
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
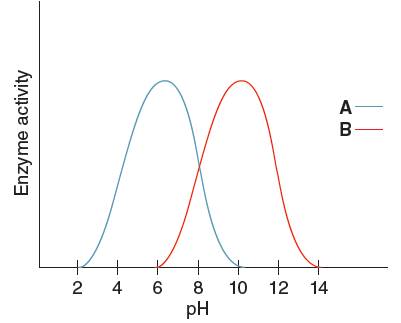
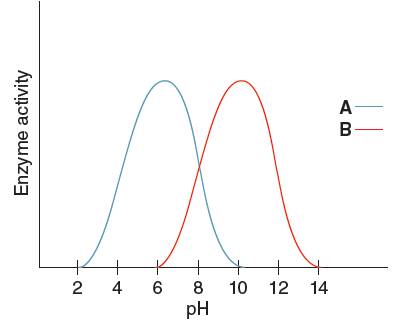
The optimum pH for enzyme 'A' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the
Answer to Problem 77P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'A' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme A is maximum at pH 6. Hence the optimum pH of enzyme A is 6.
(b)
Interpretation:
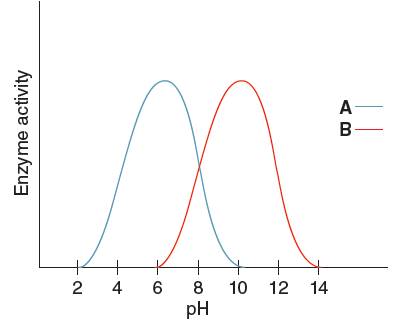
The optimum pH for enzyme 'B' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 77P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'B' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme B is maximum at pH 10.
Hence, the optimum pH of enzyme B is 10.
(c)
Interpretation:
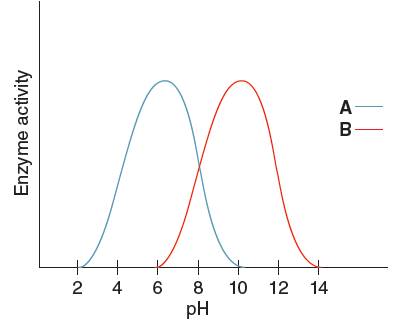
The enzyme having the higher activity when pH is
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 77P
Enzyme 'A' will have higher pH at
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards. So, before pH 2 enzyme A is inactive and before pH 6 enzyme B is inactive. Therefore, at pH 4 the activity of enzyme A is higher than that of enzyme B.
(d)
Interpretation:
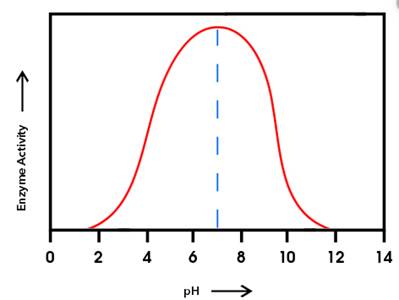
The enzyme having the higher activity at pH
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 77P
Enzyme 'B' will have the higher activity at pH
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 10and then activity of enzyme starts decreasing. And activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 6 and then starts decreasing.
At pH 9, activity of enzyme A is decreasing and that of enzyme B is increasing. Hence, at pH 9 activity of enzyme B is higher than that of enzyme A.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- 1) Chemoselectivity (why this functional group and not another?) 2) Regioselectivity (why here and not there?) 3) Stereoselectivity (why this stereoisomer?) 4) Changes in oxidation state. Everything in detail and draw out and write it.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration 3/5 Izabella A chemist titrates 120.0 mL of a 0.7191M dimethylamine ((CH3)2NH) solution with 0.5501 M HBr solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pk of dimethylamine is 3.27. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HBr solution added. pH = ☐ ✓ 18 Ar Boarrow_forwardAlcohols can be synthesized using an acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene. An alkene is combined with aqueous acid (e.. sulfuric acid in water). The reaction mechanism typically involves a carbocation intermediate. > 3rd attempt 3343 10 8 Draw arrows to show the reaction between the alkene and hydronium ion. that 2nd attempt Feedback 1st attempt تعمال Ju See Periodic Table See Hint F D Ju See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism for the reaction of acetone and CHgLi to give the major product. 4th attempt Π Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism T 3rd attempt Feedback Ju See Periodic Table See Hint H -H H -I H F See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardSelect the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Then draw a mechanism on the Grignard reagent using curved arrow notation to show how it is converted to the final product. 4th attempt Part 1 (0.5 point) Select the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Choose one: OA Mg in ethanol (EtOH) OB. 2 Li in THF O C. Li in THF D. Mg in THF O E Mg in H2O Part 2 (0.5 point) Br Part 1 Bri Mg CH B CH, 1 Draw intermediate here, but no arrows. © TE See Periodic Table See Hint See Hint ין Harrow_forwardSelect the product for the following reaction. HO HO PCC OH ○ OH O HO ○ HO HO HOarrow_forward
- 5:45 Х Select the final product for the following reaction sequence. O O 1. Mg. ether 2.D.Oarrow_forwardBased on the chart Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages. Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages. Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.arrow_forwardplease help fill in the tablearrow_forward
- Answer F pleasearrow_forward4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





