
Concept explainers
If one hydrogen in a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen
a. n-pentane
b. 2-methylbutane
c. 2,4-dimethylpentane
d. methylcyclobutane
(a)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in n-pentane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Three isomers are obtained when one hydrogen atom of n-pentane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane has five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of first carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
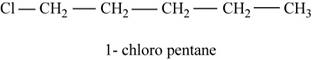
Figure 1
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane has five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of second carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
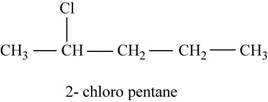
Figure 2
The parent chain contains five carbon atom and chlorine group is attached to second carbon.
The compound
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane have five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of third carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
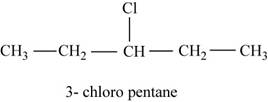
Figure 3
The compound
(b)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Nine isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
In the given compound,
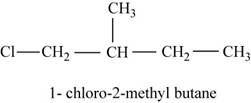
Figure 4
The isomer is
In the given compound,
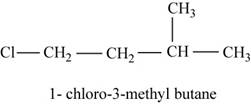
Figure 5
The isomer is
In the given compound,
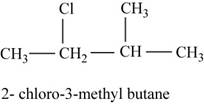
Figure 6
The isomer is
In the given compound,
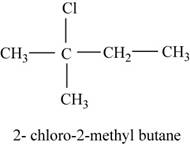
Figure 7
The isomer is
In the given compound,
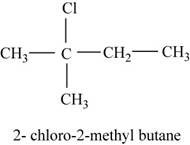
Figure 8
The isomer is
In the given compound,
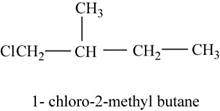
Figure 9
The isomer is
In the given compound,
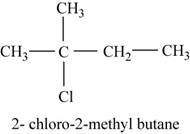
Figure 10
The isomer is
In the given compound,

Figure 11
The isomer is
In the given compound,

Figure 12
(c)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Two isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
The given compound
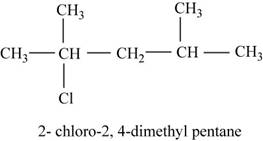
Figure 13
The isomer is
The given compound
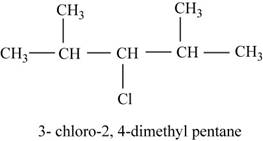
Figure 14
(d)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in methylcyclobutane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Three isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of methylcyclobutane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the methyl group is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
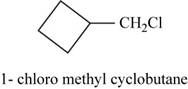
Figure 15
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the second carbon of the ring is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
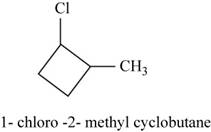
Figure 16
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the third carbon of the ring is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
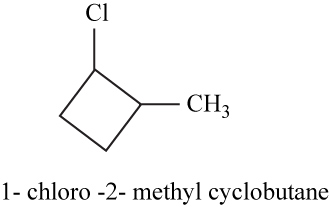
Figure 17
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach, Loose-leaf Version, 2nd + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- When two solutions, one of 0.1 M KCl (I) and the other of 0.1 M MCl (II), are brought into contact by a membrane. The cation M cannot cross the membrane. At equilibrium, x moles of K+ will have passed from solution (I) to (II). To maintain the neutrality of the two solutions, x moles of Cl- will also have to pass from I to II. Explain this equality: (0.1 - x)/x = (0.1 + x)/(0.1 - x)arrow_forwardCalculate the variation in the potential of the Pt/MnO4-, Mn2+ pair with pH, indicating the value of the standard potential. Data: E0 = 1.12.arrow_forwardGiven the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt. Calculate the emf of the cell as a function of pH.arrow_forward
- The decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward2. Add the following group of numbers using the correct number of significant figures for the answer. Show work to earn full credit such as rounding off the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Replace the question marks with the calculated answers or write the calculated answers near the question marks. 10916.345 37.40832 5.4043 3.94 + 0.0426 ? (7 significant figures)arrow_forwardThe emf at 25°C of the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt was 612 mV. When solution X was replaced by normal phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 6.86, the emf was 741 mV. Calculate the pH of solution X.arrow_forward
- Indicate how to calculate the potential E of the reaction Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e ⇄ 2Hg + 2Cl- as a function of the concentration of Cl- ions. Data: the solubility product of Hg2Cl2.arrow_forwardHow can Beer’s Law be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide an in-depth discussion and examples of this.arrow_forwardb) H3C- H3C Me CH 3 I HN Me H+arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning  World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





