
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 15P
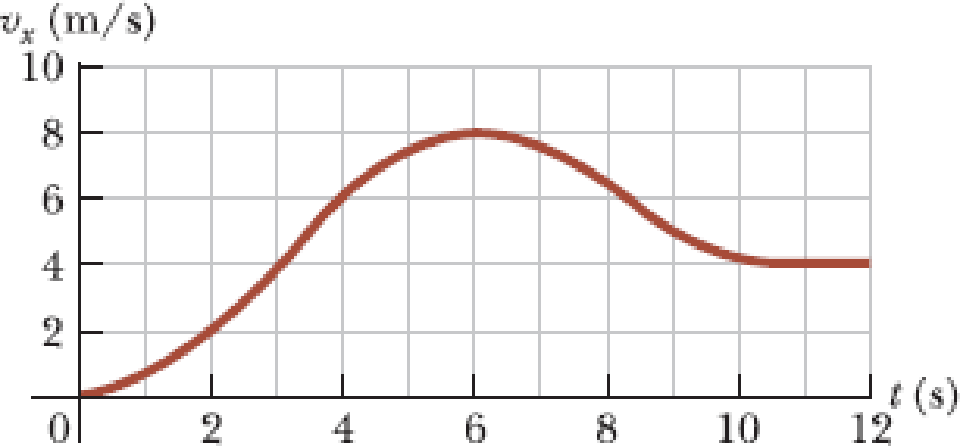
Figure P2.15 shows a graph of vx versus t for the motion of a motorcyclist as he starts from rest and moves along the road in a straight line. (a) Find the average acceleration for the time interval t = 0 to t = 6.00 s. (b) Estimate the time at which the acceleration has its greatest positive value and the value of the acceleration at that instant. (c) When is the acceleration zero? (d) Estimate the maximum negative value of the acceleration and the time at which it occurs.
Figure P2.15
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Consider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Let R = 12.0 (2.)
25.0 V
10.0
www
10.0 Ω
b
www
5.00 Ω
w
R
5.00 Ω
i
(a) Find the current in the 12.0-0 resistor.
1.95
×
This is the total current through the battery. Does all of this go through R? A
(b) Find the potential difference between points a and b.
1.72
×
How does the potential difference between points a and b relate to the current through resistor R? V
3.90 ... CP A rocket designed to place small payloads into orbit
is carried to an altitude of 12.0 km above sea level by a converted
airliner. When the airliner is flying in a straight line at a constant
speed of 850 km/h, the rocket is dropped. After the drop, the air-
liner maintains the same altitude and speed and continues to fly in
a straight line. The rocket falls for a brief time, after which its
rocket motor turns on. Once its rocket motor is on, the combined
effects of thrust and gravity give the rocket a constant acceleration
of magnitude 3.00g directed at an angle of 30.0° above the hori-
zontal. For reasons of safety, the rocket should be at least 1.00 km
in front of the airliner when it climbs through the airliner's alti-
tude. Your job is to determine the minimum time that the rocket
must fall before its engine starts. You can ignore air resistance.
Your answer should include (i) a diagram showing the flight paths
of both the rocket and the airliner, labeled at several…
1. In an industrial fabrication process, a fluid, with density p = 800 kg/m and specific heat capacity
c = 5000 J/kg-C°, emerges from a tank at a temperature, T, = 400 °C. The fluid then enters a metal pipe with inner radius a = 2.0 cm and outer radius b = 3.0 cm and thermal conductivity k = 180 W/m•C°.
Outside the pipe the temperature is fixed at Tout = 15 °C.
If the fluid flows at speed v = 8.0 m/s and the length of the pipe is L = 25 m, what is the temperature
of the fluid at the end of the pipe? (Answer: 83 °C)
please I need to show All work problems step by step
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Ch. 2.1 - Under which of the following conditions is the...Ch. 2.2 - Are members of the highway patrol more interested...Ch. 2.4 - Using Active Figure 2.8, match each vxt graph on...Ch. 2.4 - If a car is traveling eastward and slowing down,...Ch. 2.5 - Which of the following statements is true? (a) If...Ch. 2.7 - A ball is thrown upward. While the ball is in...Ch. 2 - One drop of oil falls straight down onto the road...Ch. 2 - When applying the equations of kinematics for an...Ch. 2 - Prob. 3OQCh. 2 - Prob. 4OQ
Ch. 2 - When the pilot reverses the propeller in a boat...Ch. 2 - A pebble is dropped from rest from the top of a...Ch. 2 - A student at the top of a building of height h...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8OQCh. 2 - As an object moves along the x axis, many...Ch. 2 - You drop a ball from a window located on an upper...Ch. 2 - A skateboarder starts from rest and moves down a...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown straight up in the air. For which...Ch. 2 - A hard rubber ball, not affected by air resistance...Ch. 2 - Prob. 14OQCh. 2 - If a car is traveling eastward, can its...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2CQCh. 2 - (a) Can the equations of kinematics (Eqs....Ch. 2 - Prob. 4CQCh. 2 - Prob. 5CQCh. 2 - Prob. 6CQCh. 2 - Prob. 7CQCh. 2 - You throw a ball vertically upward so that it...Ch. 2 - Two cars are moving in the same direction in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1PCh. 2 - Prob. 2PCh. 2 - Prob. 3PCh. 2 - A person walks first at a constant speed of 5.00...Ch. 2 - A positiontime graph for a particle moving along...Ch. 2 - The position of a particle moving along the x axis...Ch. 2 - Find the instantaneous velocity of the particle...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8PCh. 2 - A hare and a tortoise compete in a race over a...Ch. 2 - An object moves along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - A particle moves along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - A student drives a moped along a straight road as...Ch. 2 - A particle starts from rest and accelerates as...Ch. 2 - A glider of length 12.4 cm moves on an air track...