
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Organolithium compounds can be formed by the reaction of
Answer:
The synthesis of given compound from given starting material is shown below.
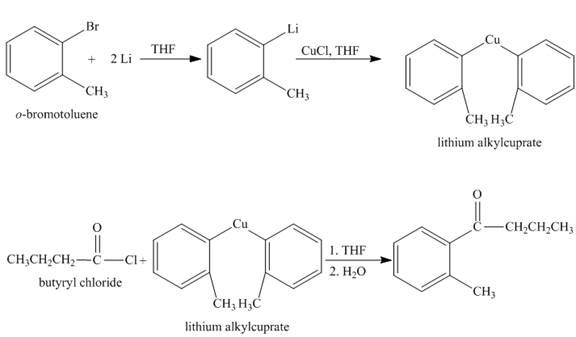
Explanation:
The given compound
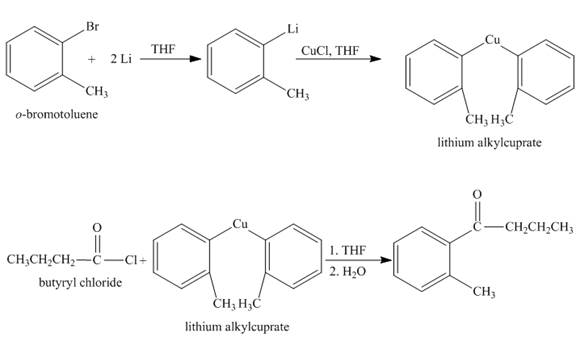
Figure 1
Conclusion:
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 1.
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound from given starting material is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The given compound

Figure 1
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent is formed when alkyl halide compound reacts with magnesium in presence of ether. Potassium dichromate is a strong oxidizing agent. It can easily oxidize alcohol group to
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound from given starting material is shown below.
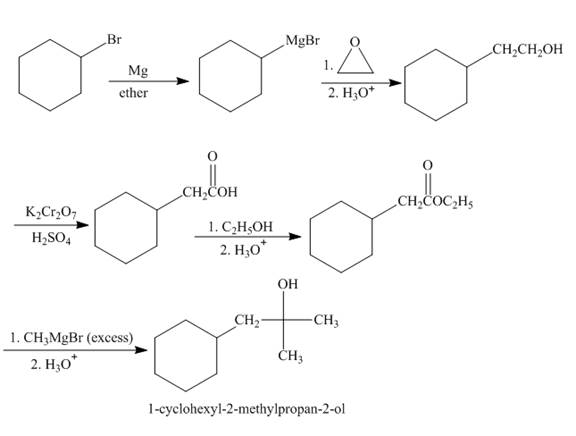
Explanation of Solution
Bromocyclohexane when reacted with magnesium in the ether, it will form grignard reagent. Then grignard reagent will react with
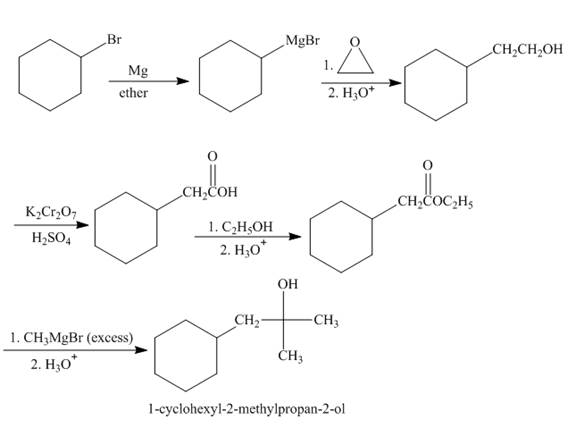
Figure 2
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The carboxylic acid compound reacts with ammonia to form the amide compound. The carbonyl carbon of acid is electrophilic in nature and the lone pair of nitrogen atom of ammonia acts as nucleophile. They will undergo the nucleophilic substitution reaction. Lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent.
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound from given starting material is shown below.
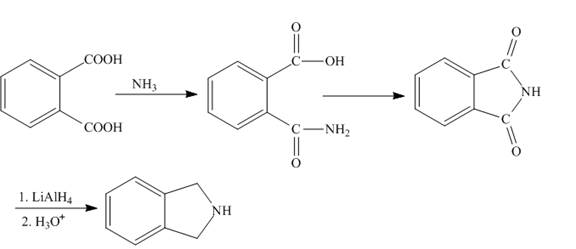
Explanation of Solution
The phthalic acid reacts with ammonia, the lone pair of ammonia nitrogen attacks the carbonyl carbon atom and then with the removal of water molecule phthalamic acid is formed. Then phthalamic acid undergoes cyclization reaction to form phthalamide. Phthalamide upon reduction with lithium aluminium hydride e form the desired product. The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.
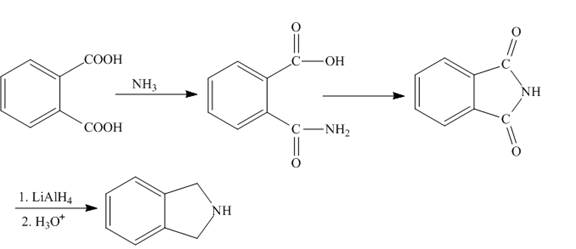
Figure 3
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Acid can be converted into acid chloride by the reaction of acid with
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound from given starting material is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The isovaleric acid reacts with

