: a. primary consumer b. autotroph c. hetero...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
1.3 Obtain a bottle of multivitamins and read the list of ingredients. What are four chemicals from the list?
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms? a. algal oil b. ethanol c. hydrogen d. met...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk(*) desig...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a toy boat moves in a pool at at a speed given by v=1.0 meter per second at t=0, and that the boat is subject to viscous damping. The damping on the boat causes the rate of speed loss to be given by the expression dv/dt=-2v. How fast will the boat be traveling after 1 second? 3 seconds? 10 seconds? Use separation of variables to solve this.arrow_forwardWhat functional form do you expect to describe the motion of a vibrating membrane without damping and why?arrow_forwardIf speed is tripled, how much larger will air drag become for an object? Show the math.arrow_forward
- What does it tell us about factors on which air drag depends if it is proportional to speed squared?arrow_forwardWhat is the net charge on a sphere that has the following? x (a) 5.75 × 106 electrons and 8.49 × 106 protons 4.39e-13 What is the charge of an electron? What is the charge of a proton? C (b) 200 electrons and 109 protons 1.60e-10 What is the charge of an electron? What is the charge of a proton? Carrow_forwardA spider begins to spin a web by first hanging from a ceiling by his fine, silk fiber. He has a mass of 0.025 kg and a charge of 3.5 μC. A second spider with a charge of 4.2 μC rests in her own web exactly 2.1 m vertically below the first spider. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field due to the charge on the second spider at the position of the first spider? 8.57e3 N/C (b) What is the tension in the silk fiber above the first spider? 0.125 How does the electric field relate to the force? How do you calculate the net force? Narrow_forward
- Point charges of 6.50 μC and -2.50 μC are placed 0.300 m apart. (Assume the negative charge is located to the right of the positive charge. Include the sign of the value in your answers.) (a) Where can a third charge be placed so that the net force on it is zero? 0.49 m to the right of the -2.50 μC charge (b) What if both charges are positive? 0.185 xm to the right of the 2.50 μC chargearrow_forwardc = ad Find the electric field at the location of q, in the figure below, given that q₁ = 9₁ = 9₁ = +4.60 nC, q=-1.00 nC, and the square is 20.0 cm on a side. (The +x axis is directed to the right.) magnitude direction N/C ° counterclockwise from the +x-axis 9a % 9 9barrow_forwardPlastic beads can often carry a small charge and therefore can generate electric fields. Three beads are oriented such that 92 is between q₁ and 93. The sum of the charge on 9₁ and 92 is 9₁ + 92 = −2.9 µС, and the net charge of the system of all three beads is zero. E field lines 93 92 What charge does each bead carry? 91 92 -1.45 What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 2.9 ✓ What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 93 2.9 μεarrow_forward
- A spider begins to spin a web by first hanging from a ceiling by his fine, silk fiber. He has a mass of 0.025 kg and a charge of 3.5 μC. A second spider with a charge of 4.2 μC rests in her own web exactly 2.1 m vertically below the first spider. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field due to the charge on the second spider at the position of the first spider? 8.57e3 N/C (b) What is the tension in the silk fiber above the first spider? 0.275 How does the electric field relate to the force? How do you calculate the net force? Narrow_forwardPlastic beads can often carry a small charge and therefore can generate electric fields. Three beads are oriented such that 92 is between 91 system of all three beads is zero. E field lines 91 92 93 X What charge does each bead carry? 91 = 92 = ?2.9 0 μC × What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 93 2.9 με and 93. The sum of the charge on 91 and 92 is 91 +92 = -2.9 μC, and the net charge of thearrow_forwardAn electron has an initial speed of 5.26 x 100 m/s in a uniform 5.73 x 105 N/C strength electric field. The field accelerates the electron in the direction opposite to its initial velocity. (a) What is the direction of the electric field? opposite direction to the electron's initial velocity same direction as the electron's initial velocity not enough information to decide × What is the direction of the force on the electron? How does it compare to the direction of the electric field, considering the sign of the electron's charge? (b) How far does the electron travel before coming to rest? 0.0781 × What kinematic equation is relevant here? How do you calculate the force due to the electric field? m (c) How long does it take the electron to come to rest? 5.27e8 What is the final velocity of the electron? s (d) What is the electron's speed when it returns to its starting point? 5.26e6 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Heat Flow, Entropy, and Microstates; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MrwW4w2nAMc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY