
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134320533
Author: Michael S. Mamlouk, John P. Zaniewski
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.19QP
Three steel bars with a diameter of 25 mm and carbon contents of 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8%, respectively. The specimens were subjected to tension until rupture. The load versus deformation results were as shown in Table P3.19.
If the gauge length is 50 mm, determine the following:
- a. a The tensile stresses and strains for each specimen at each load increment.
- b. b Plot stresses versus strains for all specimens on one graph.
TABLE P3.19
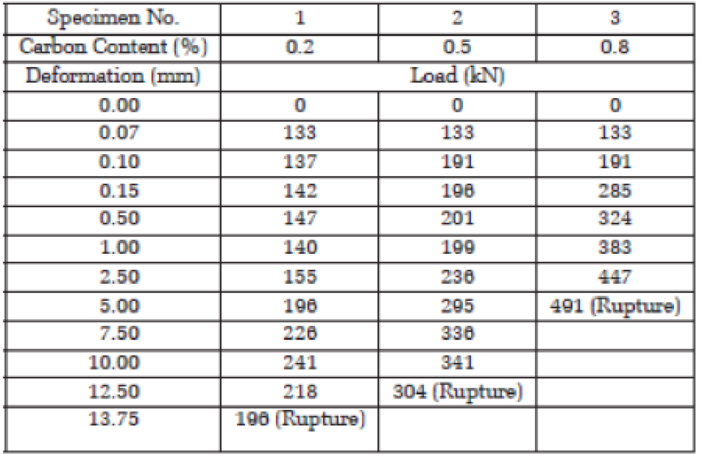
- c. The proportional limit for each specimen.
- d. The 0.2% offset yield strength for each specimen.
- e. The modulus of elasticity for each specimen.
- f. The strain at rupture for each specimen.
- g. Comment on the effect of increasing the carbon content on the following:
- i. Yield strength
- ii. Modulus of elasticity
- iii. Ductility
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Draw the shear and bending moment diagrams and find the immediate deflection for a simply
supported beam of length 20 ft. with the same live load at ½ span and cross-section as the previous
problem. Assume a reasonable Modulus of Elasticity and concrete self-weight.
Hint: You may look online for typical concrete self-weights and compressive strengths. You may
also use the ACI 318 Code equation for the Modulus of Elasticity shown below, and the supplied
Design Aids.
Problem 4. A major transmission pathway of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-
19) is through droplets and aerosols produced by violent respiratory events such as sneezes
and coughs (Fig. 1). For the purpose of providing public health guidelines, we would like
to estimate the amount of time it takes for these droplets to settle from air to the ground.
The relevant parameters are the settling time (ts), the initial height of the droplets (H),
gravitational acceleration (g), density of the droplets (pa), radius of the droplets (R), as well
as dynamic viscosity of the ambient air (Pair). Use dimensional analysis and the Buckingham
theorem to answer the following questions:
1. Find the independent dimensionless parameters using the table method. Then, express
the settling time as a function of the other relevant parameters. Your solution should
match the physical intuition that the settling time scales linearly with the initial height.
2. How would the settling change if the…
Question 4
An engineer is assigned to design a 25-stories office building which has a
building height of 75 m. Reinforced concrete shear wall system as shown in
Figure Q1(a) is adopted to resist the lateral loads. The shear wall is of
thickness t = 350 mm and length L = 8.5 m. Use the following data: Young's
modulus of concrete E = 28 kN/mm² and the lateral load intensity w = 1.20
kN/m². Assuming the frontal width of the building façade is 15 m is facing
the wind force which in turn transmitting the wind force
to the shear wall system, estimate the total value of
sway A at the roof level.
Question 5
For the Shear Wall in Question 4, if the total ultimate
gravity load of the building acted on shear wall is 6000
KN, using a partial factor of 1.2 for the wind load,
calculate the stress on the extreme right corner of the
shear wall at first storey level.
(A)
9.46 mm
(B)
189.26 mm
(C)
14.20 mm
(D)
141.95 mm
STOREY
FLOOR LEV
Shear wall
Figure Q1(a)
(A)
3.228 N/sq mm
(B)
14.029 N/sq mm
75 m…
Chapter 3 Solutions
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
Ch. 3 - What is the chemical composition of steel? What is...Ch. 3 - Why does the ironcarbon phase diagram go only to...Ch. 3 - Draw a simple ironcarbon phase diagram showing the...Ch. 3 - What is the typical maximum percent of carbon in...Ch. 3 - Calculate the amounts and compositions of phases...Ch. 3 - Briefly discuss four heat treatment methods to...Ch. 3 - Define alloy steels. Explain why alloys are added...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.8QPCh. 3 - Specifically state the shape and size of the...Ch. 3 - What are the typical uses of structural steel?
