
Concept explainers
Draw all the structural isomers for C8H18 that have the following root name (longest carbon chain). Name the structural isomers.
a. hexane
b. pentane
(a)
Interpretation: The structural isomers of
Concept introduction: Rules given by IUPAC should be followed to name an organic compound. Any organic compound has only one name that denotes that compound. The root word determines the number of carbons while counting the longest carbon chain. If more than one substituent is present, prefixes like di, tri, tetra, etc. are used and different substituents are written in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 16E
Answer
The structural isomers of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The structural isomers of
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
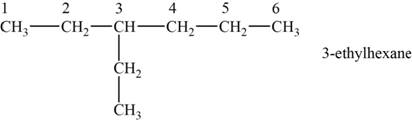
Figure 1
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has six carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “hexane” is used. Ethyl group is attached to third carbon, thus the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
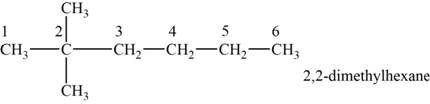
Figure 2
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has six carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “hexane” is used. Two methyl groups are attached to second carbon, thus the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the given isomer is,
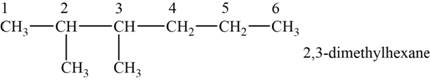
Figure 3
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has six carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “hexane” is used. Methyl group is attached to second and third carbon, thus the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
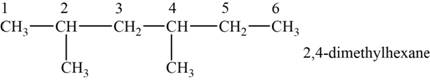
Figure 4
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has six carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “hexane” is used. Methyl group is attached to second and fourth carbon, thus the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
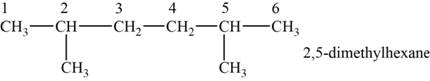
Figure 5
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has six carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “hexane” is used. Methyl group is attached to second and fifth carbon, thus the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
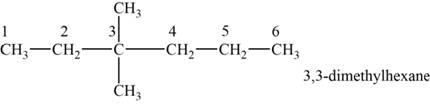
Figure 6
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has six carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “hexane” is used. Two Methyl groups are attached to third carbon, thus the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
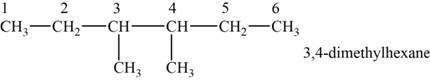
Figure 7
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has six carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “hexane” is used. Methyl groups are attached to third and fourth carbon, thus the name of the isomer is
Conclusion
The structural isomers of
(b)
Interpretation: The structural isomers of
Concept introduction: Rules given by IUPAC should be followed to name an organic compound. Any organic compound has only one name that denotes that compound. The root word determines the number of carbons while counting the longest carbon chain. If more than one substituent is present, prefixes like di, tri, tetra, etc. are used and different substituents are written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
To determine: The structural isomers of
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
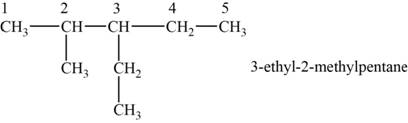
Figure 8
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has five carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “pentane” is used. Methyl group is attached to second carbon, ethyl group is attached to third carbon, therefore, the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
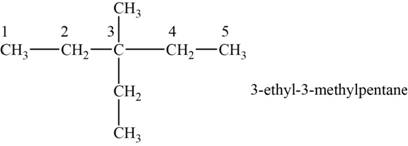
Figure 9
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has five carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “pentane” is used. Methyl group and ethyl group is attached to third carbon, therefore, the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
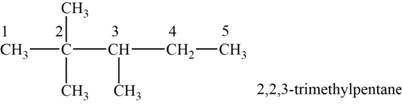
Figure 10
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has five carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “pentane” is used. Two methyl groups are attached to second carbon and one methyl group is attached to third carbon, therefore, the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
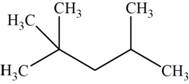
Figure 11
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has five carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “pentane” is used. Two methyl groups are attached to second carbon and one methyl group is attached to fourth carbon, therefore, the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
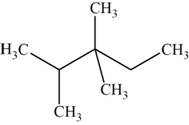
Figure 12
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has five carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “pentane” is used. Two methyl groups are attached to third carbon and one methyl group is attached to second carbon, therefore, the name of the isomer is
The structural isomer is given below and its name is
The structure of the isomer is,
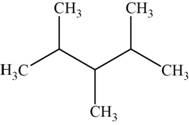
Figure 13
The general formula of alkanes is
Octane has eight carbons and
The isomer has five carbons in the parent chain. Therefore the root word “pentane” is used. Methyl group is attached to second, third carbon and fourth carbon, therefore, the name of the isomer is
Conclusion
The structural isomers of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach, Loose-leaf Version, 2nd + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- 2. Name the following hydrocarbons. (9 marks) a) HHHHHHHH H-C-C- H-O-S b) HCEC-CH3 H H H H H d) c) H C=C- H H H e) CH3 CH3 CH2CH=CH-CH=CHCH3 HHHH H-C-C-C-C-H H HH H f) large CH2CH3 pola H3C section lovels tower, able ocart firs g) Tower H3C-CH2 then in H3C-CH-CH-CH3 enblbano bne noitsidab Copyright © 2008. Durham Continuing Education CH3arrow_forwardName the molecules & Identify any chiral center CH3CH2CH2CHCH₂CH₂CH₂CH₂ OH CH₂CHCH2CH3 Br CH3 CH3CHCH2CHCH2CH3 CH3arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





