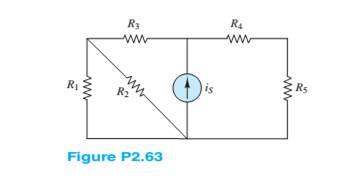
Problem 2.1HP: A free electron has an initial potential energy perunit charge (voltage) of 17 kJ/C and a velocity... Problem 2.2HP: The units for voltage, current, and resistance are the volt (V), the ampere (A), and the ohm (e),... Problem 2.3HP: A particular fully charged battery can deliver 2.7106 coulombs of charge. a. What is the capacity of... Problem 2.4HP: The charge cycle shown in Figure P2.4 is an example of a three-rate charge. The current is held... Problem 2.5HP: Batteries (e.g., lead-acid batteries) store chemical energy and convert it to electric energy on... Problem 2.6HP: What determines: a. The current through an ideal voltage source? b. The voltage across an ideal... Problem 2.7HP: An automotive battery is rated at 120 A-h. This means that under certain test conditions it can... Problem 2.8HP: A car battery kept in storage in the basement needs recharging, lf he voltage and the current... Problem 2.9HP: Suppose the current through a wire is given by the curve shown in Figure P2.9. a. Find the amount of... Problem 2.10HP: The charge cycle shown in Figure P2.10 is anexample of a two-rate charge. The current is... Problem 2.11HP: The charging scheme used in Figure P2.11 is anexample of a constant-current charge cycle. The... Problem 2.12HP: The charging scheme used in Figure P2.12 is calleda tapered-current charge cycle. The current starts... Problem 2.13HP: Use KCL to determine the unknown currents in the circuit of Figure P2.13. Assume i0=2A and i2=7A . Problem 2.14HP: Use KCL to find the current i1 and i2 in Figure P2.4. Assume that ia=3A,ib=2A,ic=1A,id=6A and ie=4A... Problem 2.15HP: Use KCL to find the current i1,i2, and i3 in the circuit of Figure P2.15. Assume that ia=2mA,ib=7mA... Problem 2.16HP: Use KVL to find the voltages v1,v2, and v3 in Figure P2.16. Assume that va=2V,vb=4V and vc=5V . Problem 2.17HP: Use KCL to determine the current i1,i2,i3, and i4 in the circuit Figure P2.17. Assume that... Problem 2.18HP: In the circuits of Figure P2.18, the directions ofcurrent and polarities of voltage have already... Problem 2.19HP: Find the power delivered by each source in Figure P2.19. Problem 2.20HP: Determine whether each element in Figure P2.20 is supplying or dissipating power, and how much Problem 2.21HP: In the circuit of Figure P2.21, determine the power absorbed by the resistor R4 and the power... Problem 2.22HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.22: a. Determine whether each component is absorbing or... Problem 2.23HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.23, determinethe power absorbed by the 5- resistor. Problem 2.24HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.24, determine which components are supplying power and which are... Problem 2.25HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.25, determine which components are supplying power and which are... Problem 2.26HP Problem 2.27HP Problem 2.28HP Problem 2.29HP Problem 2.30HP Problem 2.31HP Problem 2.32HP: In the circuit of Figure P2.32, assume v2=vs/6 and the power delivered by the source is 150 mW.... Problem 2.33HP Problem 2.34HP: An incandescent light bulb rated at 100 W will dissipate 100 W as heat and light when connected... Problem 2.35HP: An incandescent lightbulb rated at 60 W willdissipate 60 W as heat and light when connected across a... Problem 2.36HP: Refer to Figure P2.36, and assume that vs=12V,R1=5,R2=3,R3=4, and R4=5 .Find: a. The voltage vab .... Problem 2.37HP: Refer to Figure P2.37, and assume that vs=7V,Is=3A,R1=20,R2=12, and R3=10 .Find: a. The current i1... Problem 2.38HP: Refer to Figure P2.38, and assume v1=15V,v2=6V,R1=18,R2=10 . Find: a. Thecurrents ii,i2 . b. The... Problem 2.39HP Problem 2.40HP: With no load attached, the voltage at the terminals of a particular power