Ch. 3 - What is the range of thicknesses of cold-formed...Ch. 3 - Why is coil steel used for cold-formed steel...Ch. 3 - If a steel with a 33 ksi yield strength is used...Ch. 3 - Why is reinforcing steel used in concrete? Discuss...Ch. 3 - What is high-performance steel? State two HPS...Ch. 3 - Name three mechanical tests used to measure...Ch. 3 - The following laboratory tests are performed on...Ch. 3 - Sketch the stress-strain behavior of steel, and...Ch. 3 - Three steel bars with a diameter of 25 mm and...Ch. 3 - Three steel bars with a diameter of 0.5 in. and...Ch. 3 - Draw a typical stressstrain relationship for steel...Ch. 3 - Getting measurements from Figure 3.18, determine...Ch. 3 - A steel specimen is tested in tension. The...Ch. 3 - A steel specimen is tested in tension. The...Ch. 3 - A No. 10 steel rebar is tested in tension. By...Ch. 3 - A mild steel specimen originally 300 mm long is...Ch. 3 - A tension stress of 70 ksi was applied on a 12-in....Ch. 3 - A tensile stress is applied along the long axis of...Ch. 3 - A cylindrical steel alloy rod with a 0.5 in....Ch. 3 - A round steel alloy bar with a diameter of 0.75...Ch. 3 - A 19-mm reinforcing steel bar and a gauge length...Ch. 3 - Testing a round steel alloy bar with a diameter of...Ch. 3 - During the tension test on a steel rod within the...Ch. 3 - A grade 36 round steel bar with a diameter of 0.5...Ch. 3 - A high-yield-strength alloy steel bar with a...Ch. 3 - Estimate the cross-sectional area of a 350S125-27...Ch. 3 - An ASTM A615 grade 60 number 10 rebar with a gauge...Ch. 3 - A 32-mm rebar with a gauge length of 200 mm was...Ch. 3 - A steel pipe having a length of 3 ft. an outside...Ch. 3 - A steel pipe having a length of 1 m, an outside...Ch. 3 - A drill rod with a diameter of 10 mm is made of...Ch. 3 - A drill rod with, a diameter of 1/2 in. is made of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.43QPCh. 3 - An engineering technician performed a tension test...Ch. 3 - A Charpy V Notch (CVN) test was performed on a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.46QPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.47QPCh. 3 - How can the flaws in steel and welds be detected?...Ch. 3 - Determine the welding zone classification of A36...Ch. 3 - Briefly define steel corrosion. What are the four...Ch. 3 - Discuss the main methods used to protect steel...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 4 An engineer is assigned to design a 25-stories office building which has a building height of 75 m. Reinforced concrete shear wall system as shown in Figure Q1(a) is adopted to resist the lateral loads. The shear wall is of thickness t = 350 mm and length L = 8.5 m. Use the following data: Young's modulus of concrete E = 28 kN/mm² and the lateral load intensity w = 1.20 kN/m². Assuming the frontal width of the building façade is 15 m is facing the wind force which in turn transmitting the wind force to the shear wall system, estimate the total value of sway A at the roof level. Question 6 If the similar building in Question 4 is designed using rigid frame method is to be designed to ensure the sway is within the allowable limit. If the building width is B, and with the same building height H=75m. Using a rough estimation method, calculate the maximum allowable deflection A at the roof level. (A) 9.46 mm (B) 189.26 mm (C) 14.20 mm 町 141.95 mm 1ST STOREY FLOOR LEV. Shear wall…arrow_forwardWhat are the biggest challenges estimators' face during the quantity takeoff and pricing phases?arrow_forwardQuestion IV (30%): A 22 m thick normally consolidated clay layer has a load of 150 kPa applied to it over a large areal extent. The clay layer is located below a 3.5 m thick granular fill (p= 1.8 Mg/m³). A dense sandy gravel is found below the clay. The groundwater table is located at the top of the clay layer, and the submerged density of the clay soil is 0.95 Mg/m³. Consolidation tests performed on 2.20 cm thick doubly drained samples indicate the time for 50% consolidation completed as t50 = 10.5 min for a load increment close to that of the loaded clay layer. Compute the effective stress in the clay layer at a depth of 16 m below the ground surface 3.5 years after the application of the load.arrow_forward
- 13-3. Use the moment-distribution method to determine the moment at each joint of the symmetric bridge frame. Supports at F and E are fixed and B and C are fixed connected. Use Table 13-2. The modulus of elasticity is constant and the members are each 0.25 m thick. The haunches are parabolic. *13-4. Solve Prob. 13-3 using the slope-deflection equations. 13 0.5 m 1 m 64 kN/m D BC 1.5 m 2.25 m 2 m 6.25 m -0.5 m E -7.5 m -10 m- -7.5 m. Probs. 13-3/4arrow_forward2. Find the equivalent concentrated load(s) for the bags of cement stacked on the dock as shown here. Each bag weighs 100 lbs and is 12 inches long. Draw the loading conditions for each showing the equivalent concentrated load(s). 1 bag = 100lbs L= 12 ft L= 6 ft L= 8ftarrow_forwardI have a question for this problem in the first one wouldn't it be finding the total weight of the bags which =4800lbs and the multiply that by 12ft to find the concentrated load?? but if this is the case the load would end up as lbs/ft so I'm not too sure that is right.arrow_forward
- Q.2 The girder AB as shown in Fig. 2 has a span of 18m and supports concentrated loads located as shown. Determine the plastic moment capacity MP and the plastic collapse load Pc for the given load conditions. Use either Equilibrium drVirtual Work method in your solution. [30 marks] 5P 5P C d B 6 m 6 m 6 m 18 m Fig. 2 - Prismatic Continuousarrow_forward337 kN -Weld -25° 6 mm PROBLEM 1.33 A steel pipe of 300 mm outer diameter is fabricated from 6 mm thick plate by welding along a helix which forms an angle of 25° with a plane perpendicular to the axis of the pipe. Knowing that the maximum allowable normal and shearing stresses in directions respectively normal and tangential to the weld are σ = 50 MPa and 7 = 30 MPa, determine the magnitude P of the largest axial force that can be applied to the pipe.arrow_forward2.2 Identify the Zero Force Members for the truss shown. Show your final answer with a sketch and mark the zero force bars with "0". D 700 N 500 Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337094740
Author:Segui, William T.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305086272
Author:William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Material Properties 101; Author: Real Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHZALtqAjeM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY