
Interpretation : To describe the formation of
Concept Introduction : Polymers are compounds that are formed due to the combination of monomers. The polymers that are formed are characterized by the process that monomers undergo to form polymers.
Explanation of Solution
Polymers are synthetic as well as natural substances that are made up of large molecules called macromolecules. These macromolecules are the multiples of monomers which are simple chemicals.
In this case, the tetrafluoroethylene reactant is the monomer and the Teflon that is formed as a product is the polymer.
Let ethylene be considered. If single hydrogen in this ethylene molecule is replaced with the chlorine molecule, then the monomers which are Vinyl chloride will combine to form Polyvinyl Chloride which is a polymer.
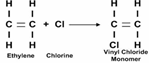
The first step involves the replacement of hydrogen with chlorine to form vinyl chloride
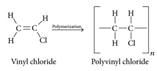
The second step involves the addition
Polymers are a combination of monomers and are generally large in size. The important polymers may contain nitrogen or oxygen in the backbone chain along with carbon. Materials containing oxygen in them are called polyacetals. Proteins and casein that is found in milk are generally polyamides.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- If 10 mL of a commercial sodium silicate solution is added, the water required to obtain a 20% solids solution (SiO2+Na2O) is added. Indicate the final grams of Na2SiO3.arrow_forwardPlease help me figure out the mechanism with arrows of the following reactionarrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups Predicting the reactants or products of acetal hydrolysis termine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: H* H* + H₂O Y ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X, Y, and Z. You may draw that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure Explanation Check @2 W Click and drag to start drawing a structure. #4 # 3 LU E % 67 olo 5 66 R T Y & 7 AcGraw Hill LLC. All Rights R Xarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





