
(a)
Interpretation:Name of the parent

Concept introduction:Total number of protons in an element is known as its
Formula to calculate the mass number
To calculate the group number of the atom, we have to consider its electronic configuration.
Formula to calculate the period number of an atom is as follows:
Formula to calculate the groupnumber of s-block elements are as follows:
Formula to calculate the groupnumber of p-block elements are as follows:
Formula to calculate the groupnumber of d-block elements are as follows:
Inert gases are placed in group number 18 in the modern periodic table.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Number of protons in the ionic depiction is 8. Hence its atomic number is 8. So the parent atom is oxygen
Formula to calculate the mass number
Atomic number of oxygen is 8.
Neutron number of oxygen is 9.
Substitute the values in above formula.
Number electrons present in the parent atom of the atomic depiction is equal to its atomic number, that is equal to 8. Hence electronic configuration will be
Formula to calculate the period number of oxygen is as follows:
Principle quantum number of valance shell of oxygen is 2.
Substitute the values in the above formula.
Formula to calculate the group number of p-block element oxygen is as follows:
Number of electrons in last
Substitute the value in the above formula.
(b)
Interpretation: Name of the parent atom, its mass number and its group and period numbers of bellow mentioned ionic depiction should be given.
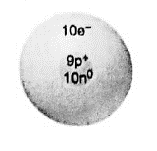
Concept introduction:Total number of protons in an element is known as its atomic number and it is represented with symbol
Formula to calculate the mass number
To calculate the group number of the atom, we have to consider its electronic configuration.
Formula to calculate the period number of an atom is as follows:
Formula to calculate the group number of s-block elements are as follows:
Formula to calculate the group number of p-block elements are as follows:
Formula to calculate the group number of d-block elements are as follows:
Inert gases are placed in group number 18 in the modern periodic table.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Number of protons in the ionic depiction is 9. Hence its atomic number is 9. So the parent atom is fluorine
Formula to calculate the mass number
Atomic number of fluorine is 9.
Neutron number of fluorine is 10.
Substitute the values in the above formula.
Number electrons present in the parent atom of the atomic depiction is equal to its atomic number, that is 9. Hence electronic configuration will be
Formula to calculate the period number of fluorine is as follows:
Principle quantum number of valance shell of fluorine is 2.
Substitute the values in the above formula.
Formula to calculate the groupnumber of p-block element fluorine is as follows:
Number of electrons in last
Substitute the value in the above formula.
(c)
Interpretation: Name of the parent atom, its mass number and its group and period numbers of bellow mentioned ionic depiction should be given.

Concept introduction:Total number of protons in an element is known as its atomic number and it is represented with symbol
Formula to calculate the mass number
To calculate the group number of the atom, we have to consider its electronic configuration.
Formula to calculate the period number of an atom is as follows:
Formula to calculate the group number of s-block elements are as follows:
Formula to calculate the group number of p-block elements are as follows:
Formula to calculate the group number of d-block elements are as follows:
Inert gases are placed in group number 18 in the modern periodic table.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Number of protons in the ionic depiction is 20. Hence its atomic number is 20. So the parent atom is calcium
Formula to calculate the mass number
Atomic number of calcium is 20.
Neutron number of calcium is 20.
Substitute the values in the above formula.
Number electrons present in the parent atom of the atomic depiction is equal to its atomic numbe, that is equal to 20. Hence electronic configuration will be
Formula to calculate the period number of calcium is as follows:
Principle quantum number of valance shell of calcium is 4.
Substitute the values in the above formula.
Formula to calculate the group number of s-block element, calcium is as follows:
Number of electrons in last
Substitute the value in the above formula.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of General Chemistry
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





