
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The empirical formula of the given acid has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Empirical formula of a compound is the smallest integer ratio of numbers of each element presented in that compound.
Molecular formula of a compound is integer multiple of empirical formula, the integer is depend upon the mass of empirical formula and the molecular mass of the compound.
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation,
(a)
Answer to Problem 121SCQ
Empirical formula of the acid is
Explanation of Solution
Assuming the molecular formula of the compound is
It dissociates into carbondioxide and water. The equation is as follows.
Let’s calculate the moles of C in
Let’s calculate the moles of
Weight of Hydrogen =
Let’s calculate the weight of Oxygen:
Let’s calculate the mole of Oxygen:
Let’s calculate the mole ratio of each element:
Therefore, the empirical formula of the given compound is
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula of the given acid has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Empirical formula of a compound is the smallest integer ratio of numbers of each element presented in that compound.
Molecular formula of a compound is integer multiple of empirical formula, the integer is depend upon the mass of empirical formula and the molecular mass of the compound.
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation,
(b)
Answer to Problem 121SCQ
Molecular formula of the acid is
Explanation of Solution
According to the law of gram equivalents, equivalent acid is equal to the equivalents of base.
Let’s calculate the molecular formula:
Substitute the ‘n’ value we get molecular formula of acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given acid has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure indicates the all unpaired electrons present in the atom in the molecules.
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.
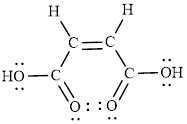
(d)
Interpretation:
The hybridization used by the carbon atom in the given acid compound has to be described.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure indicates the all unpaired electrons present in the atom in the molecules.
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.

The geometry around the entire carbon atoms in the molecule is trigonal planar, which means these carbon atoms used
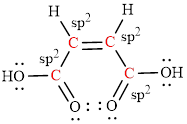
(e)
Interpretation:
The bond angles around each C-atom in the given molecule has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.

The geometry around the entire carbon atoms in the molecule is trigonal planar, which means these carbon atoms used

The geometry around each carbon atom in the given compound is trigonal planar and so the bond angle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