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.15 shows a graph of vx versus t for the...Ch. 2 - Draw motion diagrams for (a) an object moving to...Ch. 2 - Prob. 17PCh. 2 - The minimum distance required to stop a car moving...Ch. 2 - Prob. 19PCh. 2 - Prob. 20PCh. 2 - Prob. 21PCh. 2 - Prob. 22PCh. 2 - The driver of a car slams on the brakes when he...Ch. 2 - In the particle under constant acceleration model,...Ch. 2 - A truck on a straight road starts from rest,...Ch. 2 - A particle moves along the x axis. Its position is...Ch. 2 - A speedboat travels in a straight line and...Ch. 2 - In a classic clip on Americas Funniest Home...Ch. 2 - Prob. 29PCh. 2 - A baseball is hit so that it travels straight...Ch. 2 - Prob. 31PCh. 2 - It is possible to shoot an arrow at a speed as...Ch. 2 - A student throws a set of keys vertically upward...Ch. 2 - At time t = 0, a student throws a set of keys...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown directly downward with an initial...Ch. 2 - Prob. 36PCh. 2 - Prob. 37PCh. 2 - Prob. 38PCh. 2 - A steam catapult launches a jet aircraft from the...Ch. 2 - An object is at x = 0 at t = 0 and moves along the...Ch. 2 - Colonel John P. Stapp, USAF, participated in...Ch. 2 - A woman is reported to have fallen 144 ft from the...Ch. 2 - A ball starts from rest and accelerates at 0.500...Ch. 2 - A glider of length moves through a stationary...Ch. 2 - Prob. 45PCh. 2 - The Acela is an electric train on the...Ch. 2 - Liz rushes down onto a subway platform to find her...Ch. 2 - A commuter train travels between two downtown...Ch. 2 - Prob. 49PCh. 2 - A motorist drives along a straight road at a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 51PCh. 2 - Astronauts on a distant planet toss a rock into...Ch. 2 - Prob. 53PCh. 2 - A hard rubber ball, released at chest height,...Ch. 2 - A man drops a rock into a well. (a) The man hears...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 2 - Two objects, A and B, are connected by a rigid rod...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In an isothermal process, you are told that heat is being added to the system. Which of the following is not true? (a) The pressure of the gas is decreasing. (b) Work is being done on the system. (c) The average kinetic energy of the particles is remaining constant. (d) The volume of the gas is increasing. (e) Work is being done by the system.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward8.114 CALC A Variable-Mass Raindrop. In a rocket-propul- sion problem the mass is variable. Another such problem is a rain- drop falling through a cloud of small water droplets. Some of these small droplets adhere to the raindrop, thereby increasing its mass as it falls. The force on the raindrop is dp dv dm Fext = + dt dt dt = Suppose the mass of the raindrop depends on the distance x that it has fallen. Then m kx, where k is a constant, and dm/dt = kv. This gives, since Fext = mg, dv mg = m + v(kv) dt Or, dividing by k, dv xgx + v² dt This is a differential equation that has a solution of the form v = at, where a is the acceleration and is constant. Take the initial velocity of the raindrop to be zero. (a) Using the proposed solution for v, find the acceleration a. (b) Find the distance the raindrop has fallen in t = 3.00 s. (c) Given that k = 2.00 g/m, find the mass of the raindrop at t = 3.00 s. (For many more intriguing aspects of this problem, see K. S. Krane, American Journal of…arrow_forward
- 8.13 A 2.00-kg stone is sliding Figure E8.13 F (kN) to the right on a frictionless hori- zontal surface at 5.00 m/s when it is suddenly struck by an object that exerts a large horizontal force on it for a short period of 2.50 time. The graph in Fig. E8.13 shows the magnitude of this force as a function of time. (a) What impulse does this force exert on t (ms) 15.0 16.0 the stone? (b) Just after the force stops acting, find the magnitude and direction of the stone's velocity if the force acts (i) to the right or (ii) to the left.arrow_forwardPlease calculate the expectation value for E and the uncertainty in E for this wavefunction trapped in a simple harmonic oscillator potentialarrow_forwardIf an object that has a mass of 2m and moves with velocity v to the right collides with another mass of 1m that is moving with velocity v to the left, in which direction will the combined inelastic collision move?arrow_forward
- Please solve this questionarrow_forwardPlease solvearrow_forwardQuestions 68-70 Four hundred millilitres (mL) of a strong brine solution at room temperature was poured into a measuring cylinder (Figure 1). A piece of ice of mass 100 g was then gently placed in the brine solution and allowed to float freely (Figure 2). Changes in the surface level of the liquid in the cylinder were then observed until all the ice had melted. Assume that the densities of water, ice and the brine solution are 1000 kg m-3, 900 kg m3 and 1100 kg m3, respectively. 68 Figure 1 400 400 Figure 2 1m² = 1x10 mL After the ice was placed in the brine solution and before any of it had melted, the level of the brine solution was closest to 485 mL. B 490 mL. C 495 mL. Displaced volume by ice. D 500 mL. weight of ice 69 The level of the brine solution after all the ice had melted was A 490 mL B 495 mL D 1100kg/m² = 909 xious mis 70 Suppose water of the same volume and temperature had been used instead of the brine solution. In this case, by the time all the ice had melted, the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY