
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
16th Edition
ISBN: 9780134475585
Author: Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 23.34P
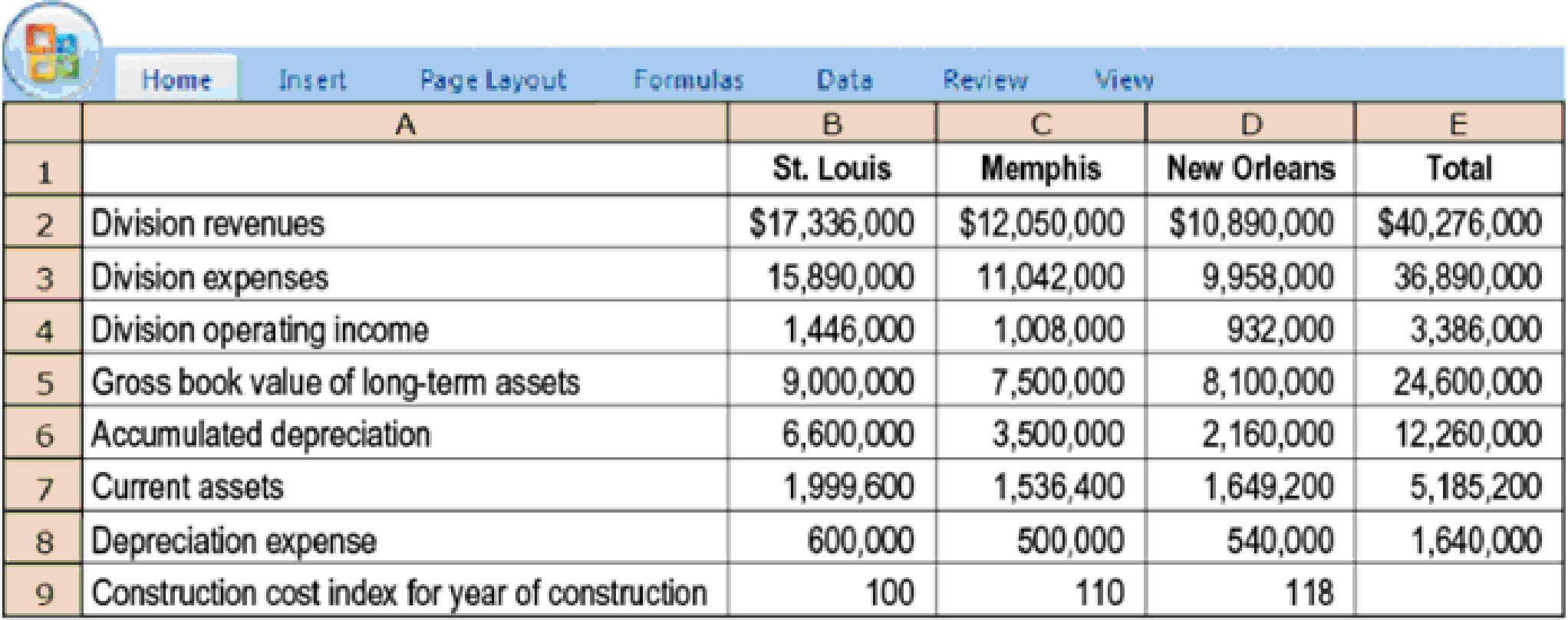
- 1. Calculate ROI for each division using net book value of total assets. Required
- 2. Using the technique in Figure 23-2, compute ROI using current-cost estimates for long-term assets and
depreciation expense. The construction cost index for 2017 is 122. Estimated useful life of operational assets is 15 years. - 3. How does the choice of long-term asset valuation affect management decisions regarding new capital investments? Why might this choice be more significant to the St. Louis division manager than to the New Orleans division manager?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Bonnie and Clyde are the only two shareholders in Getaway Corporation. Bonnie owns 60 shares with a basis of $3,000, and Clyde owns the remaining 40 shares with a basis of $12,000. At year-end, Getaway is considering different alternatives for redeeming some shares of stock. Evaluate whether each of these stock redemption transactions qualify for sale or exchange treatment.
