
Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780073529592
Author: Giorgio Rizzoni Professor of Mechanical Engineering, James A. Kearns Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.66HP
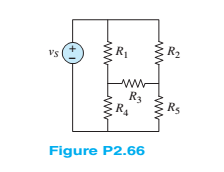
Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source in Figure P2.66. How many nodes are in the circuit?Assume:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For the amplifier shown, if β = 150:
Calculate the input impedance at the base.
Calculate the input impedance of the stage.
53. Obtain an expression for i(t) as labeled in the circuit diagram of Fig. 8.84, and
determine the power being dissipated in the 40 2 resistor at t = 2.5 ms.
t=0
i(t)
30 Ω
w
200 mA 4002
30 m
100 mA(
7.2
At t = 0, the switch in the circuit shown moves
instantaneously from position a to position b.
a) Calculate v, for t≥ 0.
b) What percentage of the initial energy stored
in the inductor is eventually dissipated in
the 4
resistor?
6Ω
a
w
+
10 0.32 H3 403
6.4 A
=0
b
Answer: (a) -8e-10 V, t = 0;
(b) 80%.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering
Ch. 2 - A free electron has an initial potential energy...Ch. 2 - The units for voltage, current, and resistance are...Ch. 2 - A particular fully charged battery can deliver...Ch. 2 - The charge cycle shown in Figure P2.4 is an...Ch. 2 - Batteries (e.g., lead-acid batteries) store...Ch. 2 - What determines: a. The current through an ideal...Ch. 2 - An automotive battery is rated at 120 A-h. This...Ch. 2 - A car battery kept in storage in the basement...Ch. 2 - Suppose the current through a wire is given by the...Ch. 2 - The charge cycle shown in Figure P2.10 is...
Ch. 2 - The charging scheme used in Figure P2.11 is...Ch. 2 - The charging scheme used in Figure P2.12 is...Ch. 2 - Use KCL to determine the unknown currents in the...Ch. 2 - Use KCL to find the current i1 and i2 in Figure...Ch. 2 - Use KCL to find the current i1,i2, and i3 in the...Ch. 2 - Use KVL to find the voltages v1,v2, and v3 in...Ch. 2 - Use KCL to determine the current i1,i2,i3, and i4...Ch. 2 - In the circuits of Figure P2.18, the directions...Ch. 2 - Find the power delivered by each source in Figure...Ch. 2 - Determine whether each element in Figure P2.20 is...Ch. 2 - In the circuit of Figure P2.21, determine the...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.22: a....Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.23,...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.24, determine...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.25, determine...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.26HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.27HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.28HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.29HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.30HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.31HPCh. 2 - In the circuit of Figure P2.32, assume v2=vs/6 and...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.33HPCh. 2 - An incandescent light bulb rated at 100 W will...Ch. 2 - An incandescent lightbulb rated at 60 W...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.36, and assume that...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.37, and assume that...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.38, and assume...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.39HPCh. 2 - With no load attached, the voltage at the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.41HPCh. 2 - For the circuits of Figure P2.42, determine the...Ch. 2 - At an engineering site, a 1-hp motor is placed...Ch. 2 - Cheap resistors are fabricated by depositing a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.45HPCh. 2 - Use KCL and Ohm’s law to determine the current...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.13. Assume R0=1,R1=2,R2=3,R3=4...Ch. 2 - Apply KCL and Ohm’s law to find the power supplied...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.49 and assume...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.49 and assume...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.51HPCh. 2 - The voltage divider network of Figure P2.52 is...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source...Ch. 2 - In the circuit of Figure P2.55, the power absorbed...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.57, find the...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.58,find the...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.59. Assume...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.61. assume...Ch. 2 - Determine the equivalent resistance of the...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.58, assume...Ch. 2 - In the circuit of Figure P2.64, find the...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.64 and determine the equivalent...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance seen by the source...Ch. 2 - Determine the voltage vo between nodes A and Bin...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.68 and assume...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.69HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.70HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.71HPCh. 2 - The circuit of Figure P2.72 is used to measure the...Ch. 2 - Consider the practical ammeter, depicted in Figure...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.74HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.75HPCh. 2 - Prob. 2.76HPCh. 2 - A voltmeter is used to determine the voltage...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.78HPCh. 2 - Figure P2.79 shows an aluminum cantilevered beam...Ch. 2 - Refer to Figure P2.79 but assume that the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- At t = 0, the switch closes. Find the IL(t) and VL(t) for t≥ 0 in t and s domain. Can you help me? 1) (+. 24V ง Anahtar t=0 anında kapatılıyor. to icin TL(t) ve bulunuz. J 3√√√2 ww مفروم + t=0 $6.5 5H VLCH) 2.2 Vilt)arrow_forward"For the network in the figure, determine RE and RB if A₁ Zb = BRE." = -10 and re = 3.8. Assume thatarrow_forward2.a. Simplify and determine Zk+ for: 2.x. 60 [Hz] ⚫ 2.y. 180 [Hz] a.x. 60[Hz] a.y. 180 [Hz] Joo (127 2[H] w 240 [√]arrow_forward
- P3. Given the following network, determine: ⚫ 3.a. Equivalent Y ⚫ 3.b. Equivalent A 2 R[2] 10 8 b 20 30 5arrow_forward[Electrical Circuits] P1. Using the mesh current method, calculate the magnitude and direction of: 1.a. I and I (mesh currents) 1.b. I10 (test current in R10 = 1082) 1.c. (Calculate the magnitude and signs of V10) 6[A] 12 [√] بي 10 38 20 4A] Iw -800arrow_forwardNeed handwritten solution do not use chatgptarrow_forward
- [07/01, 16:59] C P: Question: Calculate the following for 100Hz and 500Hz (express all answers in phasor form). Show all work. A) Xc and ZTB) VR1 and VC1 C) IT Handwritten Solution Pleasearrow_forward1. Sketch the root loci of a system with the following characteristic equation: s²+2s+2+K(s+2)=0 2. Sketch the root loci for the following loop transfer function: KG(s)H(s)=- K(s+1) s(s+2)(s²+2s+4)arrow_forward3. For the unity feedback system with forward path transfer function, G(s), below: G(s)= K(s² +8) (s+4)(s+5) Sketch the root locus and show the breakaway/break-in point(s) and jo-axis crossing. Determine the angle of arrival and K value at the breakaway/break- in point(s). Give your comment the system is stable or unstable.arrow_forward
- Find the step response of each of the transfer functions shown in Eqs. (4.62) through (4.64) and compare them. [Shown in the image]Book: Norman S. Nise - Control Systems Engineering, 6th EditionTopic: Chapter-4: Time Response, Example 4.8Solve the math with proper explanation. Please don't give AI response. Asking for a expert verified answer.arrow_forward2. With respect to the circuit shown in Figure 2 below V2 -R1 R2 R4 w R3 R5 Figure 2: DC Circuit 2 a. Using Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws calculate the current flowing through R3 and so determine wattage rating of R3. b. Verify your results with simulations. Note: you must use the values for the components in Table 2. Table 2 V2 (Volts) R1 (KQ) R2 (KQ) R3 (KQ) R4 (KQ) R5 (KQ) 9 3.3 5 10 6 1 3.3arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer i will report your answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Star Delta Starter Explained - Working Principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h89TTwlNnpY;License: Standard Youtube License