
Concept explainers
Decide if the side chains of the amino acid residues in the following peptides are nonpolar or polar, and label the hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of each peptide.
- VLLFGEDEK
- RKVSFLGAA
(a)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the side chains of the amino acid residue in the given peptide should be determined and also label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends of the given peptide.
VLLFGEDEK
Concept Introduction:
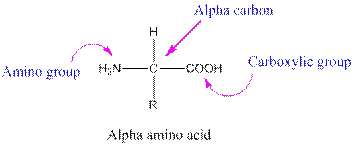
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. Amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha amino acids.
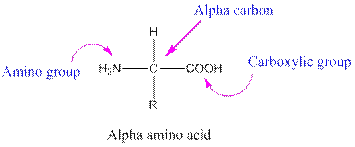
This table gives information about the polarity of the side chains:
| Name of Amino Acid | One-letter abbreviation | Structure | Side chain Polarity | Side chain |
| Alanine | A | 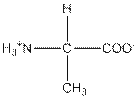 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Asparagine | N | 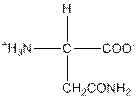 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Cysteine | C | 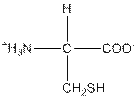 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Glutamine | Q | 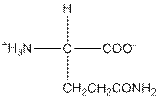 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Glycine | G | 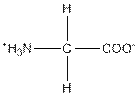 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Isoleucine | I | 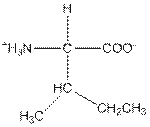 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Leucine | L | 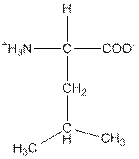 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Methionine | M | 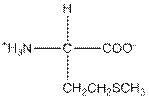 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Phenylalanine | F | 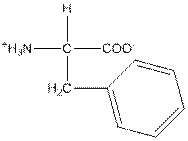 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Proline | P | 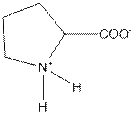 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Serine | S | 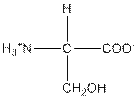 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Threonine | T | 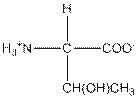 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Tryptophan | W | 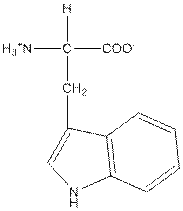 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Tyrosine | Y | 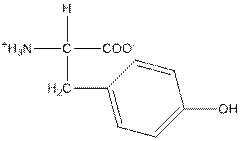 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Valine | V | 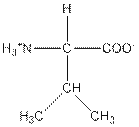 | Nonpolar | Hydrophobic |
| Aspartic acid | D | 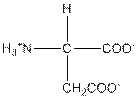 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Glutamic acid | E | 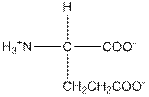 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Arginine | R | 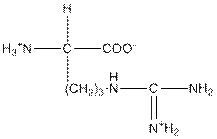 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Histidine | H | 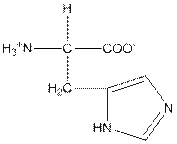 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
| Lysine | K | 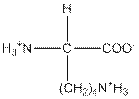 | Polar | Hydrophilic |
Answer to Problem 56P
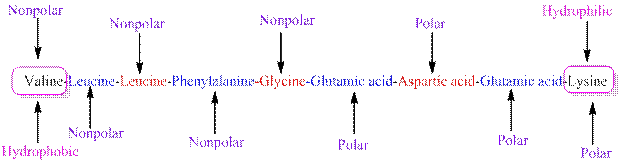
The polarity of the side chains of amino acids are shown along with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of the given peptide 'VLLFGEDEK' as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Side chains of amino acids are non-polar because only carbon and hydrogen atoms are present having very small dipole moment and tends to repel water. That's why non-polar amino acids are hydrophobic in nature.
Side chains of amino acids are polar because these proteins have those toms which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds have very high dipole moment and tends to attract water. That's why polar amino acids are hydrophilic in nature.
From the table, the sequence of peptide contains the following amino acids:
V = Valine is a non-polar amino acid.
L = Leucine is a non-polar amino acid.
F = Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid.
G = Glycine is a non-polar amino acid.
E = Glutamic acid is a polar amino acid.
D = Aspartic acid is a polar amino acid.
K = Lysine is a polar amino acid.
From the given peptide sequence 'VLLFGEDEK', Valine present at the right end and Lysine present at the left end of the sequence.
Valine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophobic in nature.
Lysine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophilic in nature.
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends along with polar and non-polar amino acids are indicated in the given sequence as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The polarity of the side chains of the amino acid residue in the given peptide should be determined and also label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends of the given peptide.
RKYSFLGAA
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. Amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha amino acids.