Getaway redeems 29 of Bonnie’s shares for $10,000. Getaway has $26,000 of E&P at year-end and Bonnie is unrelated to Clyde.
Novak supply company a newly formed corporation , incurred the following expenditures related to the land , to buildings, and to machinery and equipment.
abstract company's fee for title search $1,170
architect's fee $7,133
cash paid for land and dilapidated building thereon $195,750
removal of old building $45,000
LESS: salvage $12,375 $32,625
Interest on short term loans during construction…
Year
Cash Flow
0
-$ 27,000
1
11,000
2
3
14,000
10,000
What is the NPV for the project if the required return is 10 percent?
Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.
NPV
$ 1,873.28
At a required return of 10 percent, should the firm accept this project?
No
Yes
What is the NPV for the project if the required return is 26 percent?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.1QCh. 23 - Prob. 23.2QCh. 23 - What factors affecting ROI does the DuPont method...Ch. 23 - RI is not identical to ROI, although both measures...Ch. 23 - Describe EVA.Ch. 23 - Give three definitions of investment used in...Ch. 23 - Distinguish between measuring assets based on...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.8QCh. 23 - Why is it important to distinguish between the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.10Q
Ch. 23 - Managers should be rewarded only on the basis of...Ch. 23 - Explain the role of benchmarking in evaluating...Ch. 23 - Explain the incentive problems that can arise when...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.14QCh. 23 - Prob. 23.15QCh. 23 - During the current year, a strategic business unit...Ch. 23 - Assuming an increase in price levels over time,...Ch. 23 - If ROI Is used to evaluate a managers performance...Ch. 23 - The Long Haul Trucking Company is developing...Ch. 23 - ABC Inc. desires to maintain a capital structure...Ch. 23 - ROI, comparisons of three companies. (CMA,...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.22ECh. 23 - ROI and RI. (D. Kleespie, adapted) The Sports...Ch. 23 - ROI and RI with manufacturing costs. Excellent...Ch. 23 - ROI, RI, EVA. Hamilton Corp. is a reinsurance and...Ch. 23 - Goal incongruence and ROI. Comfy Corporation...Ch. 23 - ROI, RI, EVA. Performance Auto Company operates a...Ch. 23 - Capital budgeting, RI. Ryan Alcoa, a new associate...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.29ECh. 23 - ROI, RI, EVA, and performance evaluation. Cora...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.31ECh. 23 - Prob. 23.32ECh. 23 - ROI performance measures based on historical cost...Ch. 23 - ROI, measurement alternatives for performance...Ch. 23 - Multinational firms, differing risk, comparison of...Ch. 23 - ROI, Rl, DuPont method, investment decisions,...Ch. 23 - Division managers compensation, levers of control...Ch. 23 - Executive compensation, balanced scorecard. Acme...Ch. 23 - Financial and nonfinancial performance measures,...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.40PCh. 23 - Prob. 23.41PCh. 23 - RI, EVA, measurement alternatives, goal...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following were selected from among the transactions completed by Babcock Company during November of the current year: Nov. 3 Purchased merchandise on account from Moonlight Co., list price $85,000, trade discount 25%, terms FOB destination, 2/10, n/30. 4 Sold merchandise for cash, $37,680. The cost of the goods sold was $22,600. 5 Purchased merchandise on account from Papoose Creek Co., $47,500, terms FOB shipping point, 2/10, n/30, with prepaid freight of $810 added to the invoice. 6 Returned merchandise with an invoice amount of $13,500 ($18,000 list price less trade discount of 25%) purchased on November 3 from Moonlight Co. 8 Sold merchandise on account to Quinn Co., $15,600 with terms n/15. The cost of the goods sold was $9,400. 13 Paid Moonlight Co. on account for purchase of November 3, less return of November 6. 14 Sold merchandise with a list price of $236,000 to customers who used VISA and who redeemed $8,000 of pointof- sale coupons. The cost…arrow_forwardHello teacher please solve this questionsarrow_forwardHelp me to solve this questionsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337902663
Author:WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College
Introduction to Divisional performance measurement - ACCA Performance Management (PM); Author: OpenTuition;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pk8Mzoqr4VA;License: Standard Youtube License