Figure 4
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Sodium borohyride is a reducing agent. It reduces the
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound from given starting material is shown below.
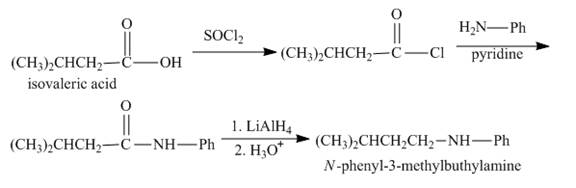
Explanation of Solution
The given starting material reacts with sodium borohydride to convert the carbonyl group into the alcohol group. The reaction of alcohol with hydrogen bromide forms bromoalkene compound. Bromoalkene reacts with the sodium cyanide to form nitrile compound. The nitrile upon reduction forms amine. The amine functional group when reacts with the acid chloride it forms the amide. The synthesis is shown below.

Figure 5
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Cyanohydrin can be formed on reaction of ketone with cyanide. It is a nucleophilic addition reaction. The cyanide ion acts as nucleophile and carbonyl carbon is electrophile. Nitrile group can be converted into amine by reduction with lithium aluminium hydride.
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound from given starting material is shown below.
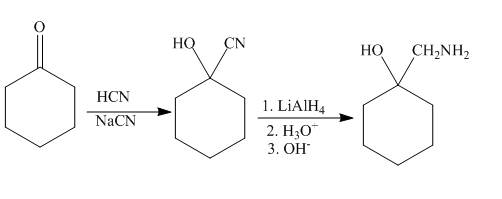
Explanation of Solution
Ketones react with the hydrogen cyanide to form cyanohydrin. The cyanide ion acts as the nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group. The cyano hydrin formed will undergo reduction in presence of lithium aluminium hydride to reduce the cyanide group to amine group. The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.

Figure 6
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Nitration reaction is the reaction in which nitro derivatives are formed. The mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is used as the nitrating mixture. Benzoic acid upon nitration form meta nitrobenzoic acid. The reaction of carboxylic acid with sodium hydroxide produces sodium salt of carboxylic acid.
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
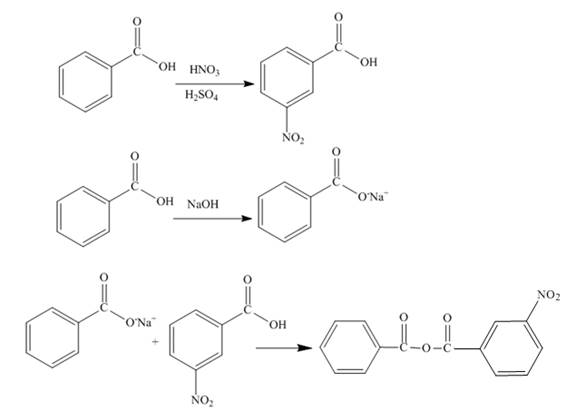
Explanation of Solution
The benzoic acid undergoes nitration reaction in presence of nitric acid and sulfuric acid. The meta product is formed upon nitration of benzoic acid. The meta-nitrobenzoic acid is formed on nitration of benzoic acid. Sodium salt of benzoic acid is formed when benzoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide. The reaction between the meta-nitrobenzoic acid and sodium salt of benzoic acid forms the desired product. The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.