Answer to Problem 56P
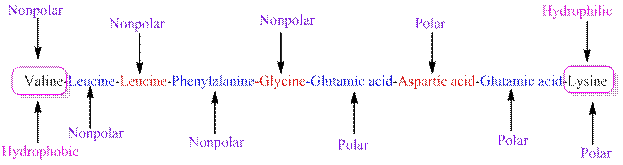
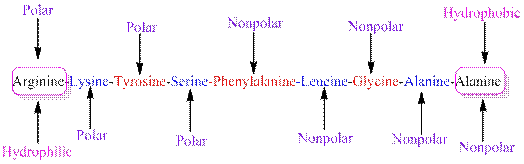
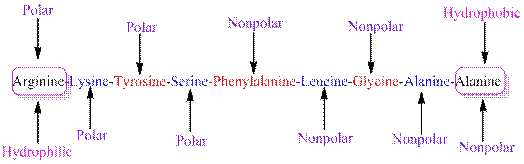
The polarity of the side chains of amino acids are shown along with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end of the given peptide 'RKYSFLGAA' as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Side chains of amino acids are non-polar because only carbon and hydrogen atoms are present having very small dipole moment and tends to repel water. That's why non-polar amino acids are hydrophobic in nature.
Side chains of amino acids are polar because these proteins have those toms which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds have very high dipole moment and tends to attract water. That's why polar amino acids are hydrophilic in nature.
From the table, the sequence of peptide 'RKYSFLGAA' contains the following amino acids:
R = Arginine is a polar amino acid.
K = Lysine is a polar amino acid.
Y = Tyrosine is a polar amino acid.
S = Serine acid is a polar amino acid.
F = Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid.
L = Leucine is a non-polar amino acid.
G = Glycine is a non-polar amino acid.
A = Alanine is a non-polar amino acid.
From the given peptide sequence 'RKYSFLGAA', Arginine present at the right end and Alanine present at the left end of the sequence.
Arginine is a polar amino acid and hydrophilic in nature.
Alanine is a non-polar amino acid and hydrophobic in nature.
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends along with polar and non-polar amino acids are indicated in the given sequence as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- The following 'H NMR spectrum was taken with a 750 MHz spectrometer: 1.0 0.5 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 ' 2.0 1.0 0.0 (ppm) What is the difference Av in the frequency of RF ac Δν ac radiation absorbed by the a and c protons? (Note: it's not equal to the difference in chemical shifts.) Round your answer to 2 significant digits, and be sure it has an appropriate unit symbol. = O O a will shift left, c will shift right. O a will shift right, c will shift left. a and c will both shift left, with more space between them. Suppose a new spectrum is taken with a 500 MHz spectrometer. What will be true about this new spectrum? O a and c will both shift left, with less space between them. O a and c will both shift right, with more space between them. O a and c will both shift right, with less space between them. Which protons have the largest energy gap between spin up and spin down states? O None of the above. ○ a Ob Explanation Check C Ar B 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved.…arrow_forwardWhat mass of Na2CO3 must you add to 125g of water to prepare 0.200 m Na2CO3? Calculate mole fraction of Na2CO3, mass percent, and molarity of the resulting solution. MM (g/mol): Na2CO3 105.99; water 18.02. Final solution density is 1.04 g/mL.arrow_forward(ME EX2) Prblms Can you please explain problems to me in detail, step by step? Thank you so much! If needed color code them for me.arrow_forward
- Experiment #8 Electrical conductivity & Electrolytes. Conductivity of solutions FLINN Scientific Scale RED LED Green LED LED Conductivity 0 OFF OFF 1 Dim OFF 2 medium OFF 3 Bright Dim Low or Nowe Low Medium High 4 Very Bright Medium nd very high AA Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ SE=Strong Electrolyte, FE = Fair Electrolyte CWE = Weak Electrolyte, NE= Noni Electrolyte, #Solutions 1 0.1 M NaCl 2/1x 102 M NaCl, 3/1X103 M Nall Can Prediction M Observed Conductivity Very bright red Bright red Dim red you help me understand how I'm supposed to find the predictions of the following solutions? I know this is an Ionic compound and that the more ions in a solution means it is able to carry a charge, right? AAAA Darrow_forward(SE EX 2) Prblsm 4-7: Can you please explain problems 4-7 and color code if needed for me. (step by step) detail explanationsarrow_forward(SE EX 2) Problems 8-11, can you please explain them to me in detail and color-code anything if necessary?arrow_forward
- (ME EX2) Problems 15-16 Could you please explain problems 15 through 16 to me in detail, step by step? Thank you so much! If necessary, please color-code them for me.arrow_forward1.)show any electrophilic aromatic substitution, identify the electriphile, nucleophile and transition statearrow_forward(SE EX 2) Problems 15-16, can you please explain them to me in detail and color-code anything if necessary?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





