
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The explanation for alanine which has different optical rotation in water,
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
Each solvent rotates the alanine molecule to a different angle due to the formation of different complex formation and so it gives rise to different optical rotation in different solvents.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of alanine is shown below.
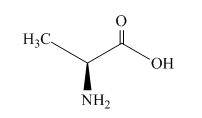
Figure 1
Alanine is an optically active compound. It rotates the plane of polarized light. The reaction of alanine with water,
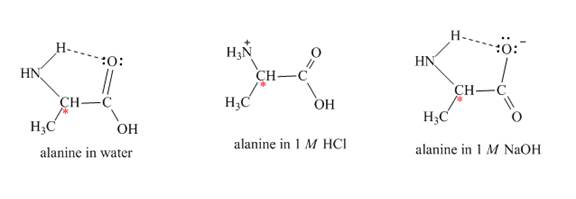
Figure 2
The optical rotation of alanine is measure by Circular Dichroism (CD). It involves circularly polarized light absorption. It measures the angle at which the plane-polarized light is rotated by the molecule. Each solvent rotates the alanine molecule to a different angle, due to this it gives rise to different optical rotation in different solvents.
The alanine has different optical rotation in water,
(b)
Interpretation:
The explanation for two known mono
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group,
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
Due to the presence of two amine groups in lysine molecule. It may undergo acetylation reaction from either side and form mono
Explanation of Solution
The structure of amino acid lysine is shown below.
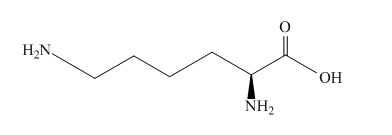
Figure 3
The structure of the lysine molecule contains two amine group one at the
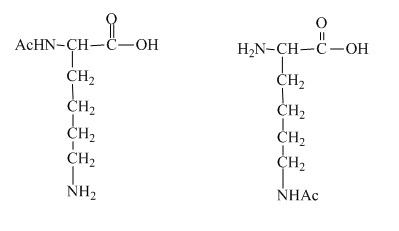
Figure 4
The two mono
(c)
Interpretation:
The explanation for fact that the peptide
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
The compound urea under basic conditions acts as a denaturation agent which breakdown the protein molecule bonding. Due to this, the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
The protein molecule is composed of four types of structure primary, secondary, tertiary and quarternary. The enzyme trypsin hydrolyzes the peptide,
The peptide
(d)
Interpretation:
The explanation for the peptide containing cysteine on reaction with
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group,
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
The generation of lysine type molecule at the end of the reaction which is cleaved by trypsin enzyme. Due to this, the peptide containing cysteine on reaction with
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the cysteine molecule is shown below.
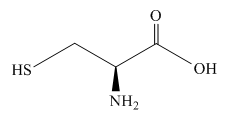
Figure 5
The same molecule in peptides exists as a disulfide bond. The disulfide bond of cysteine in the protein molecule is shown below.
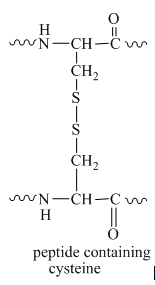
Figure 6
When this protein molecule with a disulfide bond is treated with
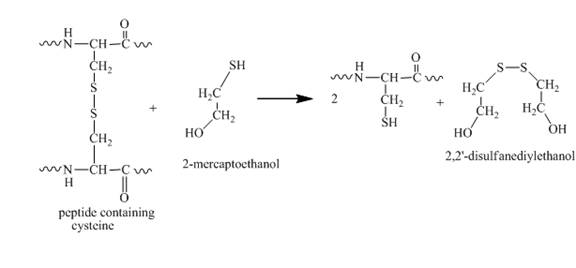
Figure 7
The thiol group is then reacted with the aziridine molecule which results in the formation of a lysine type molecule. This reaction is shown below.
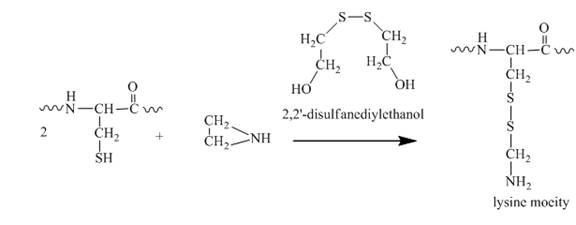
Figure 8
This lysine type molecule then reacts with trypsin enzyme which cleaves arginine and lysine molecule. Due to this, the trypsin enzyme reacts with the modified cysteine residues.