Figure 7
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Acid can be converted into acid chloride by the reaction of acid with
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
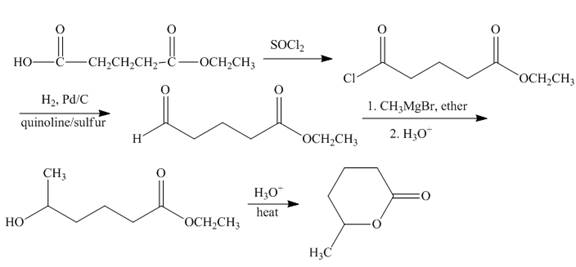
Explanation of Solution
The carboxylic acid group is converted into the acid chloride group by reaction of acid with thionyl chloride. Acid chloride undergoes catalytic reduction to form aldehyde group. Methyl magnesiumbromide converted the product into alkylated secondary alcohol. The formed hydroxy ester compound undergoes cyclization reaction to form the lactone. The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.

Figure 8
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidizing agent. It will oxidize the alkyl group directly to the carboxylic acid group. Thionyl chloride is used for chlorinating the carboxylic acid group. Acid chloride and amines reacts to form the amide linkage.
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
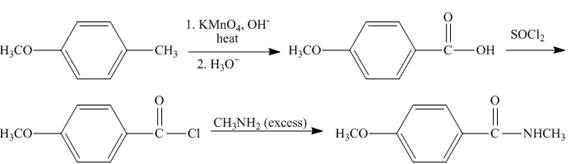
Explanation of Solution
The compound,

Figure 9
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Chloro formic esters and carbonates are formed when phosgene reacts with alcohol compounds. The carbon of phosgene is electrophilic in nature. The phosgene reacts with alcohol and amines. Lone pair of oxygen atom in the alcohol compounds acts as the nucleophilie. Thus nucleophilic substitution reaction can occur.
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
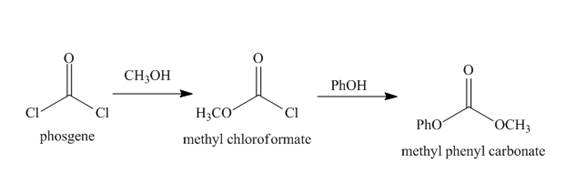
Explanation of Solution
Phosgene has an electrophilic carbon centre. The lone pair of oxygen atom of alcohol acts as nucleophile and attacks at the electrophilic carbon of phosgene. Chloride ion acts as the leaving group. The phosgene reacts with methanol to form methyl chloroformate. Then methyl chloroformate reacts with phenol to form the methyl phenyl carbonate. The complete synthesis is shown below.

Figure 10
The synthesis of given organic compound is shown in Figure 10.
(k)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound from the given starting material is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The formation of biaryls by the coupling of aryl halides is known as Ullmann reaction. The reaction takes place in the presence of copper. The reaction proceeds via radical mechanism. The thoinyl chloride reacts with acid to form acid chloride. Potassium permangenate is a strong oxidizing agent which convert alkyl group directly into acid group.
Answer to Problem 21.56AP
The synthesis of given organic compound is shown below.
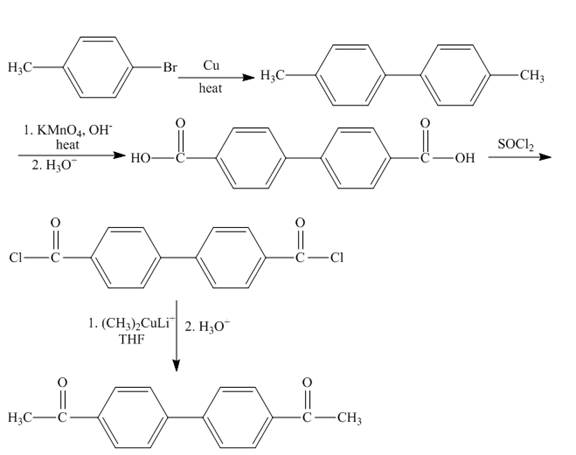
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 11
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 11.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
