
(a)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of
(a)
Answer to Problem 72E
Answer
The monomer is vinyl fluoride. It is an
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is vinyl fluoride. It is an addition polymer whose structure is shown in Figure 1.
The structure of the monomer is,
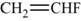
Figure 1
The polymer contains a repeating chain of vinyl fluoride, which on adding polymerization forms a polymer known as polyvinyl fluoride. Hence, the monomer is vinyl fluoride.
(b)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(b)
Answer to Problem 72E
Answer
The monomer is
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is
The structure of the monomer is,
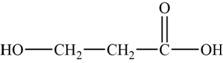
Figure 2
The polymer contains a repeating chain of
(c)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(c)
Answer to Problem 72E
Answer
The monomers are
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomers are
The structures of the monomers are,
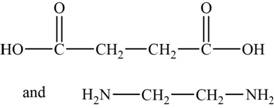
Figure 3
The polymer chain consists of the repeating units of ethane on which carboxylic group is present on carbon 1 and 2 respectively indicates that one monomer is
(d)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(d)
Answer to Problem 72E
Answer
The monomer is
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is
The structure of the monomer is,
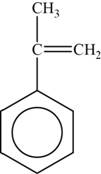
Figure 4
The repeating unit of polymer has
(e)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(e)
Answer to Problem 72E
Answer
The monomer is
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer is
The structure of the monomer is,
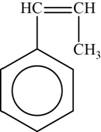
Figure 5
The repeating unit of polymer has
(f)
Interpretation: The monomers of the given polymers, their classification (condensation or addition polymers) and copolymers are to be stated.
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. Depending upon the mode of polymerization, polymerization mainly occurs by the addition and condensation polymerization reactions. Copolymers are defined as polymers in which repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomers.
(f)
Answer to Problem 72E
Answer
The monomer are
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The monomer of the given polymer.
The monomer are and
The structures of the monomers are,
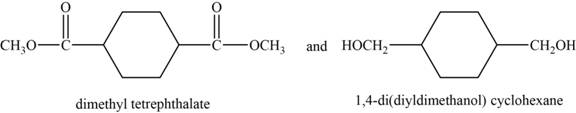
Figure 6
DMT is an organic compound. It is the diester formed from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: AN ATOMS FIRST APPROACH
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardDraw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forward
- I have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forward
- First image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





