
Concept explainers
(a)
The time interval for which the rocket is in motion above the ground.
(a)
Answer to Problem 49P
The time interval for which the rocket is in motion above the ground is
Explanation of Solution
Initially the rocket moves vertically upward with initial speed
The diagram is shown below.
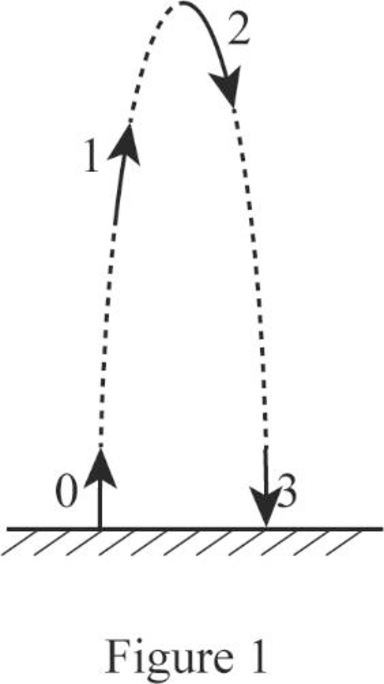
Write the kinematics equation.
Here,
Apply equation (I) for the motion of the rocket from point
Here,
Substitute
Write the kinematics equation.
Here,
Apply equation (II) for the motion of the rocket from point
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
Substitute
Apply equation (I) for the motion of the rocket from point
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
At the maximum altitude the speed of the rocket will be zero.
Substitute
Apply equation (II) for the motion of the rocket from point
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
Substitute
Apply equation (I) for the motion of the rocket from point
Here,
Write the equation for
Substitute
Substitute
The velocity is negative since it is directed downward.
Apply equation (II) for the motion of the rocket from point
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
Substitute
Write the equation for the time interval the rocket is in motion above the ground.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the time interval for which the rocket is in motion above the ground is
(b)
The maximum altitude of the rocket.
(b)
Answer to Problem 49P
The maximum altitude of the rocket is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the maximum altitude.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum altitude of the rocket is
(c)
The velocity of the rocket just before it hits the ground.
(c)
Answer to Problem 49P
The velocity of the rocket just before it hits the ground is
Explanation of Solution
Equation (III) gives the velocity with which the rocket strikes the ground.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the velocity of the rocket just before it hits the ground is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