The peptide containing cysteine on reaction with
(e)
Interpretation:
The explanation for the formation of two separable methionine sulfoxides from the oxidation of
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group,
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
The application of a certain amount of energy which converts one form to another form of structure. Due to this, the formation of two separable methionine sulfoxides from the oxidation of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of methionine is shown below.
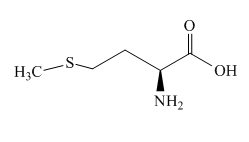
Figure 9
The resonance structure of sulfoxides with two different groups is shown below.
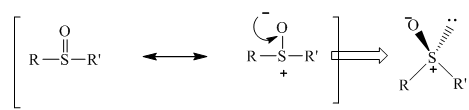
Figure 10
The conversion of one structure to another structure at room temperature requires a certain amount of energy. Therefore, on the application of that amount of energy, the two forms of
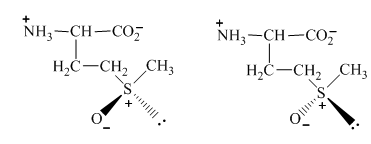
Figure 11
The formation of two separable methionine sulfoxides from the oxidation of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- on x Fina X Sign X Sign x lab X Intro X Cop X chat X My x Grac x Laur x Laur x ashes x S Shox S SHE x a eve.macmillanlearning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/d591b3f2-d5f7-4983-843c-0d00c1c0340b/f2b47861-07c4-4d1b-a1ee-e7db27d6b4ee?actualCourseld=d591b3f2-c stions estion. ct each urces. +95 Macmillan Learning Draw the product formed by the reaction of potassium t-butoxide with (15,25)-1-bromo-2-methyl-1-phenylbutane (shown). Clearly show the stereochemistry of the product. H BH (CH3)3CO-K+ +100 H3CW (CH3)3COH +85 H3CH2C +95 ossible ↓ Q Search Select Draw Templates More C H 0 bp A Erase 2Q 112 Resouarrow_forwardIdentify the structure of the PTH derivative generated after two rounds of Edman degradation.arrow_forwardUse the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 31 0.5 30 26 29 22 28 100 27 33 26 23 15 4 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. 妊 n ? Previous Nextarrow_forward
- for this question. Write the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M+ = 98.1106. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 1.008 12C 98.90 12.000 14N 99.63 14.003 160 99.76 15.995 Molecular formula (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forwardPLEASE READ!!! I DONT WANT EXAMPLES, I DONT WANT WORDS OR PARAGRAPHS!!! PLEASE I UNDERSTAND THE BASICS BUT THIS IS AN EXCEPTION THAT EVEN THE INTERNET CANT HELP!!!! THIS IS THE THIRD TIME I'VE SENT THOSE QUESTIONS SO PLEASE DONT RESEND THE SAME STUFF, ITS NOT HELPING ME!!! I ALSO ALREADY TRIED TO DRAW THE MECHANISM MYSELF, SO IF ITS RIGHT PLEASE TELL ME OR TELL ME WHAT I HAVE TO CHANGE!!! First image: I have to SHOW (DRAWING) the mechanism (with arows and structures of molecules) NOT WORDS PLEASE! of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mechanism (IMAGE) (with arrows and structures of the molecules) NOT WORDS PLEASE !! for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion HOMEWORK, NOT EXAM!! ALL DETAILS ARE IN THE IMAGES PLEASE LOOK AT THE IMAGES, DONT LOOK AT THE AI GENERATED TEXT!!!arrow_forwardWrite the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M+ = 85.0899. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 1.008 12C 98.90 12.000 14N 99.63 14.003 160 99.76 15.995 Molecular formula (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forward
- Use the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 59 3.0 58 64 43 100 15 23 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. •You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. + n[] 85 // ? CH4 Previous Nextarrow_forwardWrite the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M* = 128.0632. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 12C 98.90 14N 99.63 160 99.76 Molecular formula 1.008 12.000 14.003 15.995 (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this? And can I please the lowest possible significant number?arrow_forward
- What is the molar mass of a gas that takes three times longer to effuse than helium?arrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism (with arows and structures) of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mecanism (with arrows and structures) for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion its not an examarrow_forwardwhat is the skeletal structure of a tertiary alkyl fluoride with six carbon atoms and no rings.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

