
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The monomer required to produce the given polymer needs to be determined.
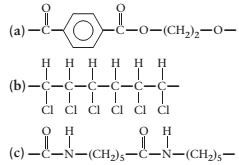
Concept Introduction:
A polymer is a long chain consists of large number of monomer units. The monomers are repeated units in a polymer they are linked to each other in different orders to produce different
These monomer units are linked to each other either through the formation of peptide linkage or glycosidic linkage or by removal of any moiety such as a water molecule.
Polyvinyl chloride, bakelite, polystyrene are some of the example of polymers.
(b)
Interpretation:
The monomer required to produce the given polymer needs to be determined.
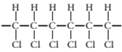
Concept Introduction:
A polymer is a long chain consists of large number of monomer units. The monomers are repeated units in a polymer they are linked to each other in different orders to produce different polymers.
These monomer units are linked to each other either through the formation of peptide linkage or glycosidic linkage or by removal of any moiety such as a water molecule.
Polyvinyl chloride, bakelite, polystyrene are some of the example of polymers.
(c)
Interpretation:
The monomer required to produce the given polymer needs to be determined.
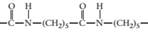
Concept Introduction:
A polymer is a long chain consists of large number of monomer units. The monomers are repeated units in a polymer they are linked to each other in different orders to produce different polymers.
These monomer units are linked to each other either through the formation of peptide linkage or glycosidic linkage or by removal of any moiety such as a water molecule.
Polyvinyl chloride, bakelite, polystyrene are some of the example of polymers.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- A 0.552-g sample of an unknown acid was dissolved in water to a total volume of 20.0 mL. This sample was titrated with 0.1103 M KOH. The equivalence point occurred at 29.42 mL base added. The pH of the solution at 10.0 mL base added was 3.72. Determine the molar mass of the acid. Determine the Ka of the acid.arrow_forwardAs the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will its major product: 2,0° with a new C-C bond as If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing aree below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and desh bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new C-C bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank.arrow_forwardwrite the mechanism of the nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, please give an examplearrow_forward
- The compound in the figure is reacted with 10 n-butyllihium, 2° propanone, and 3º H2O. Draw and name the products obtained. SiMe3arrow_forwardCaffeine (C8H10N4O2, pictured below) is a weak base. The pKb of caffeine is 10.4. What is the pH of a 0.0155 M solution of caffeine?arrow_forward2-Cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction of 1-cyclohexyl-2,2-dimethylpropan-1-one with CH3CO3H (). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardWrite chemical equations for: the reaction of benzoic acid chloride with grignard reagent [CH3MgX] the reaction of butanoic acid with methyl amine [CH3NH2]arrow_forward2-(3-Aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw the structures of the products.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve number 2arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 오 Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O Problem 22 of 35 A Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O H2/Pt B pressure OH 1. NaBH4 C 2. H3O+ D DMP (Dess-Martin Periodinane) CH2Cl2 CrO3 Done Dramabana_Minor Submitarrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of Cycloheptanone with pyrrolidine (cat. H+). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