supply is 50.8 V. When a... Problem 2.41HP Problem 2.42HP: For the circuits of Figure P2.42, determine the resistor values (including the power rating)... Problem 2.43HP: At an engineering site, a 1-hp motor is placed adistance d from a portable generator, as depicted in... Problem 2.44HP: Cheap resistors are fabricated by depositing a thin layer of carbon onto a non-conducting... Problem 2.45HP Problem 2.46HP: Use KCL and Ohm’s law to determine the current through each of the resistors R4,R5, and R6 in... Problem 2.47HP: Refer to Figure P2.13. Assume R0=1,R1=2,R2=3,R3=4 , and vs=10V .Use KCL and Ohm’s law to find the... Problem 2.48HP: Apply KCL and Ohm’s law to find the power supplied by the voltage source in Figure P2.48.Assume... Problem 2.49HP: Refer to Figure P2.49 and assume R0=2,R1=1,R2=43,R3=6 , and Vs=12V . Use KVL and Ohm’s law to find:... Problem 2.50HP: Refer to Figure P2.49 and assume R0=2,R1=2,R2=5,R3=4A , and Vs=24V . Use KVL and Ohm’s law to find:... Problem 2.51HP Problem 2.52HP: The voltage divider network of Figure P2.52 is designed to provide vout=vs/2 . However, in practice,... Problem 2.53HP: Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source in Figure P2.53. Use the result to find i,i1, and... Problem 2.54HP: Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source and the current i in the circuit of Figure P2.54. Problem 2.55HP: In the circuit of Figure P2.55, the power absorbed by the 15- resistor is 15 W. Find R. Problem 2.56HP: Find the equivalent resistance between terminals aandb in the circuit of Figure P2.56. Problem 2.57HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.57, find the equivalent resistance seen by the source. How much... Problem 2.58HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.58,find the equivalent resistance seen by the current source. How... Problem 2.59HP: Refer to Figure P2.59. Assume vs=20V,R1=10,R2=5,R3=8,R4=2,R5=4,R6=2,R7=1, and R8=10 .How many nodes... Problem 2.60HP: Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source in Figure P2.60. How many nodes are in the... Problem 2.61HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.61. assume vs=20V,R1=9,R2=4,R3=4,R4=5, and R5=4 . Find: a. The... Problem 2.62HP: Determine the equivalent resistance of the infinite network of resistors in the circuit of Figure... Problem 2.63HP: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.58, assume is=5A,R1=10,R2=7,R3=8,R4=4, and R5=2 . Find: a. The... Problem 2.64HP: In the circuit of Figure P2.64, find the equivalent resistance between terminals a andb if terminals... Problem 2.65HP: Refer to Figure P2.64 and determine the equivalent resistance between terminals a andb if terminal c... Problem 2.66HP: Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source in Figure P2.66. How many nodes are in the... Problem 2.67HP: Determine the voltage vo between nodes A and Bin Figure P2.67. vs=12VR1=11kR3=6.8kR2=220kR4=0.22M Problem 2.68HP: Refer to Figure P2.68 and assume vs=15V,R1=12,R2=5,R3=8,R4=2,R5=4,R6=2,R7=1 and R8=R9=10 . Find: a.... Problem 2.69HP Problem 2.70HP Problem 2.71HP Problem 2.72HP: The circuit of Figure P2.72 is used to measure the internal impedance of a battery. The battery... Problem 2.73HP: Consider the practical ammeter, depicted in Figure P2.73. consisting of an ideal ammeter in series... Problem 2.74HP Problem 2.75HP Problem 2.76HP Problem 2.77HP: A voltmeter is used to determine the voltage acrossa resistive element in the circuit of Figure... Problem 2.78HP Problem 2.79HP: Figure P2.79 shows an aluminum cantilevered beam loaded by the force F. Strain gauges R1,R2,R3, and... Problem 2.80HP: Refer to Figure P2.79 but assume that the cantilevered beam loaded by a force F is made of steel.... format_list_bulleted


 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,




