
Concept explainers
An object is at x = 0 at t = 0 and moves along the x axis according to the velocity–time graph in Figure P2.40. (a) What is the object’s acceleration between 0 and 4.0 s? (b) What is the object’s acceleration between 4.0 s and 9.0 s? (c) What is the object’s acceleration between 13.0 s and 18.0 s? (d) At what time(s) is the object moving with the lowest speed? (e) At what time is the object farthest from x = 0? (f) What is the final position x of the object at t = 18.0 s? (g) Through what total distance has the object moved between t = 0 and t = 18.0 s?
Figure P2.40
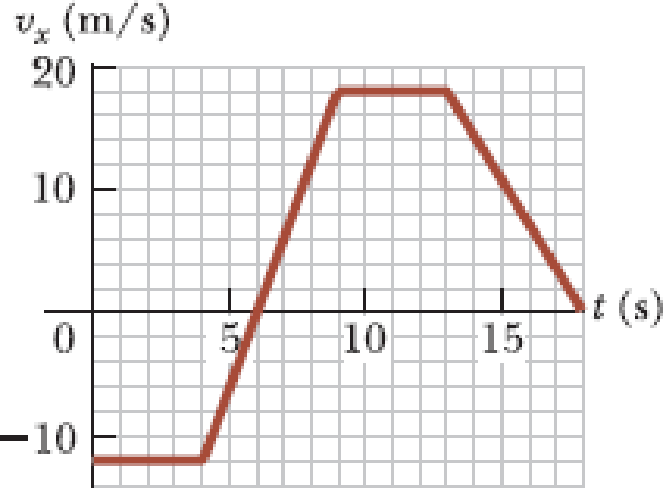
(a)
The object’s acceleration between
Answer to Problem 40P
The object’s acceleration between
Explanation of Solution
Acceleration is a measure of how rapidly the velocity is changing. It is defined as the change in velocity per unit time. The slope of the velocity versus time graph in a particular time interval gives the acceleration during that interval.
In the given velocity versus time graph, the curve is a straight parallel to the time axis between
Conclusion:
Therefore, the object’s acceleration between
(b)
The object’s acceleration between
Answer to Problem 40P
The object’s acceleration between
Explanation of Solution
The slope of the graph in the given interval gives the acceleration of the object during it.
Write the equation for the acceleration of the object between
Here,
Conclusion:
From the graph, the value of
Substitute
Therefore, the object’s acceleration between
(c)
The object’s acceleration between
Answer to Problem 40P
The object’s acceleration between
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the acceleration of the object between
Here,
Conclusion:
From the graph, the value of
Substitute
Therefore, the object’s acceleration between
(d)
The times at which the object moves with the lowest speed.
Answer to Problem 40P
The times at which the object moves with the lowest speed are
Explanation of Solution
In a velocity versus time graph, the velocity of an object will be plotted as a function of time. The velocity at a particular instant of time can be directly observed from the graph. Speed is the magnitude of velocity.
Speed can never be negative. The lowest possible value of speed is zero. In the graph, the velocity of the object is zero at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the times at which the object moves with the lowest speed are
(e)
The time at which the object is farthest from
Answer to Problem 40P
The time at which the object is farthest from
Explanation of Solution
The given velocity versus time graph is of an object starting from
From
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time at which the object is farthest from
(f)
The final position of the object at
Answer to Problem 40P
The final position of the object at
Explanation of Solution
The cumulative area under the graph gives the maximum distance attained by the object.
The velocity versus time graph is shown below.
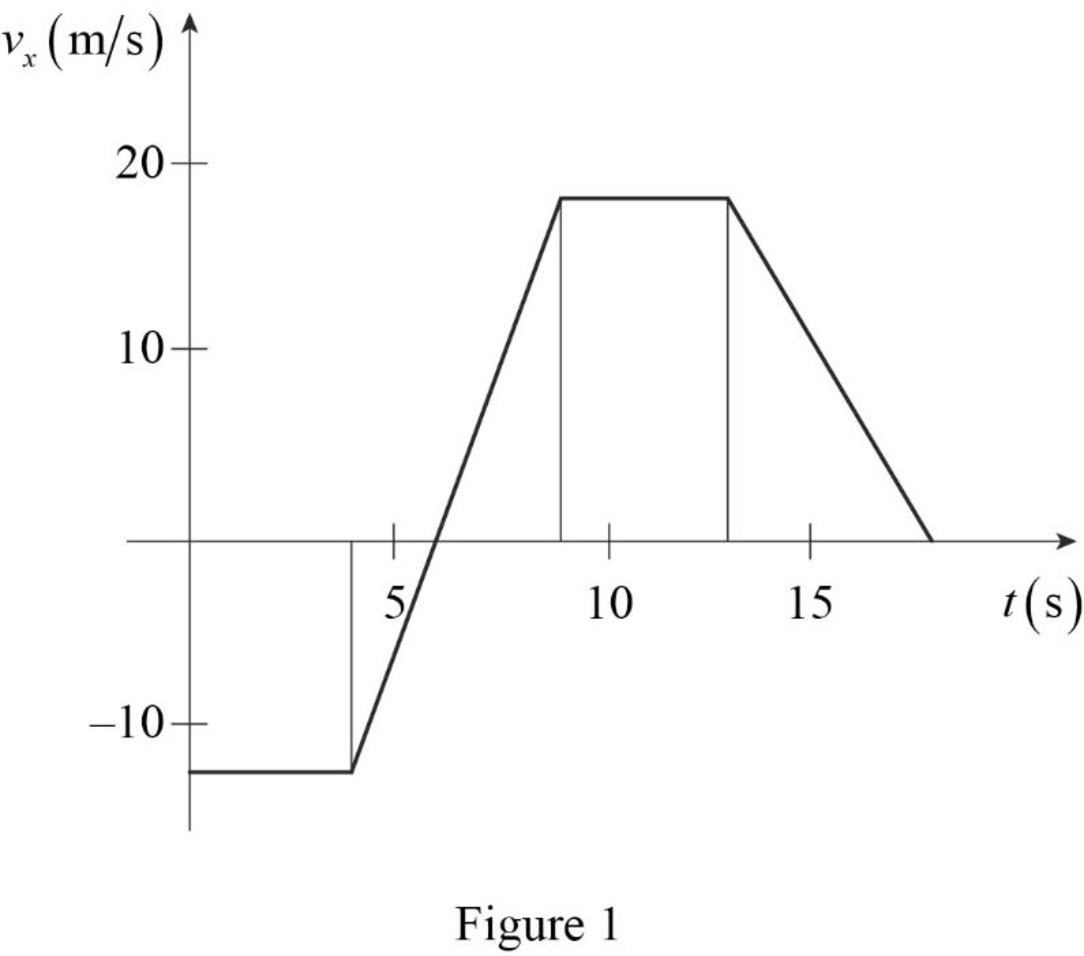
Write the equation for the area of a rectangle.
Here,
Write the equation for the area of a triangle.
Here,
The area from
In figure 1, the length of the rectangle from
Substitute
Here,
The area from
In figure 1, the base of the triangle from
Substitute
Here,
The area from
In figure 1, the base of the triangle from
Substitute
Here,
The area from
In figure 1, the length of the rectangle from
Substitute
Here,
The area from
In figure 1, the base of the triangle from
Substitute
Here,
Write the equation for the farthest distance.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the final position of the object at
(g)
The total distance the object has moved between
Answer to Problem 40P
The total distance the object has moved between
Explanation of Solution
The total distance travelled can be calculated by counting all contributions computed in part (f) as positive.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Here,
Therefore, the total distance the object has moved between
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- Lab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





